Chemistry:Hydrocortisone acetate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cortisol 21-acetate |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; Glucocorticoid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
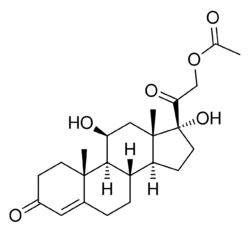
| Formula | C23H32O6 |
| Molar mass | 404.503 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Hydrocortisone acetate is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and a corticosteroid ester.[1]
The acetate group helps to protect the hydrocortisone molecule from being broken down by enzymes in the body (prolongs the duration of action of hydrocortisone) and allows it to be absorbed more easily.
Oral bioavailability
Hydrocortisone has a lower bioavailability than hydrocortisone acetate when taken orally, because hydrocortisone is rapidly metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys before reaching its target tissue. On the other hand, hydrocortisone acetate is more stable and less susceptible to metabolism, allowing a higher proportion of the drug to be absorbed and reach systemic circulation. Therefore, hydrocortisone acetate is often preferred for oral administration over hydrocortisone.[2]
References
- ↑ "Hydrocortisone Acetate". National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cortell#section=Top. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- ↑ "[Comparative study of prednisolone versus hydrocortisone acetate for treatment of patients with the classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency]" (in Portuguese). Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 52 (1): 101–8. February 2008. doi:10.1590/s0004-27302008000100014. PMID 18345402.
 |

