Chemistry:Vindesine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 65-75% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 24 hours |
| Excretion | Biliary and renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
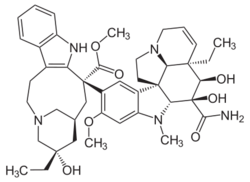
| Formula | C43H55N5O7 |
| Molar mass | 753.941 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Vindesine, also termed Eldisine, is a semisynthetic vinca alkaloid derived from the flowering plant Catharanthus roseus.[1] Like the natural (e.g. vinblastine and vincristine) and semisynthetic vinca alkaloids (e.g. vinorelbine and vinflunine) derived from this plant, vindesine is an inhibitor of mitosis that is used as a chemotherapy drug.[2] By inhibiting mitosis, vinedsine blocks the proliferation of cells, particularly the rapidly proliferation cells of certain types of cancer. It is used, generally in combination with other chemotherapeutic drugs, in the treatment of various malignancies such as leukaemia, lymphoma, melanoma, breast cancer, and lung cancer.[3]
References
- ↑ "Alkaloids for cancer prevention and therapy: Current progress and future perspectives". European Journal of Pharmacology 858: 172472. September 2019. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172472. PMID 31228447.
- ↑ "Vinca alkaloids and analogues as anti-cancer agents: Looking back, peering ahead". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 28 (17): 2816–2826. September 2018. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.06.044. PMID 30122223.
- ↑ "Vindesine (Eldisine) | Cancer information | Cancer Research UK". https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/cancer-in-general/treatment/cancer-drugs/drugs/vindesine.
 |
