Chemistry:Aclarubicin
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
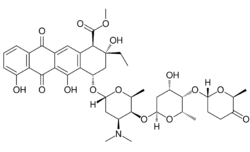
| Formula | C42H53NO15 |
| Molar mass | 811.878 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 151 to 153 °C (304 to 307 °F) (decomposes) |
| |
| |
| | |
Aclarubicin (INN) or aclacinomycin A[1] is an anthracycline drug[2] that is used in the treatment of cancer. Soil bacteria Streptomyces galilaeus can produce aclarubicin. It can induce histone eviction from chromatin upon intercalation.[3][4]
References
- ↑ CID 451415 from PubChem
- ↑ "Antagonistic effect of aclarubicin on daunorubicin-induced cytotoxicity in human small cell lung cancer cells: relationship to DNA integrity and topoisomerase II". Cancer Res. 51 (19): 5093–9. October 1991. PMID 1655244. http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1655244.
- ↑ "Drug-induced histone eviction from open chromatin contributes to the chemotherapeutic effects of doxorubicin". Nature Communications 4: 1908. 2013. doi:10.1038/ncomms2921. PMID 23715267.
- ↑ "Chemical profiling of the genome with anti-cancer drugs defines target specificities". Nature Chemical Biology 11 (7): 472–480. 2015. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1811. PMID 25961671.
 |

