Chemistry:Dimemorfan
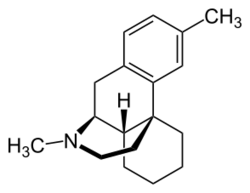 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Astomin, Datosin, Gentus |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H25N |
| Molar mass | 255.405 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dimemorfan (INN) (or dimemorphan) (brand names Astomin, Dastosirr, Tusben), or dimemorfan phosphate (JAN), also known as 3,17-dimethylmorphinan, is an antitussive (cough suppressant) of the morphinan family that is widely used in Japan and is also marketed in Spain and Italy.[1][2][3][4] It was developed by Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical (now Astellas Pharma) and introduced in Japan in 1975.[3] It was later introduced in Spain in 1981 and Japan in 1985.[5]
Side effects
Adverse effects include nausea, somnolence, dry mouth, and decreased appetite.[5]
Pharmacology
Dimemorfan is an analogue of dextromethorphan (DXM) and its active metabolite dextrorphan (DXO), and similarly to them, acts as a potent agonist of the σ1 receptor (Ki = 151 nM).[6][7] However, unlike DXM and DXO, it does not act significantly as an NMDA receptor antagonist (Ki = 16,978 nM), and for this reason, lacks dissociative effects, thereby having reduced side effects and abuse potential in comparison.[8][9] Similarly to DXM and DXO, dimemorfan has only relatively low affinity for the σ2 receptor (Ki = 4,421 nM).[7]
See also
- Cough syrup
- Noscapine
- Codeine; Pholcodine
- Dextromethorphan
- Racemorphan; Dextrorphan; Levorphanol
- Butamirate
- Pentoxyverine
- Tipepidine
- Cloperastine
- Levocloperastine
References
- ↑ The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 427–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA427.
- ↑ Textbook of Palliative Medicine and Supportive Care, Second Edition. CRC Press. 15 January 2015. pp. 677–. ISBN 978-1-4441-3526-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=cdEgCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA677.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "The nonnarcotic antitussive drug dimemorfan: a review". Clinical Therapeutics 19 (2): 215–231. 1997. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(97)80111-7. PMID 9152562.
- ↑ Lexi-Comp's Drug Information Handbook International: With Canadian and International Drug Monographs. Lexi-Comp. 1 January 2005. ISBN 978-1-59195-110-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=twBtAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Drugs Available Abroad, 1st Edition. Derwent Publications Ltd.. 1991. p. 66. ISBN 0-8103-7177-4.
- ↑ "The pharmacology of sigma-1 receptors". Pharmacology & Therapeutics 124 (2): 195–206. November 2009. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.07.001. PMID 19619582.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Therapeutic Targets: Modulation, Inhibition, and Activation. John Wiley & Sons. 20 April 2012. pp. 234–. ISBN 978-1-118-18552-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=3XJ8PXFCXq4C&pg=PA234.
- ↑ "Binding of dimemorfan to sigma-1 receptor and its anticonvulsant and locomotor effects in mice, compared with dextromethorphan and dextrorphan". Brain Research 821 (2): 516–519. March 1999. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(99)01125-7. PMID 10064839.
- ↑ "The dextromethorphan analog dimemorfan attenuates kainate-induced seizures via sigma1 receptor activation: comparison with the effects of dextromethorphan". British Journal of Pharmacology 144 (7): 908–918. April 2005. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705998. PMID 15723099.
 |

