Chemistry:Bismuth(III) iodide
| |
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bismuth(III) iodide
| |
| Other names
Bismuth iodide, bismuth triiodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BiI3 | |
| Molar mass | 589.69 g/mol |
| Appearance | Greenish-black crystals |
| Density | 5.778 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 408.6 °C (767.5 °F; 681.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 542 °C (1,008 °F; 815 K)[2] |
| 0.7761 mg/100 mL (20 °C) | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
7.71×10−19[1] |
| Solubility | 50 g/100 mL ethanol 50 g/100 mL 2 M hydrochloric acid |
| −200.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| Trigonal, hR24 | |
| R-3, No. 148 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Bismuth(III) fluoride Bismuth(III) chloride Bismuth(III) bromide |
Other cations
|
Nitrogen triiodide Phosphorus triiodide Antimony triiodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bismuth(III) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula BiI3. This gray-black salt is the product of the reaction of bismuth and iodine, which once was of interest in qualitative inorganic analysis.[3][4]
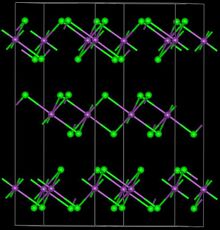
Bismuth(III) iodide adopts a distinctive crystal structure, with iodide centres occupying a hexagonally closest-packed lattice, and bismuth centres occupying either none or two-thirds of the octahedral holes (alternating by layer), therefore it is said to occupy one third of the total octahedral holes.[5][6]
Synthesis
Bismuth(III) iodide forms upon heating an intimate mixture of iodine and bismuth powder:[7][8]
- 2Bi + 3I2 → 2BiI3
BiI3 can also be made by the reaction of bismuth oxide with aqueous hydroiodic acid:[9]
- Bi2O3(s) + 6HI(aq) → 2BiI3(s) + 3H2O(l)
Reactions
Since bismuth(III) iodide is insoluble in water, an aqueous solution can be tested for the presence of Bi3+ ions by adding a source of iodide such as potassium iodide. A black precipitate of bismuth(III) iodide indicates a positive test.[10]
Bismuth(III) iodide forms iodobismuth(III) anions when heated with halide donors:[11]
- 2 NaI + BiI3 → Na2[BiI5]
Bismuth(III) iodide catalyzes the Mukaiyama aldol reaction. Bi(III) is also used in a Barbier type allylation of carbonyl compounds in combination with a reducing agent such as zinc or magnesium.
References
- ↑ John Rumble (June 18, 2018) (in English). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–188. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ↑ Norman, Nicholas C. (1998), Chemistry of Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth, Springer, p. 95, ISBN 0-7514-0389-X, https://books.google.com/books?id=vVhpurkfeN4C&pg=PA187, retrieved 2008-06-03
- ↑ "Bismuth iodide", McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific and Technical Terms, McGraw-Hill, 2003, http://www.answers.com/topic/bismuth-iodide?cat=technology, retrieved 2008-06-19
- ↑ Turner, Jr., Francis M.; Berolzheimer, Daniel D.; Cutter, William P.; Helfrich, John (1920), The Condensed Chemical Dictionary, New York: Chemical Catalog Company, p. 107, https://books.google.com/books?id=y8y0XE0nsYEC&q=%22Bismuth+triiodide%22&pg=PA107, retrieved 2008-06-19
- ↑ Smart, Lesley; Moore, Elaine A. (2005), Solid State Chemistry: An Introduction, CRC Press, p. 40, ISBN 0-7487-7516-1, https://books.google.com/books?id=vDPZLVAoRqQC&q=%22Bismuth+triiodide%22&pg=PA40, retrieved 2008-06-19
- ↑ Mackay, Rosemary Ann; Henderson, W. (2002), Introduction to Modern Inorganic Chemistry, CRC Press, pp. 122–6, ISBN 0-7487-6420-8, https://books.google.com/books?id=e9SjYftJmOYC&q=%22Bismuth+triiodide%22&pg=PA126, retrieved 2008-06-19
- ↑ Watt, George W.; Hakki, Wafai W.; Choppin, Gregory R. (1953). Bismuth(III) Iodide (Bismuth Triiodide). Inorganic Syntheses. 4. pp. 114–116. doi:10.1002/9780470132357.ch38.
- ↑ Erdmann, Hugo; Dunlap, Frederick Leavy (1900), Handbook of Basic Tables for Chemical Analysis, New York: John Wiley & Sons, p. 76, https://books.google.com/books?id=IxlIAAAAIAAJ&q=%22Bismuth+iodide%22&pg=PA76, retrieved 2008-06-19
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 559. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ Bruno, Thomas J.; Svoronos, Paris D. N. (2003), Handbook of Basic Tables for Chemical Analysis, CRC Press, p. 549, ISBN 0-8493-1573-5, https://books.google.com/books?id=AFY2gKwh4AsC&q=%22Bismuth(III)+iodide%22&pg=PA549, retrieved 2008-06-19
- ↑ Norman, Nicholas C. (1998), Chemistry of Arsenic, Antimony and Bismuth, Springer, pp. 168–70, ISBN 0-7514-0389-X, https://books.google.com/books?id=vVhpurkfeN4C&q=%22Bismuth(III)+iodide%22&pg=PA187, retrieved 2008-06-19
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |


