Chemistry:Bromine nitrate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Bromine mononitrate, bromo nitrate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BrNO3 | |
| Molar mass | 141.91 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow liquid |
| Melting point | −42 °C (−44 °F; 231 K) |
| Boiling point | 0 °C (32 °F; 273 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
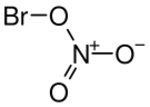
Bromine mononitrate is an inorganic compound, derived from bromine and nitric acid with the chemical formula BrNO3. The compound is a yellow liquid that decomposes at temperatures above 0 °C.[1]
This compounds is extremely reactive due to its intrinsic instability, which makes handling and synthesis challenging. Because of its explosive potential and corrosive character, this substance is mostly used for study in restricted laboratory settings. About its particular characteristics and uses outside of its use as a chemical research subject, not much is known.
Synthesis
Bromine nitrate can be prepared by several methods:
1. Reaction of silver nitrate on an alcoholic solution of bromine:
- Br
2 + AgNO
3 → BrNO
3 + AgBr
2. Reaction of bromine chloride with chlorine nitrate at low temperatures:
- BrCl + ClNO
3 → BrNO
3 + Cl
2
Physical properties
Bromine mononitrate forms an unstable yellow liquid that decomposes at temperatures above 0 °C.
The molecule has the structure BrONO2.[2][3]
The compound is easily soluble in trichlorofluoromethane and carbon tetrachloride.
Applications
Bromine nitrate plays a role in tropospheric chemistry as it reacts with sulfuric acid.[4][5]
References
- ↑ "Bromine nitrate properties - SpringerMaterials". materials.springer.com. https://materials.springer.com/substanceprofile/docs/smsid_zutgcekqnkjjrjlr.
- ↑ Colussi, Agustín J.; Grela, María A. (1998). "Thermochemical kinetics of bromine nitrate, bromine nitrite, halogen hydroperoxides, dichlorine pentoxide, peroxycarboxylic acids, and diacyl peroxides" (in en). International Journal of Chemical Kinetics 30 (1): 41–45. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4601(1998)30:1<41::AID-KIN5>3.0.CO;2-U. ISSN 1097-4601. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/%28SICI%291097-4601%281998%2930%3A1%3C41%3A%3AAID-KIN5%3E3.0.CO%3B2-U. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ↑ Parthiban, Srinivasan; Lee, Timothy J. (8 July 1998). "Ab initio investigation of the atmospheric molecule bromine nitrate: Equilibrium structure, vibrational spectrum, and heat of formation". The Journal of Chemical Physics 109 (2): 525–530. doi:10.1063/1.476589. ISSN 0021-9606. https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.476589. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ↑ Sander, R.; Rudich, Y.; Glasow, R. von; Crutzen, P. J. (1999). "The role of BrNO3 in marine tropospheric chemistry: A model study" (in en). Geophysical Research Letters 26 (18): 2857–2860. doi:10.1029/1999GL900478. ISSN 1944-8007. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/1999GL900478. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
- ↑ Spencer, John E.; Rowland, F. S. (1 January 1978). "Bromine nitrate and its stratospheric significance". The Journal of Physical Chemistry 82 (1): 7–10. doi:10.1021/j100490a002. ISSN 0022-3654. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/j100490a002. Retrieved 31 October 2021.
| HNO3 | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiNO3 | Be(NO3)2 | B(NO3)−4 | C | NO−3, NH4NO3 |
O | FNO3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| NaNO3 | Mg(NO3)2 | Al(NO3)3 | Si | P | S | ClONO2 | Ar | ||||||||||
| KNO3 | Ca(NO3)2 | Sc(NO3)3 | Ti(NO3)4 | VO(NO3)3 | Cr(NO3)3 | Mn(NO3)2 | Fe(NO3)3, Fe(NO3)2 |
Co(NO3)2, Co(NO3)3 |
Ni(NO3)2 | Cu(NO3)2 | Zn(NO3)2 | Ga(NO3)3 | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| RbNO3 | Sr(NO3)2 | Y(NO3)3 | Zr(NO3)4 | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd(NO3)2 | AgNO3 | Cd(NO3)2 | In | Sn | Sb(NO3)3 | Te | I | Xe(NO3)2 |
| CsNO3 | Ba(NO3)2 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg2(NO3)2, Hg(NO3)2 |
Tl(NO3)3, TlNO3 |
Pb(NO3)2 | Bi(NO3)3 BiO(NO3) |
Po | At | Rn | |
| FrNO3 | Ra(NO3)2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La(NO3)3 | Ce(NO3)3, Ce(NO3)4 |
Pr | Nd(NO3)3 | Pm | Sm | Eu(NO3)3 | Gd(NO3)3 | Tb(NO3)3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac(NO3)3 | Th(NO3)4 | Pa | UO2(NO3)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |
