Chemistry:Nelarabine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Arranon, Atriance |
| Other names | 506U78 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607077 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | <25% |
| Metabolism | By adenosine deaminase, to 9-β-D-arabinofuranosylguanine |
| Elimination half-life | 30 minutes (nelarabine) 3 hours (ara-G) |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
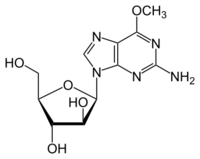
| Formula | C11H15N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 297.271 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Nelarabine, sold under the brand names Arranon (US) and Atriance (EU), is a chemotherapy medication used for the treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL).[1][2]
Nelarabine is a prodrug of arabinosylguanine nucleotide triphosphate (araGTP), a type of purine nucleoside analog, which causes inhibition of DNA synthesis and cytotoxicity.[3] Pre-clinical studies suggest that T-cells are particularly sensitive to nelarabine. In October 2005, it was approved by the FDA for acute lymphoblastic leukemia and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma that has not responded to or has relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens.[4] It was later approved in the European Union in October 2005.[2] It is available as a generic medication.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Arranon- nelarabine injection". 11 June 2020. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=fffa5d75-0dba-4ad7-a252-5f60fa28489a.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Atriance EPAR". https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/atriance.
- ↑ "Nelarabine". IUPHAR/BPS. http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=7090.
- ↑ "FDA drug approval summary: nelarabine (Arranon) for the treatment of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma". The Oncologist 13 (6): 709–14. June 2008. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2006-0017. PMID 18586926.
- ↑ "Competitive Generic Therapy Approvals". 29 June 2023. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/generic-drugs/competitive-generic-therapy-approvals.
External links
- "Nelarabine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/name/nelarabine.
- "Nelarabine". NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/nelarabine.
 |

