Schröder–Hipparchus number
| Named after | Ernst Schröder, Hipparchus, Eugène Charles Catalan |
|---|---|
| Publication year | 1870 (Schröder) |
| No. of known terms | infinity |
| Formula | [math]\displaystyle{ x_n = \sum_{i=1}^n \frac{1}{n}{n\choose i}{n\choose i-1} k^{i-1} }[/math] |
| First terms | 1, 1, 3, 11, 45, 197, 903 |
| OEIS index |
|
In combinatorics, the Schröder–Hipparchus numbers form an integer sequence that can be used to count the number of plane trees with a given set of leaves, the number of ways of inserting parentheses into a sequence, and the number of ways of dissecting a convex polygon into smaller polygons by inserting diagonals. These numbers begin
They are also called the super-Catalan numbers, the little Schröder numbers, or the Hipparchus numbers, after Eugène Charles Catalan and his Catalan numbers, Ernst Schröder and the closely related Schröder numbers, and the ancient Greek mathematician Hipparchus who appears from evidence in Plutarch to have known of these numbers.
Combinatorial enumeration applications
The Schröder–Hipparchus numbers may be used to count several closely related combinatorial objects:[1][2][3][4]
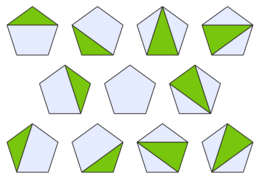
- The nth number in the sequence counts the number of different ways of subdividing of a polygon with n + 1 sides into smaller polygons by adding diagonals of the original polygon.
- The nth number counts the number of different plane trees with n leaves and with all internal vertices having two or more children.
- The nth number counts the number of different ways of inserting parentheses into a sequence of n + 1 symbols, with each pair of parentheses surrounding two or more symbols or parenthesized groups, and without any parentheses surrounding the entire sequence.
- The nth number counts the number of faces of all dimensions of an associahedron Kn + 1 of dimension n − 1, including the associahedron itself as a face, but not including the empty set. For instance, the two-dimensional associahedron K4 is a pentagon; it has five vertices, five faces, and one whole associahedron, for a total of 11 faces.
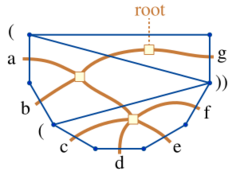
As the figure shows, there is a simple combinatorial equivalence between these objects: a polygon subdivision has a plane tree as a form of its dual graph, the leaves of the tree correspond to the symbols in a parenthesized sequence, and the internal nodes of the tree other than the root correspond to parenthesized groups. The parenthesized sequence itself may be written around the perimeter of the polygon with its symbols on the sides of the polygon and with parentheses at the endpoints of the selected diagonals. This equivalence provides a bijective proof that all of these kinds of objects are counted by a single integer sequence.[2]
The same numbers also count the number of double permutations (sequences of the numbers from 1 to n, each number appearing twice, with the first occurrences of each number in sorted order) that avoid the permutation patterns 12312 and 121323.[5]
Related sequences
The closely related large Schröder numbers are equal to twice the Schröder–Hipparchus numbers, and may also be used to count several types of combinatorial objects including certain kinds of lattice paths, partitions of a rectangle into smaller rectangles by recursive slicing, and parenthesizations in which a pair of parentheses surrounding the whole sequence of elements is also allowed. The Catalan numbers also count closely related sets of objects including subdivisions of a polygon into triangles, plane trees in which all internal nodes have exactly two children, and parenthesizations in which each pair of parentheses surrounds exactly two symbols or parenthesized groups.[3]
The sequence of Catalan numbers and the sequence of Schröder–Hipparchus numbers, viewed as infinite-dimensional vectors, are the unique eigenvectors for the first two in a sequence of naturally defined linear operators on number sequences.[6][7] More generally, the kth sequence in this sequence of integer sequences is (x1, x2, x3, ...) where the numbers xn are calculated as the sums of Narayana numbers multiplied by powers of k. This can be expressed as a hypergeometric function:
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_n = \sum_{i=1}^n N(n,i)\, k^{i-1} = \sum_{i=1}^n \frac{1}{n}{n\choose i}{n\choose i-1} k^{i-1}={}_2F_1(1-n,-n;2;k). }[/math]
Substituting k = 1 into this formula gives the Catalan numbers and substituting k = 2 into this formula gives the Schröder–Hipparchus numbers.[7]
In connection with the property of Schröder–Hipparchus numbers of counting faces of an associahedron, the number of vertices of the associahedron is given by the Catalan numbers. The corresponding numbers for the permutohedron are respectively the ordered Bell numbers and the factorials.
Recurrence
As well as the summation formula above, the Schröder–Hipparchus numbers may be defined by a recurrence relation:
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_n=\frac{1}{n}\left((6n-9)x_{n-1}-(n-3)x_{n-2}\right). }[/math]
Stanley proves this fact using generating functions[8] while Foata and Zeilberger provide a direct combinatorial proof.[9]
History
Plutarch's dialogue Table Talk contains the line:
- Chrysippus says that the number of compound propositions that can be made from only ten simple propositions exceeds a million. (Hipparchus, to be sure, refuted this by showing that on the affirmative side there are 103,049 compound statements, and on the negative side 310,952.)[8]
This statement went unexplained until 1994, when David Hough, a graduate student at George Washington University, observed that there are 103049 ways of inserting parentheses into a sequence of ten items.[1][8][10] The historian of mathematics Fabio Acerbi (CNRS) has shown that a similar explanation can be provided for the other number: it is very close to the average of the tenth and eleventh Schröder–Hipparchus numbers, 310954, and counts bracketings of ten terms together with a negative particle.[10]
The problem of counting parenthesizations was introduced to modern mathematics by (Schröder 1870).[11]
Plutarch's recounting of Hipparchus's two numbers records a disagreement between Hipparchus and the earlier Stoic philosopher Chrysippus, who had claimed that the number of compound propositions that can be made from 10 simple propositions exceeds a million. Contemporary philosopher Susanne Bobzien (2011) has argued that Chrysippus's calculation was the correct one, based on her analysis of Stoic logic. Bobzien reconstructs the calculations of both Chrysippus and Hipparchus, and says that showing how Hipparchus got his mathematics correct but his Stoic logic wrong can cast new light on the Stoic notions of conjunctions and assertibles.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Stanley, Richard P. (1997, 1999), Enumerative Combinatorics, Cambridge University Press. Exercise 1.45, vol. I, p. 51; vol. II, pp. 176–178 and p. 213.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Bijections for the Schröder numbers", Mathematics Magazine 73 (5): 369–376, 2000, doi:10.2307/2690814.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Some problems of non-associative combinations (I)", Edinburgh Mathematical Notes 32: 1–6, 1940, doi:10.1017/S0950184300002639.
- ↑ Holtkamp, Ralf (2006), "On Hopf algebra structures over free operads", Advances in Mathematics 207 (2): 544–565, doi:10.1016/j.aim.2005.12.004.
- ↑ Chen, William Y. C.; Mansour, Toufik; Yan, Sherry H. F. (2006), "Matchings avoiding partial patterns", Electronic Journal of Combinatorics 13 (1): Research Paper 112, 17 pp. (electronic), doi:10.37236/1138, http://www.combinatorics.org/Volume_13/Abstracts/v13i1r112.html.
- ↑ Bernstein, M. (1995), "Some canonical sequences of integers", Linear Algebra and Its Applications 226/228: 57–72, doi:10.1016/0024-3795(94)00245-9.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Coker, Curtis (2004), "A family of eigensequences", Discrete Mathematics 282 (1–3): 249–250, doi:10.1016/j.disc.2003.12.008.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "Hipparchus, Plutarch, Schröder, and Hough", American Mathematical Monthly 104 (4): 344–350, 1997, doi:10.2307/2974582, http://www-math.mit.edu/~rstan/papers/hip.pdf.
- ↑ "A classic proof of a recurrence for a very classical sequence", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 80 (2): 380–384, 1997, doi:10.1006/jcta.1997.2814.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Acerbi, F. (2003), "On the shoulders of Hipparchus: A reappraisal of ancient Greek combinatorics", Archive for History of Exact Sciences 57: 465–502, doi:10.1007/s00407-003-0067-0, archived from the original on 2011-07-21, https://web.archive.org/web/20110721023220/http://stl.recherche.univ-lille3.fr/sitespersonnels/acerbi/acerbipub5.pdf.
- ↑ "Vier kombinatorische Probleme", Zeitschrift für Mathematik und Physik 15: 361–376, 1870.
- ↑ "The Combinatorics of Stoic Conjunction: Hipparchus refuted, Chrysippus vindicated", Oxford Studies in Ancient Philosophy XL: 157–188, Summer 2011, http://ancphil.lsa.umich.edu/-/downloads/osap/40-Bobzien.pdf.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Super Catalan Number". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/SuperCatalanNumber.html.
- The Hipparchus Operad, The n-Category Café, April 1, 2013
 |