Chemistry:Nitrosourea
From HandWiki
Revision as of 09:20, 10 August 2021 by imported>NBrushPhys (url)
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
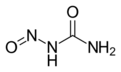
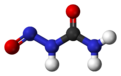
Nitrosourea
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH3N3O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 89.054 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
Nitrosourea is both the name of a molecule, and a class of compounds that include a nitroso (R-NO) group and a urea.
Examples
Examples include:
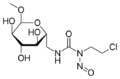
- Arabinopyranosyl-N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (Aranose)
- Carmustine (BCNU, BiCNU)
- Chlorozotocin
- Ethylnitrosourea (ENU)
- Fotemustine
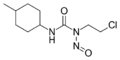
- Lomustine (CCNU)
- Nimustine
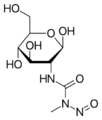
- N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU)
- Ranimustine (MCNU)
- Semustine
- Streptozocin (Streptozotocin)
Nitrosourea compounds are DNA alkylating agents and are often used in chemotherapy.[1] They are lipophilic and thus can cross the blood–brain barrier, making them useful in the treatment of brain tumors such as glioblastoma multiforme.[2]
Side effects
Some nitrosoureas (e.g. lomustine) have been associated with the development of interstitial lung disease.[3]
References
- ↑ "Antineop". http://faculty.swosu.edu/scott.long/phcl/antineop.htm.
- ↑ Takimoto CH, Calvo E. "Principles of oncologic pharmacotherapy". in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (Eds) Cancer management: a multidisciplinary approach. 11 ed. 2008.
- ↑ "Lomustine (CCNU)-induced pulmonary fibrosis". Tumori 72 (1): 95–8. 1986. doi:10.1177/030089168607200114. PMID 3952821.
External links
- Nitrosourea+Compounds at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- DDB 9052
 |