Chemistry:Belzutifan
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /bɛlˈzuːtɪfæn/ bel-ZOO-ti-fan |
| Trade names | Welireg |
| Other names | MK-6482, PT2977 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Antineoplastic |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
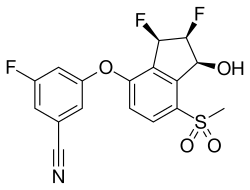
| Formula | C17H12F3NO4S |
| Molar mass | 383.34 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Belzutifan, sold under the brand name Welireg, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of von Hippel–Lindau disease-associated renal cell carcinoma.[6][7][8][9][10][11] It is taken by mouth.[6] Belzutifan is an hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha (HIF-2α) inhibitor.[6][7][12]
Belzutifan's capacity to reduce serum erythropoietin verified its clinically useful for the treatment of malignancies linked to von Hippel-Lindau (VHL), such as renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with clear cell histology (ccRCC), pancreatic lesions, neuroendocrine tumors, and CNS hemangioblastomas or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) but do not require immediate surgery. Belzutifan obtained a disease control rate of 80% in pretreated ccRCC during a phase I trial[13]
The most common side effects include decreased hemoglobin, anemia, fatigue, increased creatinine, headache, dizziness, increased glucose, and nausea.[7]
Belzutifan is the first drug to be awarded an "innovation passport" from the UK Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).[14][9] Belzutifan was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2021.[7][15] Belzutifan is the first hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha inhibitor therapy approved in the US.[15] The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[16]
Medical uses
Belzutifan is indicated for treatment of adults with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease who require therapy for associated renal cell carcinoma (RCC), central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastomas, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET), not requiring immediate surgery.[7] Belzutifan was also found to be efficacious in an adolescent who had Pacak–Zhuang syndrome with polycythemia and paragangliomas.[17]
Adverse effects
Belzutifan was well tolerated, according to the previously available data, and its adverse effect profile was acceptable. Anemia, tiredness, headaches, vertigo, nausea, and dyspnea were the most typical side effects. All participants in the phase II trial reported a hemoglobin reduction of at least 1.9 g/dL; however, only a small number of individuals needed transfusions or erythropoietin-stimulating medications. Because of the downstream effect of HIF-2 inhibition, anemia was a predicted negative outcome of inhibiting the EPO gene. The majority of negative outcomes were grade 1 or 2, while 33% of patients experienced grade 3 to 5 occurrences. In 43% of patients, the course of treatment was discontinued, and in 15% of patients, the dosage had to be adjusted. 2% of patients stopped receiving therapy as a result of a treatment-related. fatigue, increased creatinine, headache, dizziness, elevated hyperglycemia, and nausea were the most frequent side effects, including laboratory abnormalities, recorded in 20% or less of patients. Belzutifan has the potential to harm fetuses and embryos during pregnancy and can render some hormonal contraceptives ineffective Belzutifan had a good safety profile and was well tolerated throughout the three-year follow-up following the phase I trial. There were no new substantial safety concerns or grade 4 or 5 adverse events.[18][19]
History
The FDA granted the application for belzutifan orphan drug designation.[16]
Merck announced in May 2019, that it had acquired Peloton Therapeutics for the development of novel small-molecule therapeutic candidates targeting HIF-2, with belzutifan as the lead candidate. The purchase was completed in July 2019. Merck has patent protection for belzutifan in the United States that is valid until 2034, as of May 2021.[20]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Welireg". 4 January 2023. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/auspmd/welireg.
- ↑ "Welireg (Merck Sharp & Dohme (Australia) Pty Ltd)". 13 January 2023. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/prescription-medicines-registrations/welireg-merck-sharp-dohme-australia-pty-ltd.
- ↑ "Welireg belzutifan 40 mg film-coated tablet bottle (355338)". 23 December 2022. https://www.tga.gov.au/resources/artg/355338.
- ↑ "Product monograph. Belzutifan tablets". https://pdf.hres.ca/dpd_pm/00066615.PDF.
- ↑ "Summary Basis of Decision - Welireg". 23 October 2014. https://hpr-rps.hres.ca/reg-content/summary-basis-decision-detailTwo.php?lang=en&linkID=SBD00616&lang=en.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Welireg- belzutifan tablet, film coated". https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=13e15ee0-d679-4fa9-9430-e2e2170474da.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 "FDA approves belzutifan for cancers associated with von Hippel-Lindau". 13 August 2021. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-belzutifan-cancers-associated-von-hippel-lindau-disease.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Belzutifan". 18 March 2021. https://www.sps.nhs.uk/medicines/belzutifan/.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "MHRA awards first 'innovation passport' under new pathway". RAPS (Press release). Retrieved 25 April 2021.
- ↑ "Merck Receives Priority Review From FDA for New Drug Application for HIF-2α Inhibitor Belzutifan (MK-6482)" (Press release). Merck. 16 March 2016. Retrieved 25 April 2021 – via Business Wire.
- ↑ "FDA Grants Priority Review to Belzutifan for von Hippel-Lindau Disease–Associated RCC". 16 March 2021. https://www.cancernetwork.com/view/fda-grants-priority-review-to-belzutifan-for-von-hippel-lindau-disease-associated-rcc.
- ↑ "Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in renal cell carcinoma with belzutifan: a phase 1 trial and biomarker analysis". Nature Medicine 27 (5): 802–805. May 2021. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01324-7. PMID 33888901.
- ↑ "Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in renal cell carcinoma with belzutifan: a phase 1 trial and biomarker analysis". Nature Medicine 27 (5): 802–805. May 2021. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01324-7. PMID 33888901.
- ↑ "First Innovation Passport awarded to help support development and access to cutting-edge medicines". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) (Press release). 26 February 2021. Retrieved 14 August 2021.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "FDA Approves Merck's Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2 Alpha (HIF-2α) Inhibitor Welireg (belzutifan) for the Treatment of Patients With Certain Types of Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) Disease-Associated Tumors" (Press release). Merck. 13 August 2021. Retrieved 13 August 2021 – via Business Wire.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 (PDF) Advancing Health Through Innovation: New Drug Therapy Approvals 2021 (Report). 13 May 2022. https://www.fda.gov/media/155227/download. Retrieved 22 January 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Belzutifan, a Potent HIF2α Inhibitor, in the Pacak-Zhuang Syndrome". The New England Journal of Medicine 385 (22): 2059–2065. November 2021. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110051. PMID 34818480.
- ↑ "Belzutifan for Renal Cell Carcinoma in von Hippel-Lindau Disease". The New England Journal of Medicine 385 (22): 2036–2046. November 2021. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2103425. PMID 34818478.
- ↑ "FDA Approval Summary: Belzutifan for von Hippel-Lindau Disease-Associated Tumors". Clinical Cancer Research 28 (22): 4843–4848. November 2022. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-1054. PMID 35727604.
- ↑ "Belzutifan: First Approval". Drugs 81 (16): 1921–1927. November 2021. doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01606-x. PMID 34613603.
External links
- Clinical trial number NCT04195750 for "A Study of Belzutifan (MK-6482) Versus Everolimus in Participants With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (MK-6482-005)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03401788 for "A Phase 2 Study of Belzutifan (PT2977, MK-6482) for the Treatment of Von Hippel Lindau (VHL) Disease-Associated Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) (MK-6482-004)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
 |

