Chemistry:Miotine
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
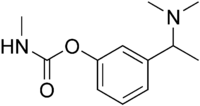
| IUPAC name
[3-[1-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]phenyl] N-methylcarbamate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H18N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 222.288 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Miotine is an anticholinesterase drug. Miotine was the first synthetic carbamate that was used clinically.[1]
Unlike the miotine analog neostigmine, it doesn't have a quaternary ammonium group to give it a permanent positive charge. It can exist as an uncharged free base which could allow it to cross the blood–brain barrier and cause unwanted central nervous system (CNS) side effects.[2]
See also
References
 |

