Order-4 apeirogonal tiling
This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (July 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Order-4 apeirogonal tiling | |
|---|---|
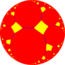
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic regular tiling |
| Vertex configuration | ∞4 |
| Schläfli symbol | {∞,4} r{∞,∞} t(∞,∞,∞) t0,1,2,3(∞,∞,∞,∞) |
| Wythoff symbol | 4 | ∞ 2 2 | ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ | ∞ |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [∞,4], (*∞42) [∞,∞], (*∞∞2) [(∞,∞,∞)], (*∞∞∞) (*∞∞∞∞) |
| Dual | Infinite-order square tiling |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, face-transitive edge-transitive |
In geometry, the order-4 apeirogonal tiling is a regular tiling of the hyperbolic plane. It is a way of covering the hyperbolic plane—a non-Euclidean surface with constant negative curvature—with a repeating pattern of identical shapes without gaps or overlaps.
This tiling is constructed from apeirogons, which are polygons with an infinite number of sides. In this specific pattern, four of these apeirogons meet at each vertex. It can be seen as the hyperbolic equivalent of the familiar square tiling of the Euclidean plane, where four squares meet at each vertex. Its Schläfli symbol is {∞,4}, with the "4" indicating that four polygons meet at a vertex and the "∞" indicating that the polygon used is an apeirogon.
Symmetry
This tiling represents the mirror lines of *2∞ symmetry. Its dual tiling represents the fundamental domains of orbifold notation *∞∞∞∞ symmetry, a square domain with four ideal vertices.
- 120px
Uniform colorings
Like the Euclidean square tiling there are 9 uniform colorings for this tiling, with 3 uniform colorings generated by triangle reflective domains. A fourth can be constructed from an infinite square symmetry (*∞∞∞∞) with 4 colors around a vertex. The checker board, r{∞,∞}, coloring defines the fundamental domains of [(∞,4,4)], (*∞44) symmetry, usually shown as black and white domains of reflective orientations.
| 1 color | 2 color | 3 and 2 colors | 4, 3 and 2 colors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [∞,4], (*∞42) | [∞,∞], (*∞∞2) | [(∞,∞,∞)], (*∞∞∞) | (*∞∞∞∞) | |||
| {∞,4} | r{∞,∞} = {∞,4}1⁄2 |
t0,2(∞,∞,∞) = r{∞,∞}1⁄2 |
t0,1,2,3(∞,∞,∞,∞) = r{∞,∞}1⁄4 = {∞,4}1⁄8 | |||
| 80px (1111) |
80px (1212) |
80px (1213) |
80px (1112) |
80px (1234) |
80px (1123) |
80px (1122) |
Related polyhedra and tiling
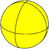
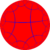
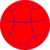
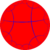
This tiling is also topologically related as a part of sequence of regular polyhedra and tilings with four faces per vertex, starting with the octahedron, with Schläfli symbol {n,4}, and Coxeter diagram ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , with n progressing to infinity.
, with n progressing to infinity.
| *n42 symmetry mutation of regular tilings: {n,4} | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic tilings | |||||
|

|

|
|
|
|

| |
| 24 | 34 | 44 | 54 | 64 | 74 | 84 | ...∞4 |
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [∞,4] family | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|

|

|
|

|
| |
| {∞,4} | t{∞,4} | r{∞,4} | 2t{∞,4}=t{4,∞} | 2r{∞,4}={4,∞} | rr{∞,4} | tr{∞,4} | |
| Dual figures | |||||||

|

|

|

|

|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | 
| |
| V∞4 | V4.∞.∞ | V(4.∞)2 | V8.8.∞ | V4∞ | V43.∞ | V4.8.∞ | |
| Alternations | |||||||
| [1+,∞,4] (*44∞) |
[∞+,4] (∞*2) |
[∞,1+,4] (*2∞2∞) |
[∞,4+] (4*∞) |
[∞,4,1+] (*∞∞2) |
[(∞,4,2+)] (2*2∞) |
[∞,4]+ (∞42) | |
= |
= |
||||||
| h{∞,4} | s{∞,4} | hr{∞,4} | s{4,∞} | h{4,∞} | hrr{∞,4} | s{∞,4} | |
|

|
|
| ||||
| Alternation duals | |||||||

|

|
||||||
| V(∞.4)4 | V3.(3.∞)2 | V(4.∞.4)2 | V3.∞.(3.4)2 | V∞∞ | V∞.44 | V3.3.4.3.∞ | |
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [∞,∞] family | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
= = |
= = |
= = |
= = |
= = |
= |
= |

|
|

|

|

|
|
|
| {∞,∞} | t{∞,∞} | r{∞,∞} | 2t{∞,∞}=t{∞,∞} | 2r{∞,∞}={∞,∞} | rr{∞,∞} | tr{∞,∞} |
| Dual tilings | ||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞ | V(∞.∞)2 | V∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V4.∞.4.∞ | V4.4.∞ |
| Alternations | ||||||
| [1+,∞,∞] (*∞∞2) |
[∞+,∞] (∞*∞) |
[∞,1+,∞] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[∞,∞+] (∞*∞) |
[∞,∞,1+] (*∞∞2) |
[(∞,∞,2+)] (2*∞∞) |
[∞,∞]+ (2∞∞) |

|
|

|

|

|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |
| h{∞,∞} | s{∞,∞} | hr{∞,∞} | s{∞,∞} | h2{∞,∞} | hrr{∞,∞} | sr{∞,∞} |
| Alternation duals | ||||||

|

|

|

| |||
| V(∞.∞)∞ | V(3.∞)3 | V(∞.4)4 | V(3.∞)3 | V∞∞ | V(4.∞.4)2 | V3.3.∞.3.∞ |
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [(∞,∞,∞)] family | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
| (∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} |
r(∞,∞,∞) h2{∞,∞} |
(∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} |
r(∞,∞,∞) h2{∞,∞} |
(∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} |
r(∞,∞,∞) r{∞,∞} |
t(∞,∞,∞) t{∞,∞} |
| Dual tilings | ||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞.∞.∞ |
| Alternations | ||||||
| [(1+,∞,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[∞+,∞,∞)] (∞*∞) |
[∞,1+,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[∞,∞+,∞)] (∞*∞) |
[(∞,∞,∞,1+)] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[(∞,∞,∞+)] (∞*∞) |
[∞,∞,∞)]+ (∞∞∞) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Alternation duals | ||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
| V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V3.∞.3.∞.3.∞ |
See also
- Tilings of regular polygons
- List of uniform planar tilings
- List of regular polytopes
References
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 19, The Hyperbolic Archimedean Tessellations)
- "Chapter 10: Regular honeycombs in hyperbolic space". The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays. Dover Publications. 1999. ISBN 0-486-40919-8.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Hyperbolic tiling". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/HyperbolicTiling.html.
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Poincaré hyperbolic disk". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/PoincareHyperbolicDisk.html.
- Hyperbolic and Spherical Tiling Gallery
- KaleidoTile 3: Educational software to create spherical, planar and hyperbolic tilings
- Hyperbolic Planar Tessellations, Don Hatch
 |


