Chemistry:Vatalanib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | High |
| Metabolism | Extensive hepatic metabolism (mostly CYP3A4-mediated)[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 4.6 ± 1.1 h[1] |
| Excretion | Fecal and renal[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
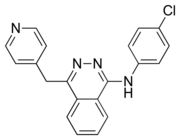
| Formula | C20H15ClN4 |
| Molar mass | 346.82 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Vatalanib (INN, codenamed PTK787 or PTK/ZK) is a small molecule protein kinase inhibitor that inhibits angiogenesis. It is being studied as a possible treatment for several types of cancer, particularly cancer that is at an advanced stage or has not responded to chemotherapy. Vatalanib is orally active, which is to say it is effective when taken by mouth.
Vatalanib is being developed by Bayer Schering and Novartis. It inhibits all known VEGF receptors, as well as platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta and c-kit, but is most selective for VEGFR-2.[1][2][3][4]
Development
Vatalanib was discovered through high-throughput screening.[2] It has been extensively investigated in Phase I, II and III clinical trials.[1][4] Two large, randomized controlled Phase III trials have studied the effect of adding vatalanib to the FOLFOX chemotherapy regimen in people with metastatic colorectal cancer: CONFIRM-1, whose participants had not yet received any treatment for their cancer; and CONFIRM-2, in which participants had received first-line treatment with irinotecan and fluoropyrimidines. Vatalanib produced no significant improvement in overall survival (the primary endpoint of the studies), although it did significantly increase progression-free survival in CONFIRM-2.[4] Both trials found that progression-free survival was improved in people with high levels of lactate dehydrogenase, an enzyme used as a marker of tissue breakdown; the reasons for and implications of this difference are still unclear.[4][5]
Adverse effects
The adverse effects of vatalanib appear similar to those of other VEGF inhibitors. In the CONFIRM trials, the most common side effects were high blood pressure, gastrointestinal upset (diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting), fatigue, and dizziness.[4]
Notable users
Patrick Swayze, a popular actor in the 1980s who starred in such films as Dirty Dancing and Road House was given this drug when he was diagnosed with Stage IV Pancreatic Cancer in 2008. Doctors hoped the drug would cut off blood supply to the tumor.[6] Despite this, Swayze died on September 14, 2009, 20 months after being diagnosed.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Metabolism and disposition of vatalanib (PTK787/ZK-222584) in cancer patients". Drug Metabolism and Disposition 34 (11): 1817–28. November 2006. doi:10.1124/dmd.106.009944. PMID 16882767.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mariani SM (2004). "Antiangiogenesis Cocktails -- Stirred or Shaken?: Highlights of the 9th Annual Drug Discovery Technology World Congress; August 8-13, 2004; Boston, Massachusetts". Medscape General Medicine 6 (4): 21. PMID 15775848. PMC 1480579. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/488203_print. Retrieved on October 29, 2008.
- ↑ "PTK787/ZK 222584, a novel and potent inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, impairs vascular endothelial growth factor-induced responses and tumor growth after oral administration". Cancer Research 60 (8): 2178–89. April 2000. PMID 10786682. http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10786682.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Target practice: lessons from phase III trials with bevacizumab and vatalanib in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer". The Oncologist 12 (4): 443–50. April 2007. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.12-4-443. PMID 17470687.
- ↑ "Vatalanib: the clinical development of a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of angiogenesis in solid tumours". Expert Opin Investig Drugs 16 (3): 367–79. March 2007. doi:10.1517/13543784.16.3.367. PMID 17302531.
- ↑ Mann, Denise. "Patrick Swayze Dies of Pancreatic Cancer" (in en). http://www.webmd.com/cancer/pancreatic-cancer/news/20090915/patrick-swayze-dies-of-pancreatic-cancer.
External links
- Ongoing and completed clinical trials of vatalanib at ClinicalTrials.gov (U.S. National Institutes of Health)
 |

