Chemistry:Parathion S
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
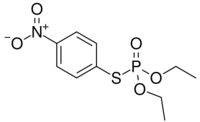
| Preferred IUPAC name
O,O-Diethyl S-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate | |
| Other names
S-Phenyl parathion
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14NO5PS | |
| Molar mass | 291.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale yellow crystalline solid |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
107 μg/kg (mice, intraperitoneal)[1] 4.41 mg/kg (rats, oral)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Parathion S is an organophosphate related to the organophosphate insecticide paraoxon and parathion. It's the structural isomer of parathion. Parathion S is a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "ChemIDplus". https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/3270-86-8.
- ↑ DIGGLE, WM; GAGE, JC (September 1951). "Cholinesterase inhibition in vitro by OO-diethyl O-p-nitrophenyl thiophosphate (parathion, E 605).". The Biochemical Journal 49 (4): 491–4. doi:10.1042/bj0490491. PMID 14886312.
- ↑ ALDRIDGE, WN; DAVISON, AN (December 1952). "The inhibition of erythrocyte cholinesterase by tri-esters of phosphoric acid. II. Diethyl p-nitrophenyl thionphosphate (E605) and analogues.". The Biochemical Journal 52 (4): 663–71. doi:10.1042/bj0520663. PMID 13018298.
 |
