Chemistry:21-Deoxycortisone
From HandWiki
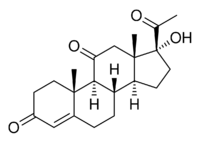
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
17α-Hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bS,9aR,9bS,11aS)-1-Acetyl-1-hydroxy-9a,11a-dimethyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,8,9,9a,9b,11,11a-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-7,10-dione | |
| Other names
21-Desoxycortisone; 11-Keto-17α-hydroxyprogesterone; 17α-Hydroxy-11-ketoprogesterone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H28O4 | |
| Molar mass | 344.451 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
21-Deoxycortisone, also known as 21-desoxycortisone, 11-keto-17α-hydroxyprogesterone, or 17α-hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,11,20-trione, is a naturally occurring, endogenous steroid and minor intermediate and metabolite in corticosteroid metabolism. It is related to 21-deoxycortisol (11β,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone) and is reversibly formed from it by 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, analogously to the reversible formation of cortisone from cortisol.[1] 21-Deoxycortisone can be transformed into cortisone by 21-hydroxylase.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Elevated urine pregnanetriolone definitively establishes the diagnosis of classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency in term and preterm neonates". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89 (12): 6087–91. 2004. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0473. PMID 15579762.
- ↑ "Irradiation and adrenal steroidogenesis: steroid transformations by irradiated isolated perfused calf adrenals". Endocrinology 56 (1): 24–9. 1955. doi:10.1210/endo-56-1-24. PMID 13220521.
 |

