Chemistry:Dehydroandrosterone
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
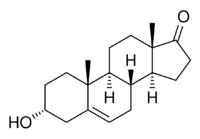
3α-Hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,7R,9aR,9bS,11aS)-7-Hydroxy-9a,11a-dimethyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-one | |
| Other names
DHA; 5-Dehydroandrosterone; 5-DHA; Androst-5-en-3α-ol-17-one; Isoandrostenolone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H28O2 | |
| Molar mass | 288.431 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Dehydroandrosterone (DHA), or 5-dehydroandrosterone (5-DHA), also known as isoandrostenolone, as well as androst-5-en-3α-ol-17-one, is an endogenous androgen steroid hormone.[1][2] It is the 3α-epimer of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; androst-5-en-3β-ol-17-one) and the 5(6)-dehydrogenated and non-5α-reduced analogue of androsterone (5α-androstan-3α-ol-17-one).[2] DHA is produced in and secreted from the adrenal glands, along with other weak androgens like DHEA, androstenediol, and androstenedione.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Wishart, David S.; Djombou Feunang, Yannick; Marcu, Ana; Guo, An Chi; Liang, Kevin; Vázquez Fresno, Rosa; Sajed, Tanvir; Johnson, Daniel et al.. "Showing metabocard for Dehydroandrosterone (HMDB05962)". http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB05962.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 641–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA641.
- ↑ Alfred E. Chang; Patricia A. Ganz; Daniel F. Hayes; Timothy Kinsella; Harvey I. Pass; Joan H. Schiller; Richard M. Stone; Victor Strecher (8 December 2007). Oncology: An Evidence-Based Approach. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 75–. ISBN 978-0-387-31056-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=vxh6u1-ETk0C&pg=PA75.
 |
