Chemistry:4-Hydroxyestradiol
From HandWiki
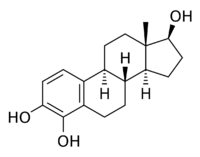
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4,17β-triol
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1S,3aS,3bR,9bS,11aS)-11a-Methyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,9b,10,11,11a-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-1,6,7-triol | |
| Other names
4-OHE2; 3,4,17β-Trihydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-triene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H24O3 | |
| Molar mass | 288.387 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
4-Hydroxyestradiol (4-OHE2), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4,17β-triol, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen and a minor metabolite of estradiol.[1] It is estrogenic, similarly to many other hydroxylated estrogen metabolites such as 2-hydroxyestradiol, 16α-hydroxyestrone, estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), and 4-hydroxyestrone but unlike 2-hydroxyestrone.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Michael Oettel; Ekkehard Schillinger (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens I: Physiology and Mechanisms of Action of Estrogens and Antiestrogens. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 224, 232, 244–245, 249. ISBN 978-3-642-58616-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0BfrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA232.
- ↑ "Comparison of pharmacokinetics of a conjugated equine estrogen preparation (premarin) and a synthetic mixture of estrogens (C.E.S.) in postmenopausal women". J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 7 (3): 175–83. 2000. doi:10.1016/s1071-5576(00)00049-6. PMID 10865186.
External links
 |
