Chemistry:Epietiocholanolone
From HandWiki
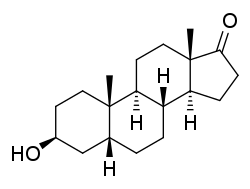
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3β-Hydroxy-5β-androstan-17-one
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,5aR,7S,9aS,9bS,11aS)-7-Hydroxy-9a,11a-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-one | |
| Other names
5β-Androstan-3β-ol-17-one; Etiocholan-3β-ol-17-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H30O2 | |
| Molar mass | 290.447 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Epietiocholanolone, also known as 3β-hydroxy-5β-androstan-17-one or as etiocholan-3β-ol-17-one, is an etiocholane (5β-androstane) steroid as well as an inactive metabolite of testosterone that is formed in the liver.[1][2][3] The metabolic pathway is testosterone to 5β-dihydrotestosterone (via 5β-reductase),[1] 5β-dihydrotestosterone to 3β,5β-androstanediol (via 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase), and 3β,5β-androstanediol to epietiocholanolone (via 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase).[3] Epietiocholanolone can also be formed directly from 5β-androstanedione (via 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase).[3][4] It is glucuronidated and sulfated in the liver and excreted in urine.[3][5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Arun Nagrath; Narendra Malhotra; Seth Shikha (31 July 2012). Progress in Obstetrics & Gynecology. JP Medical Ltd. pp. 265–. ISBN 978-93-5025-779-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=eVZ58V9C3U4C&pg=PA265.
- ↑ J. Horsky; J. Presl (6 December 2012). Ovarian Function and its Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapy. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 107–. ISBN 978-94-009-8195-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=7IrpCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA107.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 MORFIN Robert (20 December 2010). Les stéroïdes naturels de A à Z. Lavoisier. pp. 428–. ISBN 978-2-7430-1918-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=SZ31AQAAQBAJ&pg=PA428.
- ↑ Hugh L. J. Makin; D.B. Gower (4 June 2010). Steroid Analysis. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 462–. ISBN 978-1-4020-9775-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=lzdsEhKWb1gC&pg=PA462.
- ↑ "Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of 23 endogenous steroids in small quantities of primate urine". J. Chromatogr. B 862 (1–2): 100–12. 2008. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.11.009. PMID 18054529.
 |
