Chemistry:α-Ketoisovaleric acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Methyl-2-oxobutanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-Ketoisovaleric acid; α-Ketovaline
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
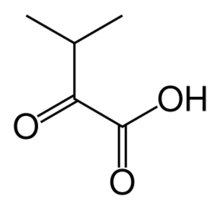
| C5H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 116.116 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless or white solid or oil |
| Melting point | 31.5 °C (88.7 °F; 304.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 170.5 °C (338.9 °F; 443.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
α-Ketoisovaleric acid is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHC(O)CO2H. It is a ketoacid. With a melting point just above room temperature, it is usually an oil or semi-solid. The compound is colorless. It is a metabolite of valine and a precursor to pantothenic acid, a prosthetic group found in several cofactors. In the biological context, is usually encountered as its conjugate base ketoisovalerate, (CH3)2CHC(O)CO2−.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
α-Ketoisovalerate undergoes hydroxymethylation to give ketopantoate:[1]
- (CH3)2CHC(O)CO2− + CH2O → HOCH2(CH3)2CC(O)CO2−
This conversion is catalyzed by ketopantoate hydroxymethyltransferase.
Like many α-ketoacids, α-ketoisovaleric acid is prone to decarboxylation to give isobutyraldehyde:
- (CH3)2CHC(O)CO2H → (CH3)2CHCHO + CO2
Genetic engineering has been used to produce the biofuel isobutanol by reduction of isobutyraldehyde obtained from ketoisovalerate.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Leonardi, Roberta; Jackowski, Suzanne (April 2007). "Biosynthesis of Pantothenic Acid and Coenzyme A". EcoSal Plus 2 (2). doi:10.1128/ecosalplus.3.6.3.4. ISSN 2324-6200. PMID 26443589.
- ↑ Atsumi, Shota; Hanai, Taizo; Liao, James C. (2008). "Non-Fermentative Pathways for Synthesis of Branched-Chain Higher Alcohols as Biofuels". Nature 451 (7174): 86–89. doi:10.1038/nature06450. PMID 18172501. Bibcode: 2008Natur.451...86A.
 |

