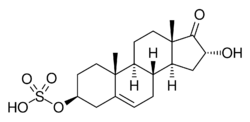
Chemistry:16α-Hydroxy-DHEA sulfate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
16α-Hydroxy-17-oxoandrost-5-en-3β-yl hydrogen sulfate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3aS,3bR,7S,9aR,9bS,11aS)-2-Hydroxy-9a,11a-dimethyl-1-oxo-2,3,3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-yl hydrogen sulfate | |
| Other names
16α-Hydroxy-17-oxoandrost-5-en-3β-yl sulfate; 16α-OH-DHEA-S
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H28O6S | |
| Molar mass | 384.49 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
16α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (16α-OH-DHEA-S), also known as 16α-hydroxy-17-oxoandrost-5-en-3β-yl sulfate, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and a metabolic intermediate in the production of estriol from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) during pregnancy.[1][2] It is the C3β sulfate ester of 16α-hydroxy-DHEA.[3][4]
See also
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
- 15α-Hydroxy-DHEA sulfate
- 16α-Hydroxyandrostenedione
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- Estrone sulfate
References
- ↑ Jerome F. Strauss, III; Robert L. Barbieri (13 September 2013). Yen and Jaffe's Reproductive Endocrinology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 256–. ISBN 978-1-4557-2758-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=KZ95AAAAQBAJ&pg=PA256.
- ↑ Hiroshi Yamazaki (23 June 2014). Fifty Years of Cytochrome P450 Research. Springer. pp. 385–. ISBN 978-4-431-54992-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=9mslBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA385.
- ↑ Mike S. Lee (8 May 2012). Mass Spectrometry Handbook. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 320–. ISBN 978-0-470-53673-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=S6r8geKvKM8C&pg=PA320.
- ↑ Shlomo Melmed; Kenneth S. Polonsky; P. Reed Larsen; Henry M. Kronenberg (30 November 2015). Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 839–. ISBN 978-0-323-29738-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=YZ8_CwAAQBAJ&pg=PA839.
 |

