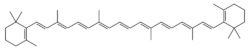
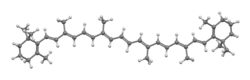
Chemistry:Β-Carotene
 | |
 | |
 | |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
β,β-Carotene
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,1′-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-3,7,12,16-Tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaene-1,18-diyl]bis(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-ene) | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1917416 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C40H56 | |
| Molar mass | 536.888 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Dark orange crystals |
| Density | 1.00 g/cm3[4] |
| Melting point | 183 °C (361 °F; 456 K) decomposes[6] |
| Boiling point | 654.7 °C (1,210.5 °F; 927.9 K) at 760 mmHg (101324 Pa) |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in CS2, benzene, CHCl3, ethanol Insoluble in glycerin |
| Solubility in dichloromethane | 4.51 g/kg (20 °C)[5] = 5.98 g/L (given BCM density of 1.3266 g/cm3 at 20°C) |
| Solubility in hexane | 0.1 g/L |
| log P | 14.764 |
| Vapor pressure | 2.71·10−16 mmHg |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.565 |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | A11CA02 (WHO) D02BB01 (WHO) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H412 | |
| P264, P273, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 103 °C (217 °F; 376 K)[6] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
β-Carotene (beta-carotene) is an organic, strongly colored red-orange pigment abundant in fungi,[7] plants, and fruits. It is a member of the carotenes, which are terpenoids (isoprenoids), synthesized biochemically from eight isoprene units and thus having 40 carbons.
Dietary β-carotene is a provitamin A compound, converting in the body to retinol (vitamin A).[8] In foods, it has rich content in carrots, pumpkin, spinach, and sweet potato.[8] It is used as a dietary supplement and may be prescribed to treat erythropoietic protoporphyria, an inherited condition of sunlight sensitivity.[9]
β-carotene is the most common carotenoid in plants.[8] When used as a food coloring, it has the E number E160a.[10]:119 The structure was deduced in 1930.[11]
Isolation of β-carotene from fruits abundant in carotenoids is commonly done using column chromatography. It is industrially extracted from richer sources such as the algae Dunaliella salina.[12] The separation of β-carotene from the mixture of other carotenoids is based on the polarity of a compound. β-Carotene is a non-polar compound, so it is separated with a non-polar solvent such as hexane.[13] Being highly conjugated, it is deeply colored, and as a hydrocarbon lacking functional groups, it is lipophilic.
Provitamin A activity
Plant carotenoids are the primary dietary source of provitamin A worldwide, with β-carotene as the best-known provitamin A carotenoid.[8] Others include α-carotene and β-cryptoxanthin.[8] Carotenoid absorption is restricted to the duodenum of the small intestine. One molecule of β-carotene can be cleaved by the intestinal enzyme β,β-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase into two molecules of vitamin A.[8][14][15]
Absorption, metabolism and excretion
As part of the digestive process, food-sourced carotenoids must be separated from plant cells and incorporated into lipid-containing micelles to be bioaccessible to intestinal enterocytes.[8] If already extracted (or synthetic) and then presented in an oil-filled dietary supplement capsule, there is greater bioavailability compared to that from foods.[16]
At the enterocyte cell wall, β-carotene is taken up by the membrane transporter protein scavenger receptor class B, type 1 (SCARB1). Absorbed β-carotene is then either incorporated as such into chylomicrons or first converted to retinal and then retinol, bound to retinol binding protein 2, before being incorporated into chylomicrons.[8] The conversion process consists of one molecule of β-carotene cleaved by the enzyme beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase, which is encoded by the BC01 gene, into two molecules of retinal.[8] When plasma retinol is in the normal range the gene expression for SCARB1 and BC01 are suppressed, creating a feedback loop that suppresses β-carotene absorption and conversion.[16]
The majority of chylomicrons are taken up by the liver, then secreted into the blood repackaged into low density lipoproteins (LDLs).[8] From these circulating lipoproteins and the chylomicrons that bypassed the liver, β-carotene is taken into cells via receptor SCARB1. Human tissues differ in expression of SCARB1, and hence β-carotene content. Examples expressed as ng/g, wet weight: liver=479, lung=226, prostate=163 and skin=26.[16]
Once taken up by peripheral tissue cells, the major usage of absorbed β-carotene is as a precursor to retinal via symmetric cleavage by the enzyme beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase, which is encoded by the BC01 gene.[8] A lesser amount is metabolized by the mitochondrial enzyme beta-carotene 9',10'-dioxygenase, which is encoded by the BC02 gene. The products of this asymmetric cleavage are two beta-ionone molecules and rosafluene. BC02 appears to be involved in preventing excessive accumulation of carotenoids; a BC02 defect in chickens results in yellow skin color due to accumulation in subcutaneous fat.[17][18]
Conversion factors
For counting dietary vitamin A intake, β-carotene may be converted either using the newer retinol activity equivalents (RAE) or the older international unit (IU).[8]
Retinol activity equivalents (RAEs)
Since 2001, the US Institute of Medicine uses retinol activity equivalents (RAE) for their Dietary Reference Intakes, defined as follows:[8][19]
- 1 µg RAE = 1 µg retinol from food or supplements
- 1 µg RAE = 2 µg all-trans-β-carotene from supplements
- 1 µg RAE = 12 µg of all-trans-β-carotene from food
- 1 µg RAE = 24 µg α-carotene or β-cryptoxanthin from food
RAE takes into account carotenoids' variable absorption and conversion to vitamin A by humans better than and replaces the older retinol equivalent (RE) (1 µg RE = 1 µg retinol, 6 µg β-carotene, or 12 µg α-carotene or β-cryptoxanthin).[19] RE was developed 1967 by the United Nations/World Health Organization Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO/WHO).[20]
International Units
Another older unit of vitamin A activity is the international unit (IU).[8] Like retinol equivalent, the international unit does not take into account carotenoid variable absorption and conversion to vitamin A by humans, as well as the more modern retinol activity equivalent. Unfortunately, food and supplement labels still generally use IU, but IU can be converted to the more useful retinol activity equivalent as follows:[19]
- 1 µg RAE = 3.33 IU retinol
- 1 IU retinol = 0.3 μg RAE
- 1 IU β-carotene from supplements = 0.3 μg RAE
- 1 IU β-carotene from food = 0.05 μg RAE
- 1 IU α-carotene or β-cryptoxanthin from food = 0.025 μg RAE1
Dietary sources
The average daily intake of β-carotene is in the range 2–7 mg, as estimated from a pooled analysis of 500,000 women living in the US, Canada, and some European countries.[21] Beta-carotene is found in many foods and is sold as a dietary supplement.[8] β-Carotene contributes to the orange color of many different fruits and vegetables. Vietnamese gac (Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng.) and crude palm oil are particularly rich sources, as are yellow and orange fruits, such as cantaloupe, mangoes, pumpkin, and papayas, and orange root vegetables such as carrots and sweet potatoes.[8]
The color of β-carotene is masked by chlorophyll in green leaf vegetables such as spinach, kale, sweet potato leaves, and sweet gourd leaves.[8][22]
The U.S. Department of Agriculture lists foods high in β-carotene content:[23]
| Food | Beta-carotene
Milligrams per 100 g |
|---|---|
| Sweet potato, skinned, boiled | 9.4 |
| Carrot juice | 9.3 |
| Carrots, raw or boiled | 9.2 |
| Kale, boiled | 8.8 |
| Pumpkin, canned | 6.9 |
| Spinach, canned | 5.9 |
No dietary requirement
Government and non-government organizations have not set a dietary requirement for β-carotene.[16]
Side effects
Excess β-carotene is predominantly stored in the fat tissues of the body.[8] The most common side effect of excessive β-carotene consumption is carotenodermia, a physically harmless condition that presents as a conspicuous orange skin tint arising from deposition of the carotenoid in the outermost layer of the epidermis.[8][9][16][24]
Carotenosis
Carotenoderma, also referred to as carotenemia, is a benign and reversible medical condition where an excess of dietary carotenoids results in orange discoloration of the outermost skin layer.[8] It is associated with a high blood β-carotene value. This can occur after a month or two of consumption of beta-carotene rich foods, such as carrots, carrot juice, tangerine juice, mangos, or in Africa, red palm oil. β-carotene dietary supplements can have the same effect. The discoloration extends to palms and soles of feet, but not to the white of the eye, which helps distinguish the condition from jaundice. Carotenodermia is reversible upon cessation of excessive intake.[25] Consumption of greater than 30 mg/day for a prolonged period has been confirmed as leading to carotenemia.[16][26]
No risk for hypervitaminosis A
At the enterocyte cell wall, β-carotene is taken up by the membrane transporter protein scavenger receptor class B, type 1 (SCARB1). Absorbed β-carotene is then either incorporated as such into chylomicrons or first converted to retinal and then retinol, bound to retinol binding protein 2, before being incorporated into chylomicrons. The conversion process consists of one molecule of β-carotene cleaved by the enzyme beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase, which is encoded by the BC01 gene, into two molecules of retinal. When plasma retinol is in the normal range the gene expression for SCARB1 and BC01 are suppressed, creating a feedback loop that suppresses absorption and conversion. Because of these two mechanisms, high intake will not lead to hypervitaminosis A.[16]
Drug interactions
β-Carotene can interact with medication used for lowering cholesterol.[8] Taking them together can lower the effectiveness of these medications and is considered only a moderate interaction.[8] Bile acid sequestrants and proton-pump inhibitors can decrease absorption of β-carotene.[27] Consuming alcohol with β-carotene can decrease its ability to convert to retinol and could possibly result in hepatotoxicity.[28]
β-Carotene and lung cancer in smokers
Chronic high doses of β-carotene supplementation increases the probability of lung cancer in smokers.[8][29] The effect is specific to supplementation dose as no lung damage has been detected in those who are exposed to cigarette smoke and who ingest a physiological dose of β-carotene (6 mg), in contrast to high pharmacological dose (30 mg). Therefore, the oncology from β-carotene is based on both cigarette smoke and high daily doses of β-carotene.[8][30]
Increases in lung cancer may be due to the tendency of β-carotene to oxidize,[31] and may hasten oxidation more than other food colors such as annatto. A β-carotene breakdown product suspected of causing cancer at high dose is trans-β-apo-8'-carotenal (common apocarotenal), which has been found in one study to be mutagenic and genotoxic in cell cultures which do not respond to β-carotene itself.[32]
Additionally, supplemental, high-dose β-carotene may increase the risk of prostate cancer, intracerebral hemorrhage, and cardiovascular and total mortality in people who smoke cigarettes or have a history of high-level exposure to asbestos.[8][9]
Industrial sources
β-carotene is industrially made either by total synthesis (see Retinol § Industrial synthesis) or by extraction from biological sources such as vegetables, microalgae (especially Dunaliella salina), and genetically-engineered microbes. The synthetic path is low-cost and high-yield.[33]
Research
Medical authorities generally recommend obtaining beta-carotene from food rather than dietary supplements.[8] A 2013 meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials concluded that high-dosage (≥9.6 mg/day) beta-carotene supplementation is associated with a 6% increase in the risk of all-cause mortality, while low-dosage (<9.6 mg/day) supplementation does not have a significant effect on mortality.[34] Research is insufficient to determine whether a minimum level of beta-carotene consumption is necessary for human health and to identify what problems might arise from insufficient beta-carotene intake.[35] However, a 2018 meta-analysis mostly of prospective cohort studies found that both dietary and circulating beta-carotene are associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality. The highest circulating beta-carotene category, compared to the lowest, correlated with a 37% reduction in the risk of all-cause mortality, while the highest dietary beta-carotene intake category, compared to the lowest, was linked to an 18% decrease in the risk of all-cause mortality.[36]
Macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) represents the leading cause of irreversible blindness in elderly people. AMD is an oxidative stress, retinal disease that affects the macula, causing progressive loss of central vision.[37] β-carotene content is confirmed in human retinal pigment epithelium.[16] Reviews reported mixed results for observational studies, with some reporting that diets higher in β-carotene correlated with a decreased risk of AMD whereas other studies reporting no benefits.[38] Reviews reported that for intervention trials using only β-carotene, there was no change to risk of developing AMD.[8][38][39]
Cancer
A meta-analysis concluded that supplementation with β-carotene does not appear to decrease the risk of cancer overall, nor specific cancers including: pancreatic, colorectal, prostate, breast, melanoma, or skin cancer generally.[8][40] High levels of β-carotene may increase the risk of lung cancer in current and former smokers.[8][41] This is likely because beta-carotene is unstable in cigarette smoke-exposed lungs where it forms oxidized metabolites that can induce carcinogen-bioactivating enzymes.[42] Results are not clear for thyroid cancer.[43]
Cataract
A Cochrane review looked at supplementation of β-carotene, vitamin C, and vitamin E, independently and combined, on people to examine differences in risk of cataract, cataract extraction, progression of cataract, and slowing the loss of visual acuity. These studies found no evidence of any protective effects afforded by β-carotene supplementation on preventing and slowing age-related cataract.[44] A second meta-analysis compiled data from studies that measured diet-derived serum beta-carotene and reported a not statistically significant 10% decrease in cataract risk.[45]
Erythropoietic protoporphyria
High doses of β-carotene (up to 180 mg per day) may be used as a treatment for erythropoietic protoporphyria, a rare inherited disorder of sunlight sensitivity, without toxic effects.[8][9]
Food drying
Foods rich in caretenoid dyes show discoloration upon drying. This is due to thermal degradation of caretenoids, possibly via isomerization and oxidation reactions.[46]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hursthouse, M. B.; Nathani, S. C.; Moss, G. P. (2004). CSD Entry: CARTEN02. Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre. doi:10.5517/cc8j3mh. https://dx.doi.org/10.5517/cc8j3mh. Retrieved 9 July 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Senge, Mathias O.; Hope, Häkon; Smith, Kevin M. (1992). "Structure and Conformation of Photosynthetic Pigments and Related Compounds 3. Crystal Structure of β-Carotene". Z. Naturforsch. C 47 (5–6): 474–476. doi:10.1515/znc-1992-0623.
- ↑ "SciFinder – CAS Registry Number 7235-40-7". https://scifinder.cas.org.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedr1 - ↑ "Beta-carotene". PubChem, US National Library of Medicine. 27 January 2024. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5280489.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Sigma-Aldrich Co., β-Carotene. Retrieved on 27 May 2014.
- ↑ Lee, Soo Chan; Ristaino, Jean B.; Heitman, Joseph (13 December 2012). "Parallels in Intercellular Communication in Oomycete and Fungal Pathogens of Plants and Humans". PLOS Pathogens 8 (12): e1003028. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003028. PMID 23271965.
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14 8.15 8.16 8.17 8.18 8.19 8.20 8.21 8.22 8.23 8.24 8.25 8.26 8.27 8.28 8.29 "α-Carotene, β-Carotene, β-Cryptoxanthin, Lycopene, Lutein, and Zeaxanthin". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis. October 2023. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/dietary-factors/phytochemicals/carotenoids.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "Beta-carotene". MedlinePlus, National Library of Medicine, US National Institutes of Health. 27 January 2023. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/natural/999.html.
- ↑ Milne, George W. A. (2005). Gardner's commercially important chemicals: synonyms, trade names, and properties. New York: Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-73518-2.
- ↑ "Pflanzenfarbstoffe XXV. Über die Konstitution des Lycopins und Carotins". Helvetica Chimica Acta 13 (5): 1084–1099. 1930. doi:10.1002/hlca.19300130532.
- ↑ Rüegg, Rudolf, "Extraction Process for Beta-Carotene", States4439629 United States patent expired 4439629, published 27 March 1984, assigned to Hoffmann-La Roche Inc.
- ↑ "Carotenoids from guava (Psidium guajava l.): isolation and structure elucidation". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 47 (1): 145–51. January 1999. doi:10.1021/jf980405r. PMID 10563863.
- ↑ Conversion of β-carotene to retinal pigment. Vitamins & Hormones. 75. 2007. pp. 117–30. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(06)75005-1. ISBN 978-0-12-709875-3.
- ↑ "Carotenoid metabolism in mammals, including man: formation, occurrence, and function of apocarotenoids". J Lipid Res 54 (7): 1719–30. July 2013. doi:10.1194/jlr.R039537. PMID 23667178.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 16.6 16.7 BP Marriott, ed (2020). "Carotenoids". Present Knowledge in Nutrition, Eleventh Edition. London, United Kingdom: Academic Press (Elsevier). pp. 531–49. ISBN 978-0-323-66162-1.
- ↑ "Characterization of the Role of β-Carotene 9,10-Dioxygenase in Macular Pigment Metabolism". J Biol Chem 290 (41): 24844–57. October 2015. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.668822. PMID 26307071.
- ↑ "Molecular aspects of β, β-carotene-9', 10'-oxygenase 2 in carotenoid metabolism and diseases". Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 241 (17): 1879–1887. November 2016. doi:10.1177/1535370216657900. PMID 27390265.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Micronutrients (2001). Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium and Zinc. (free download): National Academy Press. doi:10.17226/10026. ISBN 978-0-309-07279-3.
- ↑ Requirement of Vitamin A, Thiamine, Riboflavin and Niacin. FAO Food and Nutrition Series B. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization. 1967.
- ↑ "Intake of the major carotenoids and the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer in a pooled analysis of 10 cohort studies". International Journal of Cancer 119 (9): 2148–54. November 2006. doi:10.1002/ijc.22076. PMID 16823847.
- ↑ "Chromatographic determination of changes in pigments in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) during processing". Journal of Chromatographic Science 43 (9): 466–72. October 2005. doi:10.1093/chromsci/43.9.466. PMID 16212792.
- ↑ "USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 28". 28 October 2015. https://ods.od.nih.gov/pubs/usdandb/VitA-betaCarotene-Content.pdf#search=%22beta-carotene%22.
- ↑ BP Marriott, ed (2020). "Vitamin A". Present Knowledge in Nutrition, Eleventh Edition. London, United Kingdom: Academic Press (Elsevier). pp. 73–92. ISBN 978-0-323-66162-1.
- ↑ "Carotenoderma--a review of the current literature". Int J Dermatol 42 (3): 178–81. March 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01657.x. PMID 12653910.
- ↑ "Carotenemia". StatPearls. 11 August 2021. doi:10.1007/s00253-001-0902-7. PMID 30521299.
- ↑ Meschino Health. "Comprehensive Guide to Beta-Carotene". http://www.meschinohealth.com/books/beta_carotene.
- ↑ "Alcohol, vitamin A, and beta-carotene: adverse interactions, including hepatotoxicity and carcinogenicity". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 69 (6): 1071–85. June 1999. doi:10.1093/ajcn/69.6.1071. PMID 10357725.
- ↑ "Beta-carotene in multivitamins and the possible risk of lung cancer among smokers versus former smokers: a meta-analysis and evaluation of national brands". Cancer 113 (1): 150–7. July 2008. doi:10.1002/cncr.23527. PMID 18429004.
- ↑ Russel, R.M. (2002). "Beta-carotene and lung cancer". Pure Appl. Chem. 74 (8): 1461–1467. doi:10.1351/pac200274081461.
- ↑ "Toxicity of oxidized beta-carotene to cultured human cells". Experimental Eye Research 81 (2): 239–43. August 2005. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2005.04.002. PMID 15967438.
- ↑ "Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of beta-carotene breakdown products on primary rat hepatocytes". Carcinogenesis 25 (5): 827–31. May 2004. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh056. PMID 14688018.
- ↑ Singh, Rahul Vikram; Sambyal, Krishika (June 2022). "An overview of β-carotene production: Current status and future prospects". Food Bioscience 47: 101717. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101717.
- ↑ "Meta-regression analyses, meta-analyses, and trial sequential analyses of the effects of supplementation with beta-carotene, vitamin A, and vitamin E singly or in different combinations on all-cause mortality: do we have evidence for lack of harm?". PLOS ONE 8 (9): e74558. 2013. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074558. PMID 24040282. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...874558B.
- ↑ Stargrove, Mitchell (20 December 2007). Herb, nutrient, and drug interactions : clinical implications and therapeutic strategies (1 ed.). Mosby. ISBN 978-0323029643.
- ↑ "Dietary Antioxidants, Circulating Antioxidant Concentrations, Total Antioxidant Capacity, and Risk of All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies.". Adv Nutr 9 (6): 701–716. 2018. doi:10.1093/advances/nmy040. PMID 30239557.
- ↑ "Prevention of the Onset of Age-Related Macular Degeneration". J Clin Med 10 (15): 3297. July 2021. doi:10.3390/jcm10153297. PMID 34362080.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "The Age-Related Eye Disease 2 Study: Micronutrients in the Treatment of Macular Degeneration". Adv Nutr 8 (1): 40–53. January 2017. doi:10.3945/an.116.013177. PMID 28096126.
- ↑ "Antioxidant vitamin and mineral supplements for preventing age-related macular degeneration". Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017 (7): CD000253. July 2017. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000253.pub4. PMID 28756617.
- ↑ "Beta-carotene supplementation and cancer risk: a systematic review and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials". International Journal of Cancer 127 (1): 172–84. July 2010. doi:10.1002/ijc.25008. PMID 19876916.
- ↑ "Vitamin supplement consumption and breast cancer risk: a review". ecancermedicalscience 7: 365. October 2013. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2013.365. PMID 24171049.
- ↑ "The enigma of beta-carotene in carcinogenesis: what can be learned from animal studies". The Journal of Nutrition 134 (1): 262S–268S. January 2004. doi:10.1093/jn/134.1.262S. PMID 14704331.
- ↑ "Vitamin and mineral supplements and thyroid cancer: a systematic review". European Journal of Cancer Prevention 22 (2): 158–68. March 2013. doi:10.1097/cej.0b013e32835849b0. PMID 22926510.
- ↑ "Antioxidant vitamin supplementation for preventing and slowing the progression of age-related cataract". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 6 (6): CD004567. June 2012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004567.pub2. PMID 22696344.
- ↑ "Association of blood antioxidants and vitamins with risk of age-related cataract: a meta-analysis of observational studies". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 98 (3): 778–86. September 2013. doi:10.3945/ajcn.112.053835. PMID 23842458.
- ↑ Song, Jiangfeng; Wang, Xiaoping; Li, Dajing; Liu, Chunquan (18 December 2017). "Degradation kinetics of carotenoids and visual colour in pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima L.) slices during microwave-vacuum drying" (in en). International Journal of Food Properties 20 (sup1): S632–S643. doi:10.1080/10942912.2017.1306553. ISSN 1094-2912.
 |


