Chemistry:Salvinorin A
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Buccal/Sublingual, Smoked |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
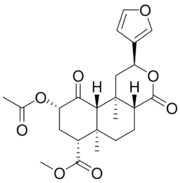
| Formula | C23H28O8 |
| Molar mass | 432.469 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Specific rotation | [α]D = -45.3° at 22 °C/ (c = 8.530 CHCl3); [α]D = -41° at 25 °C (c = 1 in CHCl3) |
| Melting point | 238 to 240 °C (460 to 464 °F) (also reported 242–244 °C)[1] |
| Boiling point | 760.2 °C (1,400.4 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 25.07 mg/L at 25 °C (water, est) mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Salvinorin A is the main active psychotropic molecule in Salvia divinorum. Salvinorin A is considered a dissociative hallucinogen.[2][3]
It is structurally distinct from other naturally occurring hallucinogens (such as DMT, psilocybin, and mescaline) because it contains no nitrogen atoms; hence, it is not an alkaloid (and cannot be rendered as a salt), but rather is a terpenoid.[2] It also differs in subjective experience, compared to other hallucinogens, and has been described as dissociative.[3]
Salvinorin A can produce psychoactive experiences in humans with a typical duration of action being several minutes to an hour or so, depending on the method of ingestion.[4]
Salvinorin A is found with several other structurally related salvinorins. Salvinorin is a trans-neoclerodane diterpenoid. It acts as a kappa opioid receptor agonist and is the first known compound acting on this receptor that is not an alkaloid.[4]
History
Salvinorin A was first described and named in 1982 by Alfredo Ortega and colleagues in Mexico. They used a combination of spectroscopy and x-ray crystallography to determine the chemical structure of the compound, which was shown to have a bicyclic diterpene structure.[5] Around the same time, Leander Julián Valdés III independently isolated the molecule as part of his PhD research, published in 1983.[6] Valdés named the chemical divinorin, and also isolated an analog that he named divinorin B. The naming was subsequently corrected to salvinorin A and B after the work was published in 1984.[7] Valdés later isolated salvinorin C.[8]
Pharmacology
Salvinorin A is a trans-neoclerodane diterpenoid with the chemical formula C23H28O8.[9] Unlike other known opioid-receptor ligands, salvinorin A is not an alkaloid, as it does not contain a basic nitrogen atom.[2][10] Salvinorin A has no action at the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor, the principal molecular target responsible for the actions of 'classical' psychedelics such as LSD and mescaline.[4][10] Salvinorin A has also been shown to have effect on cannabinoid CB1 receptors.[11] It significantly increases prolactin and inconsistently increases cortisol.[12] It causes dysphoria by stopping release of dopamine in the striatum.[13] Salvinorin A increases activity of DAT while decreasing activity of SERT.[13]
Pharmacokinetics
Salvinorin A is effectively deactivated by the gastrointestinal system, so alternative routes of administration must be used for better absorption. It is absorbed by oral mucosa.[14] It has a half-life of around 8 minutes in non-human primates.[15]
Potency and selectivity
Salvinorin A is active at doses as low as 200 µg.[9][16]Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
Detection in urine
Researchers found that humans who smoked 580 μg of the pure drug had urine salvinorin A concentrations of 2.4–10.9 µg/L during the first hour; the levels fell below the detection limit by 1.5 hours after smoking.[17]
Research
Salvinorin A has only been administered to humans in a few studies, one showing that its effects peaked at about 2 minutes, that its subjective effects may overlap with those of serotonergic psychedelics, and that it temporarily impairs recall and recognition memory.[3] Like most other agonists of kappa opioid receptors, salvinorin A produces sedation, psychotomimesis, dysphoria, anhedonia, and depression.[2][18][19] Salvinorin A has been screened for its possible use as a structural "scaffold" in medicinal chemistry in developing new drugs for treating psychiatric diseases[2][20] such as cocaine dependence.[21]
Synthesis

Biosynthesis
The biogenic origin of salvinorin A synthesis has been elucidated using nuclear magnetic resonance and ESI-MS analysis of incorporated precursors labeled with stable isotopes of carbon (carbon-13 13C) and hydrogen (deuterium 2H). It "is biosynthesized via the 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway", rather than the classic mevalonate pathway, consistent with the common plastidial localization of diterpenoid metabolism.[22]
Terpenoids are biosynthesized from two 5-carbon precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). The NMR and MS study by Zjawiony suggested that the biosynthesis of salvinorin A proceeds via the 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway. In the deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway, D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and pyruvate, the intermediates of the glycolysis, are converted into 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate via decarboxylation. Subsequent reduction with NADPH generates 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate, via the intermediates 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol and 4-diphosphocytidyl-2c-methyl-d-erythritol-2-phosphate, which then lead to IPP and DMAPP.

Subsequent addition of three 5-carbon IPP units to a single 5-carbon DMAPP unit generates the 20-carbon central precursor, geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP). Bicyclization of GGPP by the class II diterpene synthase, ent-clerodienyl diphosphate synthase (SdCPS2[23]), produces a labdanyl diphosphate carbocation, which is subsequently rearranged through a sequence of 1,2-hydride and methyl shifts to form the ent-clerodienyl diphosphate intermediate.[24] SdCPS2 catalyzes the first committed reaction in the biosynthesis of salvinorin A by producing its characteristic clerodane scaffold. A series of oxygenation, acylation and methylation reactions is then required to complete the biosynthesis of salvinorin A.[23]

Similar to many plant-derived psychoactive compounds, salvinorin A is excreted via peltate glandular trichomes, which reside external to the epidermis.[25][26]
Chemical synthesis
A total asymmetric synthesis of salvinorin A, which relies on a transannular Michael reaction cascade to construct the ring system, was achieved as a 4.5% overall yield over 30 steps,[27] then revised using 24 steps to yield salvinorin A in 0.15% yield.[28] An approach to the trans-decalin ring system of salvinorin A used an intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction/Tsuji allylation strategy,[29] and a total synthesis of salvinorin A was achieved using the intramolecular Diels-Alder / Tsuji allylation approach, combined with an asymmetric late-stage addition of the furan moiety.[30]
Associated compounds
Salvinorin A is one of several structurally related salvinorins found in the Salvia divinorum plant. Salvinorin A is the only naturally occurring salvinorin that is known to be psychoactive.[31] Salvinorin A can be synthesized from salvinorin B by acetylation, and de-acetylated salvinorin A becomes analog to salvinorin B.[32]
Research has produced a number of semi-synthetic compounds. Most derivatives are selective kappa opioid agonists as with salvinorin A, although some are even more potent, with the most potent compound salvinorin B ethoxymethyl ether being ten times stronger than salvinorin A. Some derivatives, such as herkinorin, reduce kappa opioid action and instead act as mu opioid agonists.[33][34][35][36]
The synthetic derivative RB-64 is notable because of its functional selectivity and potency.[37] Salvinorin B methoxymethyl ether is seven times more potent than salvinorin A at KOPr in GTP-γS assays.[38]
Natural occurrence
Salvinorin A occurs naturally in several Salvia species:
- S. divinorum (0.89 mg/g to 3.70 mg/g).[39]
- S. recognita (212.9 μg/g).[40]
- S. cryptantha (51.5 μg/g).[40]
- S. glutinosa (38.9 μg/g).[40]
Salvinorin B has been detected in S. potentillifolia and S. adenocaulon, however these species do not contain a measureable amount of salvinorin A.[40]
Legal status
Salvinorin A is sometimes regulated together with its host, Salvia divinorum, due to its psychoactive and analgesic effects.
United States
Salvinorin A is not scheduled at the federal level in the United States .[41] Its molecular structure is unlike any Schedule I or II drug, so possession or sales is unlikely to be prosecuted under the Federal Analogue Act.[citation needed]
Florida
"Salvinorin A" is a Schedule I controlled substance in the state of Florida making it illegal to buy, sell, or possess in Florida. There is an exception however for "any drug product approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration which contains salvinorin A or its isomers, esters, ethers, salts, and salts of isomers, esters, and ethers, if the existence of such isomers, esters, ethers, and salts is possible within the specific chemical designation."[42]
Australia
Salvinorin A is considered a Schedule 9 prohibited substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (October 2015).[43] A Schedule 9 substance is a substance which may be abused or misused, the manufacture, possession, sale or use of which should be prohibited by law except when required for medical or scientific research, or for analytical, teaching or training purposes with approval of Commonwealth and/or State or Territory Health Authorities.[43]
Sweden
Sveriges riksdags health ministry Statens folkhälsoinstitut classified salvinorin A (and Salvia divinorum) as "health hazard" under the act Lagen om förbud mot vissa hälsofarliga varor (translated Act on the Prohibition of Certain Goods Dangerous to Health) as of April 1, 2006, in their regulation SFS 2006:167 listed as "salvinorin A", making it illegal to sell or possess.[44]
See also
- Psychoactive drug
- List of entheogens
- Collybolide
- Nalfurafine
- Difelikefalin
- Enadoline
References
- ↑ salvinorin A, PubChem, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=128563#x27, retrieved 2012-11-23
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Salvinorin A, a kappa-opioid receptor agonist hallucinogen: pharmacology and potential template for novel pharmacotherapeutic agents in neuropsychiatric disorders". Frontiers in Pharmacology 6: 190. 2015. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00190. PMID 26441647.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Dose-related effects of salvinorin A in humans: dissociative, hallucinogenic, and memory effects". Psychopharmacology 226 (2): 381–392. March 2013. doi:10.1007/s00213-012-2912-9. PMID 23135605.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99 (18): 11934–11939. September 2002. doi:10.1073/pnas.182234399. PMID 12192085. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9911934R.
- ↑ "Salvinorin, a new trans-neoclerodane diterpene from Salvia divinorum (Labiatae)". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1: 2505–8. 1982. doi:10.1039/P19820002505.
- ↑ Valdés III LJ (1983). The pharmacognosy of Salvia divinorum (Epling and Jativa-M): An Investigation of Ska Maria Pastora (Mexico) (PhD thesis). University of Michigan. ProQuest 303280881.
- ↑ "Divinorin A, a psychotropic terpenoid, and divinorin B from the hallucinogenic Mexican mint Salvia divinorum". Journal of Organic Chemistry 49 (24): 4716–20. 1984. doi:10.1021/jo00198a026.
- ↑ "Salvinorin C, a new neoclerodane diterpene from a bioactive fraction of the hallucinogenic Mexican mint Salvia divinorum". Organic Letters 3 (24): 3935–3937. November 2001. doi:10.1021/ol016820d. PMID 11720573.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Psychopharmacology of the hallucinogenic sage Salvia divinorum". Life Sciences 78 (5): 527–531. December 2005. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2005.09.008. PMID 16213533.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Synthetic studies of neoclerodane diterpenes from Salvia divinorum: semisynthesis of salvinicins A and B and other chemical transformations of salvinorin A". Journal of Natural Products 69 (1): 107–112. January 2006. doi:10.1021/np050398i. PMID 16441078.
- ↑ "Salvinorin A". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/128563.
- ↑ "Time course of pharmacokinetic and hormonal effects of inhaled high-dose salvinorin A in humans". Journal of Psychopharmacology 30 (4): 323–329. April 2016. doi:10.1177/0269881116629125. PMID 26880225.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Salvinorin A regulates dopamine transporter function via a kappa opioid receptor and ERK1/2-dependent mechanism". Neuropharmacology 86: 228–240. November 2014. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.07.016. PMID 25107591.
- ↑ "Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: new pharmacologic findings". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 43 (1): 53–56. June 1994. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(94)90116-3. PMID 7526076.
- ↑ "Immediate and Persistent Effects of Salvinorin A on the Kappa Opioid Receptor in Rodents, Monitored In Vivo with PET". Neuropsychopharmacology 40 (13): 2865–2872. December 2015. doi:10.1038/npp.2015.159. PMID 26058662.
- ↑ "The pharmacological effects of Salvia species on the central nervous system". Phytotherapy Research 20 (6): 427–437. June 2006. doi:10.1002/ptr.1898. PMID 16619340. "However, when smoked (in a manner similar to free base cocaine), the compound is effective in doses of 200–500 μg and produces visions that last from 30 minutes to an hour or two, while doses over 2 mg are effective for much longer. At doses greater than 500 μg the subject is often no longer aware of their surroundings and may enter an uncontrollable delirium. This compound is the most potent naturally occurring hallucinogen thus far isolated.".
- ↑ "Quantification of the plant-derived hallucinogen Salvinorin A in conventional and non-conventional biological fluids by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry after Salvia divinorum smoking". Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 19 (12): 1649–1656. 30 June 2005. doi:10.1002/rcm.1970. PMID 15915477. Bibcode: 2005RCMS...19.1649P.
- ↑ A Literature Review on the Status and Effects of Salvia Divinorum on Cognitive, Affective, and Behavioral Functioning. Universal-Publishers. 2 December 2011. pp. 27–. ISBN 978-1-61233-777-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=UFp_x7qBPk0C&pg=PA27.
- ↑ The Interface of Neurology & Internal Medicine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2008. pp. 681–. ISBN 978-0-7817-7906-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=SRIvmTVcYBwC&pg=PA681.
- ↑ "Salvinorin A: A Mini Review of Physical and Chemical Properties Affecting Its Translation from Research to Clinical Applications in Humans". Translational Perioperative and Pain Medicine 1 (1): 9–11. 2014. PMID 25346937.
- ↑ "Salvinorin a Analogs and Other Kappa-Opioid Receptor Compounds as Treatments for Cocaine Abuse". Salvinorin A analogs and other κ-opioid receptor compounds as treatments for cocaine abuse. Advances in Pharmacology. 69. 2014. pp. 481–511. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-420118-7.00012-3. ISBN 9780124201187.
- ↑ "Biosynthesis of salvinorin A proceeds via the deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway". Phytochemistry 68 (14): 1872–1881. July 2007. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.04.034. PMID 17574635. Bibcode: 2007PChem..68.1872K.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Salvia divinorum kolavenyl diphosphate synthase (CPS2) mRNA, complete cds". December 11, 2016. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/KX424877.1.
- ↑ "Biosynthesis of the psychotropic plant diterpene salvinorin A: Discovery and characterization of the Salvia divinorum clerodienyl diphosphate synthase". The Plant Journal 89 (5): 885–897. March 2017. doi:10.1111/tpj.13427. PMID 27865008.
- ↑ "Localization of salvinorin A and related compounds in glandular trichomes of the psychoactive sage, Salvia divinorum". Annals of Botany 93 (6): 763–771. June 2004. doi:10.1093/aob/mch089. PMID 15087301.
- ↑ "Leaf glandular trichome (Salvia divinorum)". Dennis Kunkel Microscopy, Inc. 2007. https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/801352/view.
- ↑ "Asymmetric synthesis of salvinorin A, a potent kappa opioid receptor agonist". Journal of the American Chemical Society 129 (29): 8968–8969. July 2007. doi:10.1021/ja073590a. PMID 17602636.
- ↑ "Total synthesis of the hallucinogenic neoclerodane diterpenoid salvinorin A". Organic Letters 10 (7): 1365–1368. April 2008. doi:10.1021/ol800101v. PMID 18311991.
- ↑ "Intramolecular Diels-Alder/Tsuji allylation assembly of the functionalized trans-decalin of salvinorin A". Organic Letters 10 (1): 97–100. January 2008. doi:10.1021/ol7024058. PMID 18062692.
- ↑ "Total Synthesis of (-)-Salvinorin A". Chemistry: A European Journal 22 (50): 17983–17986. December 2016. doi:10.1002/chem.201604853. PMID 27758012.
- ↑ "Salvinorins D-F, new neoclerodane diterpenoids from Salvia divinorum, and an improved method for the isolation of salvinorin A". Journal of Natural Products 66 (5): 703–705. May 2003. doi:10.1021/np0205699. PMID 12762813.
- ↑ "Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological studies of new C(2) modified salvinorin A analogues". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 15 (16): 3744–3747. August 2005. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.05.048. PMID 15993589.
- ↑ "Standard protecting groups create potent and selective kappa opioids: salvinorin B alkoxymethyl ethers". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 16 (3): 1279–1286. February 2008. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.10.067. PMID 17981041.
- ↑ "Synthetic studies of neoclerodane diterpenes from Salvia divinorum: exploration of the 1-position". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 17 (22): 6111–6115. November 2007. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.09.050. PMID 17904842.
- ↑ "Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological studies of new C(4)-modified salvinorin A analogues". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 16 (21): 5498–5502. November 2006. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.08.051. PMID 16945525.
- ↑ "Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of salvinorin A analogues: effect of configuration at C(2) and substitution at C(18)". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 16 (17): 4679–4685. September 2006. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.05.093. PMID 16777411.
- ↑ "The G protein-biased κ-opioid receptor agonist RB-64 is analgesic with a unique spectrum of activities in vivo". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 352 (1): 98–109. January 2015. doi:10.1124/jpet.114.216820. PMID 25320048.
- ↑ "2-Methoxymethyl-salvinorin B is a potent kappa opioid receptor agonist with longer lasting action in vivo than salvinorin A". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 324 (3): 1073–1083. March 2008. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.132142. PMID 18089845.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects". Pharmaceuticals 14 (2): 116. February 2021. doi:10.3390/ph14020116. PMID 33546518.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 40.3 "Screening of Hallucinogenic Compounds and Genomic Characterisation of 40 Anatolian Salvia Species". Phytochemical Analysis 28 (6): 541–549. November 2017. doi:10.1002/pca.2703. PMID 28722248. Bibcode: 2017PChAn..28..541H.
- ↑ "21 CFR — Schedules of Controlled Substances §1308.11 Schedule I.". http://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/21cfr/cfr/1308/1308_11.htm.
- ↑ "Statutes & Constitution :View Statutes : Online Sunshine". http://leg.state.fl.us/statutes/index.cfm?App_mode=Display_Statute&URL=0800-0899/0893/0893.html.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 "Poisons Standard". The Australian Government. October 2015. https://www.comlaw.gov.au/Details/F2015L01534.
- ↑ "Förordning om ändring i förordningen (1999:58) om förbud mot vissa hälsofarliga varor" (in Swedish). Svensk författningssamling. 2006. http://www.notisum.se/rnp/sls/sfs/20060167.pdf.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Capasso2006" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Capasso2007" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Greiner1958" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Lee2005b" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Seeman2009" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
<ref> tag with name "Zhang2005" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.Further reading
- Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man (8th ed.). Foster City, CA: Biomedical Publications. 2008. pp. 1405–6. ISBN 978-0-9626523-7-0.
 |

