Biology:Tryptophan hydroxylase
| tryptophan 5-monooxygenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
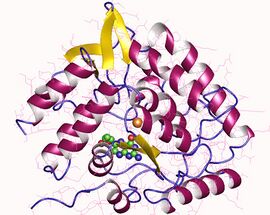 tryptophan 5-monooxygenase monomer, Human | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.14.16.4 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9037-21-2 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (tryptophan 5-monooxygenase) | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | TPH1 |
| Alt. symbols | TPRH, TPH |
| NCBI gene | 7166 |
| HGNC | 12008 |
| OMIM | 191060 |
| PDB | 1MLW |
| RefSeq | NM_004179 |
| UniProt | P17752 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 1.14.16.4 |
| Locus | Chr. 11 p15.3-p14 |
| tryptophan hydroxylase 2 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | TPH2 |
| NCBI gene | 121278 |
| HGNC | 20692 |
| OMIM | 607478 |
| RefSeq | NM_173353 |
| UniProt | Q8IWU9 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | Chr. 12 q15 |
Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) is an enzyme (EC 1.14.16.4) involved in the synthesis of the monoamine neurotransmitter serotonin. Tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylalanine hydroxylase, and tryptophan hydroxylase together constitute the family of biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. TPH catalyzes the following chemical reaction
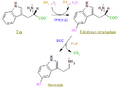
- L-tryptophan + tetrahydrobiopterin + O2 5-Hydroxytryptophan + dihydrobiopterin + H2O
It employs one additional cofactor, iron.
Function
It is responsible for addition of the -OH group (hydroxylation) to the 5 position to form the amino acid 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), which is the initial and rate-limiting step in the synthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin. It is also the first enzyme in the synthesis of melatonin.
Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) are members of a superfamily of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases, catalyzing key steps in important metabolic pathways.[1] Analogously to phenylalanine hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase, this enzyme uses (6R)-L-erythro-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and dioxygen as cofactors.[2]
In humans, the stimulation of serotonin production by administration of tryptophan has an antidepressant effect[3][4] and inhibition of tryptophan hydroxylase (e.g. by p-Chlorophenylalanine) may precipitate depression.[5]
The activity of tryptophan hydroxylase (i.e. the rate at which it converts L-tryptophan into the serotonin precursor L-5-hydroxytryptophan) can be increased when it undergoes phosphorylation. Protein Kinase A, for example, can phosphorylate tryptophan hydroxylase, thus increasing its activity.
Isoforms
In humans, as well as in other mammals, there are two distinct TPH genes. In humans, these genes are located on chromosomes 11 and 12 and encode two different homologous enzymes TPH1 and TPH2 (sequence identity 71%).[6]
- TPH1 is mostly expressed in tissues that express serotonin (a neurotransmitter) in the periphery (skin, gut, pineal gland) but it is also expressed in the central nervous system.
- On the other hand, TPH2 is exclusively expressed in neuronal cell types and is the predominant isoform in the central nervous system.
Additional images
-
The pathway for the synthesis of serotonin from tryptophan
-
Metabolic pathway from tryptophan to serotonin
See also
References
- ↑ "Conformation of the substrate and pterin cofactor bound to human tryptophan hydroxylase. Important role of Phe313 in substrate specificity". Biochemistry 40 (51): 15591–601. December 2001. doi:10.1021/bi015722x. PMID 11747434. http://www.bh4.org/pdf/mckinney.pdf.
- ↑ "tetrahydrobiopterin". BH4 Databases. BH4.org. 2005. http://www.bh4.org/BH4_Deficiency_Biochemistry.asp.
- ↑ "The effects of dietary tryptophan on affective disorders". Archives of Psychiatric Nursing 29 (2): 102–7. April 2015. doi:10.1016/j.apnu.2014.11.008. PMID 25858202.
- ↑ "Tryptophan in the treatment of depression". Lancet. Originally published as Volume 2, Issue 7527 2 (7527): 1178–80. December 1967. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91894-6. PMID 4168381.
- ↑ "Three-dimensional structure of human tryptophan hydroxylase and its implications for the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin and melatonin". Biochemistry 41 (42): 12569–74. October 2002. doi:10.1021/bi026561f. PMID 12379098.
- ↑ "A unique central tryptophan hydroxylase isoform". Biochemical Pharmacology 66 (9): 1673–80. November 2003. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00556-2. PMID 14563478.
Further reading
- "Partial purification and characterization of tryptophan hydroxylase from rabbit hindbrain". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 247 (13): 4165–73. July 1972. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)45055-2. PMID 4402511.
- "The role of intraneuronal 5-HT and of tryptophan hydroxylase activation in the control of 5-HT synthesis in rat brain slices incubated in K+-enriched medium". Journal of Neurochemistry 33 (5): 1031–42. November 1979. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05239.x. PMID 315449.
- "Enzymic studies on the biosynthesis of serotonin in mammalian brain". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 245 (7): 1699–709. April 1970. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)77149-X. PMID 5309585.
- "Further studies on tryptophan hydroxylase in rat brainstem and beef pineal". Biochemical Pharmacology 18 (5): 1071–81. May 1969. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(69)90111-7. PMID 5789774.
- "Three-dimensional structure of human tryptophan hydroxylase and its implications for the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin and melatonin". Biochemistry 41 (42): 12569–74. October 2002. doi:10.1021/bi026561f. PMID 12379098.
- "Crystal structure of tryptophan hydroxylase with bound amino acid substrate". Biochemistry 47 (46): 12087–94. November 2008. doi:10.1021/bi8015263. PMID 18937498.
External links
- Tryptophan+Hydroxylase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- See also tryptophan hydroxylase in Proteopedia
 |