Astronomy:L 98-59
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Volans |
| Right ascension | 08h 18m 07.62144s[1] |
| Declination | −68° 18′ 46.8054″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.69±0.05[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Red dwarf (main sequence) |
| Spectral type | M3V[3] |
| B−V colour index | +1.53[2] |
| R−I colour index | +1.28[2] |
| Variable type | None |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −6.10±0.19[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 94.794(18)[1] mas/yr Dec.: −340.084(20)[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 94.2664 ± 0.0155[1] mas |
| Distance | 34.599 ± 0.006 ly (10.608 ± 0.002 pc) |
| Details[3] | |
| Mass | 0.273±0.030 M☉ |
| Radius | 0.303+0.026 −0.023 R☉ |
| Luminosity (bolometric) | 0.01128±0.00042 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.86±0.13 cgs |
| Temperature | 3415±135 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.46±0.26 dex |
| Rotation | 80.9+5.0 −5.3 d |
| Age | >800 Myr |
| Other designations | |
2MASS J08180763-6818468, TOI-175, TYC 9193-2365-1, Gaia DR2 5271055243163629056 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
L 98-59 (TOI-175, TIC 307210830) is a bright M dwarf star, located in the constellation of Volans, at a distance of 10.608 parsecs (34.60 light-years), as measured by Gaia.[4]
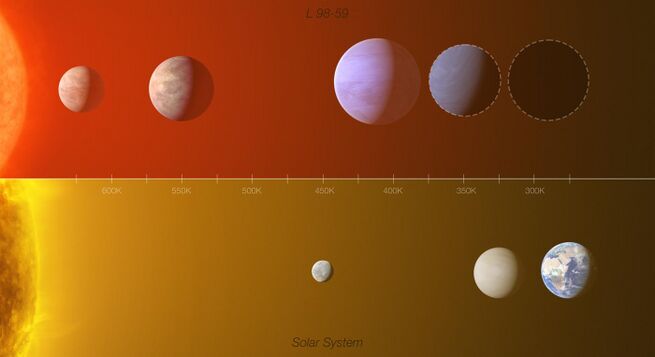
Broadband photometry shows that it is an M3 dwarf star with three confirmed terrestrial-sized planets in transit, which were announced in March 2019 by TESS,[5] as well as a fourth non-transiting planet and fifth candidate.[6]
In August 2021, new evidence was announced for a fifth, potentially habitable planet, labeled L 98-59 f. Though still unconfirmed,[6] this planet is believed to have 2.46 times Earth's mass, and an orbital period of 23.15 days.[7][8]
Planetary system
The three inner planets of L 98-59 were discovered in 2019 by TESS.[5] The potential super-Venus planet L 98-59 e was discovered in 2021, along with potentially habitable (located in the middle of the habitable zone) super-Earth candidate L 98-59 f.[3] In September 2021, suggested tests of the abilities of the Hubble Space Telescope and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope to detect and describe the atmospheric features of the three inner planets were reported.[9]
The two innermost planets, L 98-59 b and c, as well as L 98-59 e are possibly hot rocky worlds. L 98-59 d has a low density, indicating large amounts of water, potentially making up as much as 30% of its entire mass. It may therefore be covered in a deep global ocean.[7] Hubble observations of the three transiting planets in 2022 have found no clear evidence of atmospheres, with high mean molecular weight atmospheres, cloudy or hazy atmospheres, or no atmospheres being consistent with the observed flat spectra.[10][11][12] One study found some evidence of an atmosphere on L 98-59 c, which has yet to be confirmed as of 2023.[13]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 0.40+0.16 −0.15 M⊕ |
0.02191+0.00080 −0.00084 |
2.2531136+0.0000012 −0.0000015 |
0.103+0.117 −0.045 |
87.71+1.16 −0.44° |
0.85+0.061 −0.047 R⊕ |
| c | 2.22+0.26 −0.25 M⊕ |
0.0304+0.0011 −0.0012 |
3.6906777+0.0000016 −0.0000026 |
0.103+0.045 −0.058 |
88.11+0.36 −0.16° |
1.385+0.095 −0.075 R⊕ |
| d | 1.94±0.28 M⊕ | 0.0486+0.0018 −0.0019 |
7.4507245+0.0000081 −0.0000046 |
0.074+0.057 −0.046 |
88.449+0.058 −0.111° |
1.521+0.119 −0.098 R⊕ |
| e | ≥3.06+0.33 −0.37 M⊕ |
0.0717+0.0060 −0.0048 |
12.796+0.020 −0.019 |
0.128+0.108 −0.076 |
— | — |
| f (unconfirmed) | ≥2.46+0.66 −0.82 M⊕ |
0.1034+0.0042 −0.0044 |
23.15+0.60 −0.17 |
0.21+0.17 −0.11 |
— | — |
Gallery
See also
- Astronomy:List of potentially habitable exoplanets – Overview of potentially habitable terrestrial exoplanets
- Astronomy:List of exoplanets discovered in 2019
- Astronomy:TOI-700 d – Goldilocks terrestrial planet orbiting TOI-700
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Vallenari, A. et al. (2022). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940 Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Zacharias, N.; Finch, C. T.; Girard, T. M.; Henden, A. (1 February 2013). "The Fourth US Naval Observatory CCD Astrograph Catalog (UCAC4)". The Astronomical Journal 145 (2): 44. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/2/44. ISSN 0004-6256. Bibcode: 2013AJ....145...44Z. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013AJ....145...44Z/abstract.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Demangeon, Oliver D. S.Expression error: Unrecognized word "etal". (July 2021). "A warm terrestrial planet with half the mass of Venus transiting a nearby star". Astronomy & Astrophysics 653: 38. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202140728. Bibcode: 2021A&A...653A..41D. https://www.eso.org/public/archives/releases/sciencepapers/eso2112/eso2112a.pdf.
- ↑ Cloutier, R.; Astudillo-Defru, N.; Bonfils, X.; Jenkins, J. S.; Berdiñas, Z.; Ricker, G.; Vanderspek, R.; Latham, D. W. et al. (2019-09-01). "Characterization of the L 98-59 multi-planetary system with HARPS - Mass characterization of a hot super-Earth, a sub-Neptune, and a mass upper limit on the third planet" (in en). Astronomy & Astrophysics 629: A111. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935957. ISSN 0004-6361. Bibcode: 2019A&A...629A.111C. https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/abs/2019/09/aa35957-19/aa35957-19.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kostov, Veselin B.; Schlieder, Joshua E.; Barclay, Thomas; Quintana, Elisa V.; Colon, Knicole D.; Brande, Jonathan; Collins, Karen A.; Feinstein, Adina D. et al. (2019-06-27). "The L 98-59 System: Three Transiting, Terrestrial-Sized Planets Orbiting a Nearby M-dwarf". The Astronomical Journal 158 (1): 32. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab2459. ISSN 1538-3881. Bibcode: 2019AJ....158...32K.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Comparison of the L 98-59 exoplanet system with the inner Solar System" (in en). European Southern Observatory. https://www.eso.org/public/images/eso2112b/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "EarthSky | An inner solar system much like ours, 35 light-years away" (in en-US). Earth & Sky. 2021-08-06. https://earthsky.org/space/inner-solar-system-much-like-ours-l-98-59/.
- ↑ "New ESO observations show rocky exoplanet has just half the mass of Venus". European Southern Observatory. 5 August 2021. https://www.eso.org/public/news/eso2112/.
- ↑ Pidhorodetska, Daria (29 September 2021). "L 98-59: A Benchmark System of Small Planets for Future Atmospheric Characterization". The Astronomical Journal 162 (4): 169. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ac1171. Bibcode: 2021AJ....162..169P.
- ↑ Damiano, Mario et al. (November 2022). "A Transmission Spectrum of the Sub-Earth Planet L98-59 b in 1.1-1.7 μm". The Astronomical Journal 164 (5): 225. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ac9472. Bibcode: 2022AJ....164..225D.
- ↑ Zhou, Li et al. (November 2022). "Hubble WFC3 Spectroscopy of the Rocky Planet L 98-59 b: No Evidence for a Cloud-free Primordial Atmosphere". The Astronomical Journal 164 (5): 203. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ac8fe9. Bibcode: 2022AJ....164..203Z.
- ↑ Zhou, Li et al. (February 2023). "Hubble WFC3 Spectroscopy of the Terrestrial Planets L 98-59 c and d: No Evidence for a Clear Hydrogen Dominated Primary Atmosphere". Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics 23 (2): 025011. doi:10.1088/1674-4527/acaceb. Bibcode: 2023RAA....23b5011Z.
- ↑ Barclay, Thomas et al. (2023), The transmission spectrum of the potentially rocky planet L 98-59 c
External links
- New ESO observations show rocky exoplanet has just half the mass of Venus (ESO press release)
- TESS – Official Website
- Smallest exoplanet found so far (video; 1:53; NASA; June 2019)
Coordinates: ![]() 08h 18m 07.62s, −68° 18′ 46.8″
08h 18m 07.62s, −68° 18′ 46.8″
 |