Chemistry:N6-Cyclopentyladenosine
From HandWiki
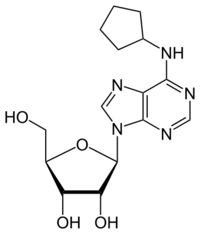
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N6-Cyclopentyladenosine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-[6-(Cyclopentylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H21N5O4 | |
| Molar mass | 335.364 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
N6-Cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) is a drug which acts as a selective adenosine A1 receptor agonist.[1] It has mainly cardiovascular effects with only subtle alterations of behavior.[2] CPA is widely used in scientific research into the adenosine receptors and has been used to derive a large family of derivatives.[3][4][5][6][7]
See also
References
- ↑ "Evaluation of the binding of the A-1 selective adenosine radioligand, cyclopentyladenosine (CPA), to rat brain tissue". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 332 (2): 179–183. February 1986. doi:10.1007/BF00511410. PMID 3703020.
- ↑ "Behavioral and cardiovascular effects of analogs of adenosine in cynomolgus monkeys". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 241 (1): 76–83. April 1987. PMID 3572798.
- ↑ "Partial A(1) adenosine receptor agonists from a molecular perspective and their potential use as chronic ventricular rate control agents during atrial fibrillation (AF)". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 4 (8): 839–854. 2004. doi:10.2174/1568026043450998. PMID 15078215.
- ↑ "A(1) adenosine receptor agonists: medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential". Current Pharmaceutical Design 10 (17): 2021–2039. 2004. doi:10.2174/1381612043384204. PMID 15279543.
- ↑ "N6-Cycloalkyl-2-substituted adenosine derivatives as selective, high affinity adenosine A1 receptor agonists". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 17 (1): 161–166. January 2007. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.09.065. PMID 17045477.
- ↑ "A1 adenosine receptor agonists and their potential therapeutic applications". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 17 (12): 1901–1910. December 2008. doi:10.1517/13543780802497284. PMID 19012505.
- ↑ "N6-Cycloalkyl- and N6-bicycloalkyl-C5'(C2')-modified adenosine derivatives as high-affinity and selective agonists at the human A1 adenosine receptor with antinociceptive effects in mice". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 52 (8): 2393–2406. April 2009. doi:10.1021/jm801456g. PMID 19317449.
 |

