Astronomy:Absolute magnitude
In astronomy, absolute magnitude (M) is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it were viewed from a distance of exactly 10 parsecs (32.6 light-years), without extinction (or dimming) of its light due to absorption by interstellar matter and cosmic dust. By hypothetically placing all objects at a standard reference distance from the observer, their luminosities can be directly compared among each other on a magnitude scale. For Solar System bodies that shine in reflected light, a different definition of absolute magnitude (H) is used, based on a standard reference distance of one astronomical unit.
Absolute magnitudes of stars generally range from approximately −10 to +20. The absolute magnitudes of galaxies can be much lower (brighter).
The more luminous an object, the smaller the numerical value of its absolute magnitude. A difference of 5 magnitudes between the absolute magnitudes of two objects corresponds to a ratio of 100 in their luminosities, and a difference of n magnitudes in absolute magnitude corresponds to a luminosity ratio of 100n/5. For example, a star of absolute magnitude MV = 3.0 would be 100 times as luminous as a star of absolute magnitude MV = 8.0 as measured in the V filter band. The Sun has absolute magnitude MV = +4.83.[1] Highly luminous objects can have negative absolute magnitudes: for example, the Milky Way galaxy has an absolute B magnitude of about −20.8.[2]
As with all astronomical magnitudes, the absolute magnitude can be specified for different wavelength ranges corresponding to specified filter bands or passbands; for stars a commonly quoted absolute magnitude is the absolute visual magnitude, which uses the visual (V) band of the spectrum (in the UBV photometric system). Absolute magnitudes are denoted by a capital M, with a subscript representing the filter band used for measurement, such as MV for absolute magnitude in the V band.
An object's absolute bolometric magnitude (Mbol) represents its total luminosity over all wavelengths, rather than in a single filter band, as expressed on a logarithmic magnitude scale. To convert from an absolute magnitude in a specific filter band to absolute bolometric magnitude, a bolometric correction (BC) is applied.[3]
Stars and galaxies
In stellar and galactic astronomy, the standard distance is 10 parsecs (about 32.616 light-years, 308.57 petameters or 308.57 trillion kilometres). A star at 10 parsecs has a parallax of 0.1″ (100 milliarcseconds). Galaxies (and other extended objects) are much larger than 10 parsecs, their light is radiated over an extended patch of sky, and their overall brightness cannot be directly observed from relatively short distances, but the same convention is used. A galaxy's magnitude is defined by measuring all the light radiated over the entire object, treating that integrated brightness as the brightness of a single point-like or star-like source, and computing the magnitude of that point-like source as it would appear if observed at the standard 10 parsecs distance. Consequently, the absolute magnitude of any object equals the apparent magnitude it would have if it were 10 parsecs away.
Some stars visible to the naked eye have such a low absolute magnitude that they would appear bright enough to outshine the planets and cast shadows if they were at 10 parsecs from the Earth. Examples include Rigel (−7.0), Deneb (−7.2), Naos (−6.0), and Betelgeuse (−5.6). For comparison, Sirius has an absolute magnitude of only 1.4, which is still brighter than the Sun, whose absolute visual magnitude is 4.83. The Sun's absolute bolometric magnitude is set arbitrarily, usually at 4.75.[4][5] Absolute magnitudes of stars generally range from approximately −10 to +20. The absolute magnitudes of galaxies can be much lower (brighter). For example, the giant elliptical galaxy M87 has an absolute magnitude of −22 (i.e. as bright as about 60,000 stars of magnitude −10). Some active galactic nuclei (quasars like CTA-102) can reach absolute magnitudes in excess of −32, making them the most luminous persistent objects in the observable universe, although these objects can vary in brightness over astronomically short timescales. At the extreme end, the optical afterglow of the gamma ray burst GRB 080319B reached, according to one paper, an absolute r magnitude brighter than −38 for a few tens of seconds.[6]
Apparent magnitude
The Greek astronomer Hipparchus established a numerical scale to describe the brightness of each star appearing in the sky. The brightest stars in the sky were assigned an apparent magnitude m = 1, and the dimmest stars visible to the naked eye are assigned m = 6.[7] The difference between them corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightness. For objects within the immediate neighborhood of the Sun, the absolute magnitude M and apparent magnitude m from any distance d (in parsecs, with 1 pc = 3.2616 light-years) are related by [math]\displaystyle{ 100^{\frac{m-M}{5}}=\frac{F_{10}}{F} = \left(\frac{d}{10\;\mathrm{pc}}\right)^{2}, }[/math] where F is the radiant flux measured at distance d (in parsecs), F10 the radiant flux measured at distance 10 pc. Using the common logarithm, the equation can be written as [math]\displaystyle{ M = m - 5 \log_{10}(d_\text{pc})+5 = m - 5 \left(\log_{10}d_\text{pc}-1\right), }[/math] where it is assumed that extinction from gas and dust is negligible. Typical extinction rates within the Milky Way galaxy are 1 to 2 magnitudes per kiloparsec, when dark clouds are taken into account.[8]
For objects at very large distances (outside the Milky Way) the luminosity distance dL (distance defined using luminosity measurements) must be used instead of d, because the Euclidean approximation is invalid for distant objects. Instead, general relativity must be taken into account. Moreover, the cosmological redshift complicates the relationship between absolute and apparent magnitude, because the radiation observed was shifted into the red range of the spectrum. To compare the magnitudes of very distant objects with those of local objects, a K correction might have to be applied to the magnitudes of the distant objects.
The absolute magnitude M can also be written in terms of the apparent magnitude m and stellar parallax p: [math]\displaystyle{ M = m + 5 \left(\log_{10}p+1\right), }[/math] or using apparent magnitude m and distance modulus μ: [math]\displaystyle{ M = m - \mu. }[/math]
Examples
Rigel has a visual magnitude mV of 0.12 and distance of about 860 light-years: [math]\displaystyle{ M_\mathrm{V} = 0.12 - 5 \left(\log_{10} \frac{860}{3.2616} - 1 \right) = -7.0. }[/math]
Vega has a parallax p of 0.129″, and an apparent magnitude mV of 0.03: [math]\displaystyle{ M_\mathrm{V} = 0.03 + 5 \left(\log_{10}{0.129} + 1\right) = +0.6. }[/math]
The Black Eye Galaxy has a visual magnitude mV of 9.36 and a distance modulus μ of 31.06: [math]\displaystyle{ M_\mathrm{V} = 9.36 - 31.06 = -21.7. }[/math]
Bolometric magnitude
The absolute bolometric magnitude (Mbol) takes into account electromagnetic radiation at all wavelengths. It includes those unobserved due to instrumental passband, the Earth's atmospheric absorption, and extinction by interstellar dust. It is defined based on the luminosity of the stars. In the case of stars with few observations, it must be computed assuming an effective temperature.
Classically, the difference in bolometric magnitude is related to the luminosity ratio according to:[7] [math]\displaystyle{ M_\mathrm{bol,\star} - M_\mathrm{bol,\odot} = -2.5 \log_{10} \left(\frac{L_\star}{L_\odot}\right) }[/math] which makes by inversion: [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{L_\star}{L_\odot} = 10^{0.4\left(M_\mathrm{bol,\odot} - M_\mathrm{bol,\star}\right)} }[/math] where
- L⊙ is the Sun's luminosity (bolometric luminosity)
- L★ is the star's luminosity (bolometric luminosity)
- Mbol,⊙ is the bolometric magnitude of the Sun
- Mbol,★ is the bolometric magnitude of the star.
In August 2015, the International Astronomical Union passed Resolution B2[9] defining the zero points of the absolute and apparent bolometric magnitude scales in SI units for power (watts) and irradiance (W/m2), respectively. Although bolometric magnitudes had been used by astronomers for many decades, there had been systematic differences in the absolute magnitude-luminosity scales presented in various astronomical references, and no international standardization. This led to systematic differences in bolometric corrections scales.[10] Combined with incorrect assumed absolute bolometric magnitudes for the Sun, this could lead to systematic errors in estimated stellar luminosities (and other stellar properties, such as radii or ages, which rely on stellar luminosity to be calculated).
Resolution B2 defines an absolute bolometric magnitude scale where Mbol = 0 corresponds to luminosity L0 = 3.0128×1028 W, with the zero point luminosity L0 set such that the Sun (with nominal luminosity 3.828×1026 W) corresponds to absolute bolometric magnitude Mbol,⊙ = 4.74. Placing a radiation source (e.g. star) at the standard distance of 10 parsecs, it follows that the zero point of the apparent bolometric magnitude scale mbol = 0 corresponds to irradiance f0 = 2.518021002×10−8 W/m2. Using the IAU 2015 scale, the nominal total solar irradiance ("solar constant") measured at 1 astronomical unit (1361 W/m2) corresponds to an apparent bolometric magnitude of the Sun of mbol,⊙ = −26.832.[10]
Following Resolution B2, the relation between a star's absolute bolometric magnitude and its luminosity is no longer directly tied to the Sun's (variable) luminosity: [math]\displaystyle{ M_\mathrm{bol} = -2.5 \log_{10} \frac{L_\star}{L_0} \approx -2.5 \log_{10} L_\star + 71.197425 }[/math] where
- L★ is the star's luminosity (bolometric luminosity) in watts
- L0 is the zero point luminosity 3.0128×1028 W
- Mbol is the bolometric magnitude of the star
The new IAU absolute magnitude scale permanently disconnects the scale from the variable Sun. However, on this SI power scale, the nominal solar luminosity corresponds closely to Mbol = 4.74, a value that was commonly adopted by astronomers before the 2015 IAU resolution.[10]
The luminosity of the star in watts can be calculated as a function of its absolute bolometric magnitude Mbol as: [math]\displaystyle{ L_\star = L_0 10^{-0.4 M_\mathrm{bol}} }[/math] using the variables as defined previously.
Solar System bodies (H)
| H | Diameter |
|---|---|
| 10 | 36 km |
| 12.7 | 10 km |
| 15 | 3.6 km |
| 17.7 | 1 km |
| 19.2 | 510 m |
| 20 | 360 m |
| 22 | 140 m |
| 22.7 | 100 m |
| 24.2 | 51 m |
| 25 | 36 m |
| 26.6 | 17 m |
| 27.7 | 10 m |
| 30 | 3.6 m |
| 32.7 | 1 m |
For planets and asteroids, a definition of absolute magnitude that is more meaningful for non-stellar objects is used. The absolute magnitude, commonly called [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math], is defined as the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it were one astronomical unit (AU) from both the Sun and the observer, and in conditions of ideal solar opposition (an arrangement that is impossible in practice).[12] Because Solar System bodies are illuminated by the Sun, their brightness varies as a function of illumination conditions, described by the phase angle. This relationship is referred to as the phase curve. The absolute magnitude is the brightness at phase angle zero, an arrangement known as opposition, from a distance of one AU.
Apparent magnitude

The absolute magnitude [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] can be used to calculate the apparent magnitude [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] of a body. For an object reflecting sunlight, [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] are connected by the relation [math]\displaystyle{ m = H + 5 \log_{10}{\left(\frac{d_{BS} d_{BO}}{d_0^2}\right)} - 2.5 \log_{10}{q(\alpha)}, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] is the phase angle, the angle between the body-Sun and body–observer lines. [math]\displaystyle{ q(\alpha) }[/math] is the phase integral (the integration of reflected light; a number in the 0 to 1 range).[13]
By the law of cosines, we have: [math]\displaystyle{ \cos{\alpha} = \frac{ d_\mathrm{BO}^2 + d_\mathrm{BS}^2 - d_\mathrm{OS}^2 } {2 d_\mathrm{BO} d_\mathrm{BS}}. }[/math]
Distances:
- dBO is the distance between the body and the observer
- dBS is the distance between the body and the Sun
- dOS is the distance between the observer and the Sun
- d0, a unit conversion factor, is the constant 1 AU, the average distance between the Earth and the Sun
Approximations for phase integral q(α)
The value of [math]\displaystyle{ q(\alpha) }[/math] depends on the properties of the reflecting surface, in particular on its roughness. In practice, different approximations are used based on the known or assumed properties of the surface. The surfaces of terrestrial planets are generally more difficult to model than those of gaseous planets, the latter of which have smoother visible surfaces.[13]
Planets as diffuse spheres
Planetary bodies can be approximated reasonably well as ideal diffuse reflecting spheres. Let [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] be the phase angle in degrees, then[14] [math]\displaystyle{ q(\alpha) = \frac23 \left(\left(1-\frac{\alpha}{180^{\circ}}\right)\cos{\alpha}+\frac{1}{\pi}\sin{\alpha}\right). }[/math] A full-phase diffuse sphere reflects two-thirds as much light as a diffuse flat disk of the same diameter. A quarter phase ([math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 90^{\circ} }[/math]) has [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{\pi} }[/math] as much light as full phase ([math]\displaystyle{ \alpha = 0^{\circ} }[/math]).
By contrast, a diffuse disk reflector model is simply [math]\displaystyle{ q(\alpha) = \cos{\alpha} }[/math], which isn't realistic, but it does represent the opposition surge for rough surfaces that reflect more uniform light back at low phase angles.
The definition of the geometric albedo [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math], a measure for the reflectivity of planetary surfaces, is based on the diffuse disk reflector model. The absolute magnitude [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math], diameter [math]\displaystyle{ D }[/math] (in kilometers) and geometric albedo [math]\displaystyle{ p }[/math] of a body are related by[15][16][17] [math]\displaystyle{ D = \frac{1329}{\sqrt{p}} \times 10^{-0.2H} \mathrm{km}, }[/math] or equivalently, [math]\displaystyle{ H = 5\log_{10}{\frac{1329}{D\sqrt{p}}}. }[/math]
Example: The Moon's absolute magnitude [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] can be calculated from its diameter [math]\displaystyle{ D=3474\text{ km} }[/math] and geometric albedo [math]\displaystyle{ p = 0.113 }[/math]:[18] [math]\displaystyle{ H = 5\log_{10}{\frac{1329}{3474\sqrt{0.113}}} = +0.28. }[/math] We have [math]\displaystyle{ d_{BS}=1\text{ AU} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ d_{BO}=384400\text{ km}=0.00257\text{ AU}. }[/math] At quarter phase, [math]\displaystyle{ q(\alpha)\approx \frac{2}{3\pi} }[/math] (according to the diffuse reflector model), this yields an apparent magnitude of [math]\displaystyle{ m = +0.28+5\log_{10}{\left(1\cdot0.00257\right)} - 2.5\log_{10}{\left(\frac{2}{3\pi}\right)} = -10.99. }[/math] The actual value is somewhat lower than that, [math]\displaystyle{ m=-10.0. }[/math] This is not a good approximation, because the phase curve of the Moon is too complicated for the diffuse reflector model.[19] A more accurate formula is given in the following section.
More advanced models
Because Solar System bodies are never perfect diffuse reflectors, astronomers use different models to predict apparent magnitudes based on known or assumed properties of the body.[13] For planets, approximations for the correction term [math]\displaystyle{ -2.5\log_{10}{q(\alpha)} }[/math] in the formula for m have been derived empirically, to match observations at different phase angles. The approximations recommended by the Astronomical Almanac[20] are (with [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] in degrees):
| Planet | Referenced calculation[21] | [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] | Approximation for [math]\displaystyle{ -2.5\log_{10}{q(\alpha)} }[/math] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | −0.4 | −0.613 | [math]\displaystyle{ +6.328\times10^{-2}\alpha - 1.6336\times10^{-3}\alpha^{2}+3.3644\times10^{-5}\alpha^{3}-3.4265\times10^{-7}\alpha^{4}+1.6893\times10^{-9}\alpha^{5}-3.0334\times10^{-12}\alpha^{6} }[/math] |
| Venus | −4.4 | −4.384 |
|
| Earth | − | −3.99 | [math]\displaystyle{ -1.060\times10^{-3}\alpha+2.054\times10^{-4}\alpha^{2} }[/math] |
| Moon[22] | 0.2 | +0.28 |
|
| Mars | −1.5 | −1.601 |
|
| Jupiter | −9.4 | −9.395 |
|
| Saturn | −9.7 | −8.914 |
|
| Uranus | −7.2 | −7.110 | [math]\displaystyle{ -8.4\times10^{-4}\phi'+6.587\times10^{-3}\alpha+1.045\times10^{-4}\alpha^{2} }[/math] (for [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \lt 3.1^{\circ} }[/math]) |
| Neptune | −6.9 | −7.00 | [math]\displaystyle{ +7.944\times10^{-3}\alpha+9.617\times10^{-5}\alpha^{2} }[/math] (for [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \lt 133^{\circ} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ t \gt 2000.0 }[/math]) |
Here [math]\displaystyle{ \beta }[/math] is the effective inclination of Saturn's rings (their tilt relative to the observer), which as seen from Earth varies between 0° and 27° over the course of one Saturn orbit, and [math]\displaystyle{ \phi' }[/math] is a small correction term depending on Uranus' sub-Earth and sub-solar latitudes. [math]\displaystyle{ t }[/math] is the Common Era year. Neptune's absolute magnitude is changing slowly due to seasonal effects as the planet moves along its 165-year orbit around the Sun, and the approximation above is only valid after the year 2000. For some circumstances, like [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \ge 179^{\circ} }[/math] for Venus, no observations are available, and the phase curve is unknown in those cases. The formula for the Moon is only applicable to the near side of the Moon, the portion that is visible from the Earth.
Example 1: On 1 January 2019, Venus was [math]\displaystyle{ d_{BS}=0.719\text{ AU} }[/math] from the Sun, and [math]\displaystyle{ d_{BO} = 0.645\text{ AU} }[/math] from Earth, at a phase angle of [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha=93.0^{\circ} }[/math] (near quarter phase). Under full-phase conditions, Venus would have been visible at [math]\displaystyle{ m=-4.384+5\log_{10}{\left(0.719 \cdot 0.645\right)}=-6.09. }[/math] Accounting for the high phase angle, the correction term above yields an actual apparent magnitude of [math]\displaystyle{ m = -6.09 + \left(-1.044 \times 10^{-3} \cdot 93.0 + 3.687\times10^{-4} \cdot 93.0^{2} - 2.814 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 93.0^{3} + 8.938 \times 10^{-9} \cdot 93.0^{4}\right) = -4.59. }[/math] This is close to the value of [math]\displaystyle{ m=-4.62 }[/math] predicted by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.[23]
Example 2: At first quarter phase, the approximation for the Moon gives [math]\displaystyle{ -2.5\log_{10}{q(90^{\circ})}=2.71. }[/math] With that, the apparent magnitude of the Moon is [math]\displaystyle{ m = +0.28+5\log_{10}{\left(1\cdot0.00257\right)}+2.71= -9.96, }[/math] close to the expected value of about [math]\displaystyle{ -10.0 }[/math]. At last quarter, the Moon is about 0.06 mag fainter than at first quarter, because that part of its surface has a lower albedo.
Earth's albedo varies by a factor of 6, from 0.12 in the cloud-free case to 0.76 in the case of altostratus cloud. The absolute magnitude in the table corresponds to an albedo of 0.434. Due to the variability of the weather, Earth's apparent magnitude cannot be predicted as accurately as that of most other planets.[20]
Asteroids


If an object has an atmosphere, it reflects light more or less isotropically in all directions, and its brightness can be modelled as a diffuse reflector. Bodies with no atmosphere, like asteroids or moons, tend to reflect light more strongly to the direction of the incident light, and their brightness increases rapidly as the phase angle approaches [math]\displaystyle{ 0^{\circ} }[/math]. This rapid brightening near opposition is called the opposition effect. Its strength depends on the physical properties of the body's surface, and hence it differs from asteroid to asteroid.[13]
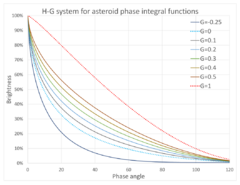
In 1985, the IAU adopted the semi-empirical [math]\displaystyle{ HG }[/math]-system, based on two parameters [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] called absolute magnitude and slope, to model the opposition effect for the ephemerides published by the Minor Planet Center.[24] [math]\displaystyle{ m = H + 5\log_{10}{\left(\frac{d_{BS}d_{BO}}{d_{0}^{2}}\right)}-2.5\log_{10}{q(\alpha)}, }[/math]
where
- the phase integral is [math]\displaystyle{ q(\alpha)=\left(1-G\right)\phi_{1}\left(\alpha\right)+G\phi_{2}\left(\alpha\right) }[/math] and
- [math]\displaystyle{ \phi_{i}\left(\alpha\right) = \exp{\left(-A_i \left(\tan{\frac{\alpha}{2}}\right)^{B_i}\right)} }[/math] for [math]\displaystyle{ i = 1 }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ 2 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ A_{1}=3.332 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ A_{2}=1.862 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ B_{1}=0.631 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ B_2 = 1.218 }[/math].[25]
This relation is valid for phase angles [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \lt 120^{\circ} }[/math], and works best when [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \lt 20^{\circ} }[/math].[26]
The slope parameter [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] relates to the surge in brightness, typically 0.3 mag, when the object is near opposition. It is known accurately only for a small number of asteroids, hence for most asteroids a value of [math]\displaystyle{ G=0.15 }[/math] is assumed.[26] In rare cases, [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] can be negative.[25][27] An example is 101955 Bennu, with [math]\displaystyle{ G=-0.08 }[/math].[28]
In 2012, the [math]\displaystyle{ HG }[/math]-system was officially replaced by an improved system with three parameters [math]\displaystyle{ H }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ G_1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ G_2 }[/math], which produces more satisfactory results if the opposition effect is very small or restricted to very small phase angles. However, as of 2022, this [math]\displaystyle{ H G_1 G_2 }[/math]-system has not been adopted by either the Minor Planet Center nor Jet Propulsion Laboratory.[13][29]
The apparent magnitude of asteroids varies as they rotate, on time scales of seconds to weeks depending on their rotation period, by up to [math]\displaystyle{ 2\text{ mag} }[/math] or more.[30] In addition, their absolute magnitude can vary with the viewing direction, depending on their axial tilt. In many cases, neither the rotation period nor the axial tilt are known, limiting the predictability. The models presented here do not capture those effects.[26][13]
Cometary magnitudes
The brightness of comets is given separately as total magnitude ([math]\displaystyle{ m_{1} }[/math], the brightness integrated over the entire visible extend of the coma) and nuclear magnitude ([math]\displaystyle{ m_{2} }[/math], the brightness of the core region alone).[31] Both are different scales than the magnitude scale used for planets and asteroids, and can not be used for a size comparison with an asteroid's absolute magnitude H.
The activity of comets varies with their distance from the Sun. Their brightness can be approximated as [math]\displaystyle{ m_{1} = M_{1} + 2.5\cdot K_{1}\log_{10}{\left(\frac{d_{BS}}{d_0}\right)} + 5\log_{10}{\left(\frac{d_{BO}}{d_0}\right)} }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ m_{2} = M_{2} + 2.5\cdot K_{2}\log_{10}{\left(\frac{d_{BS}}{d_0}\right)} + 5\log_{10}{\left(\frac{d_{BO}}{d_0}\right)}, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ m_{1,2} }[/math] are the total and nuclear apparent magnitudes of the comet, respectively, [math]\displaystyle{ M_{1,2} }[/math] are its "absolute" total and nuclear magnitudes, [math]\displaystyle{ d_{BS} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ d_{BO} }[/math] are the body-sun and body-observer distances, [math]\displaystyle{ d_{0} }[/math] is the Astronomical Unit, and [math]\displaystyle{ K_{1,2} }[/math] are the slope parameters characterising the comet's activity. For [math]\displaystyle{ K=2 }[/math], this reduces to the formula for a purely reflecting body (showing no cometary activity).[32]
For example, the lightcurve of comet C/2011 L4 (PANSTARRS) can be approximated by [math]\displaystyle{ M_{1}=5.41\text{, }K_{1}=3.69. }[/math][33] On the day of its perihelion passage, 10 March 2013, comet PANSTARRS was [math]\displaystyle{ 0.302\text{ AU} }[/math] from the Sun and [math]\displaystyle{ 1.109\text{ AU} }[/math] from Earth. The total apparent magnitude [math]\displaystyle{ m_{1} }[/math] is predicted to have been [math]\displaystyle{ m_1 = 5.41 + 2.5\cdot3.69\cdot\log_{10}{\left(0.302\right)}+5\log_{10}{\left(1.109\right)} = +0.8 }[/math] at that time. The Minor Planet Center gives a value close to that, [math]\displaystyle{ m_{1} = +0.5 }[/math].[34]
| Comet | Absolute magnitude [math]\displaystyle{ M_{1} }[/math][35] |
Nucleus diameter |
|---|---|---|
| Comet Sarabat | −3.0 | ≈100 km? |
| Comet Hale-Bopp | −1.3 | 60 ± 20 km |
| Comet Halley | 4.0 | 14.9 x 8.2 km |
| average new comet | 6.5 | ≈2 km[36] |
| C/2014 UN271 (Bernardinelli-Bernstein) | 6.7[37] | 60–200 km?[38][39] |
| 289P/Blanpain (during 1819 outburst) | 8.5[40] | 320 m[41] |
| 289P/Blanpain (normal activity) | 22.9[42] | 320 m |
The absolute magnitude of any given comet can vary dramatically. It can change as the comet becomes more or less active over time or if it undergoes an outburst. This makes it difficult to use the absolute magnitude for a size estimate. When comet 289P/Blanpain was discovered in 1819, its absolute magnitude was estimated as [math]\displaystyle{ M_{1} = 8.5 }[/math].[40] It was subsequently lost and was only rediscovered in 2003. At that time, its absolute magnitude had decreased to [math]\displaystyle{ M_{1} = 22.9 }[/math],[42] and it was realised that the 1819 apparition coincided with an outburst. 289P/Blanpain reached naked eye brightness (5–8 mag) in 1819, even though it is the comet with the smallest nucleus that has ever been physically characterised, and usually doesn't become brighter than 18 mag.[40][41]
For some comets that have been observed at heliocentric distances large enough to distinguish between light reflected from the coma, and light from the nucleus itself, an absolute magnitude analogous to that used for asteroids has been calculated, allowing to estimate the sizes of their nuclei.[43]
Meteors
For a meteor, the standard distance for measurement of magnitudes is at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) at the observer's zenith.[44][45]
See also
- Araucaria Project
- Hertzsprung–Russell diagram – relates absolute magnitude or luminosity versus spectral color or surface temperature.
- Jansky radio astronomer's preferred unit – linear in power/unit area
- List of most luminous stars
- Photographic magnitude
- Surface brightness – the magnitude for extended objects
- Zero point (photometry) – the typical calibration point for star flux
References
- ↑ "Sun Fact Sheet". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/factsheet/sunfact.html.
- ↑ Karachentsev, I. D. (2004). "A Catalog of Neighboring Galaxies". The Astronomical Journal 127 (4): 2031–2068. doi:10.1086/382905. Bibcode: 2004AJ....127.2031K.
- ↑ Flower, P. J. (September 1996). "Transformations from Theoretical Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams to Color-Magnitude Diagrams: Effective Temperatures, B-V Colors, and Bolometric Corrections". The Astrophysical Journal 469: 355. doi:10.1086/177785. Bibcode: 1996ApJ...469..355F.
- ↑ Cayrel de Strobel, G. (1996). "Stars resembling the Sun". Astronomy and Astrophysics Review 7 (3): 243–288. doi:10.1007/s001590050006. Bibcode: 1996A&ARv...7..243C.
- ↑ Casagrande, L.; Portinari, L.; Flynn, C. (November 2006). "Accurate fundamental parameters for lower main-sequence stars". MNRAS 373 (1): 13–44. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10999.x. Bibcode: 2006MNRAS.373...13C.
- ↑ Bloom, J. S.; Perley, D. A.; Li, W.; Butler, N. R.; Miller, A. A.; Kocevski, D.; Kann, D. A.; Foley, R. J. et al. (2009-01-19). "Observations of the Naked-Eye GRB 080319B: Implications of Nature's Brightest Explosion" (in en). The Astrophysical Journal 691 (1): 723–737. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/691/1/723. ISSN 0004-637X. Bibcode: 2009ApJ...691..723B.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Carroll, B. W.; Ostlie, D. A. (2007). An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics (2nd ed.). Pearson. pp. 60–62. ISBN 978-0-321-44284-0. https://archive.org/details/introductiontomo00bwca_613.
- ↑ Unsöld, A.; Baschek, B. (2013), The New Cosmos: An Introduction to Astronomy and Astrophysics (5th ed.), Springer Science & Business Media, p. 331, ISBN 978-3662043561, https://books.google.com/books?id=PrzoCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA331
- ↑ "IAU XXIX General Assembly Draft Resolutions Announced". http://www.iau.org/news/announcements/detail/ann15023/.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Mamajek, E. E.; Torres, G.; Prsa, A.; Harmanec, P.; Asplund, M.; Bennett, P. D.; Capitaine, N.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, J. et al. (13 August 2015), "IAU 2015 Resolution B2 on Recommended Zero Points for the Absolute and Apparent Bolometric Magnitude Scales", Resolutions Adopted at the General Assemblies (IAU Inter-Division A-G Working Group on Nominal Units for Stellar & Planetary Astronomy), Bibcode: 2015arXiv151006262M, https://www.iau.org/static/resolutions/IAU2015_English.pdf
- ↑ CNEOS Asteroid Size Estimator
- ↑ Luciuk, M., Astronomical Magnitudes, p. 8, http://www.asterism.org/tutorials/tut35%20Magnitudes.pdf, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 Karttunen, H.; Kröger, P.; Oja, H.; Poutanen, M.; Donner, K. J. (2016). Fundamental Astronomy. Springer. p. 163. ISBN 9783662530450. https://books.google.com/books?id=ndd2DQAAQBAJ&pg=PA163.
- ↑ Whitmell, C. T. (1907), "Brightness of a planet", The Observatory 30: 97, Bibcode: 1907Obs....30...96W, http://adsbit.harvard.edu/full/seri/Obs../0030//0000097.000.html
- ↑ Bruton, D., Conversion of Absolute Magnitude to Diameter for Minor Planets, Stephen F. Austin State University, http://www.physics.sfasu.edu/astro/asteroids/sizemagnitude.html, retrieved 12 January 2019
- ↑ The [math]\displaystyle{ 1329\text{ km} }[/math] factor can be computed as [math]\displaystyle{ 2\text{ AU}\cdot10^{H_{\text{Sun}}/5} }[/math], where [math]\displaystyle{ H_{\text{Sun}}=-26.76 }[/math], the absolute magnitude of the Sun, and [math]\displaystyle{ 1\text{ AU}=1.4959787\times10^{8}\text{ km}. }[/math]
- ↑ Pravec, P.; Harris, A. W. (2007). "Binary asteroid population 1. Angular momentum content". Icarus 190 (190): 250–259. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.02.023. Bibcode: 2007Icar..190..250P. https://www.asu.cas.cz/%7Eppravec/pravecharris07.pdf.
- ↑ Albedo of the Earth, Department of Physics and Astronomy, http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/phyopt/albedo.html, retrieved 12 January 2019
- ↑ Luciuk, M., Albedo – How bright is the Moon?, http://www.asterism.org/tutorials/tut26-1.htm, retrieved 12 January 2019
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Anthony, M.; Hilton, J. L. (October 2018). "Computing apparent planetary magnitudes for The Astronomical Almanac". Astronomy and Computing 25: 10–24. doi:10.1016/j.ascom.2018.08.002. Bibcode: 2018A&C....25...10M.
- ↑ "Encyclopedia - the brightest bodies". https://promenade.imcce.fr/en/pages5/572.html.
- ↑ Cox, A.N. (2000). Allen's Astrophysical Quantities, fourth edition. Springer-Verlag. pp. 310.
- ↑ JPL Horizons, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons.cgi, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ Minor Planet Circular 10193, Minor Planet Center, 27 December 1985, https://minorplanetcenter.net/iau/ECS/MPCArchive/1985/MPC_19851227.pdf, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Lagerkvist, C.-I.; Williams, I. (1987), "Physical studies of asteroids. XV – Determination of slope parameters and absolute magnitudes for 51 asteroids", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series 68 (2): 295–315, Bibcode: 1987A&AS...68..295L, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234236400
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Dymock, R. (2007), "The H and G magnitude system for asteroids", Journal of the British Astronomical Association 117 (6): 342–343, Bibcode: 2007JBAA..117..342D, https://www.britastro.org/asteroids/dymock4.pdf, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ JPL Horizons (Version 3.75), Jet Propulsion Laboratory, 4 April 2013, p. 27, ftp://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/pub/ssd/Horizons_doc.pdf, retrieved 11 January 2013
- ↑ JPL Small-Body Database Browser – 101955 Bennu, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, 19 May 2018, https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=101955;old=0;orb=0;cov=0;log=0;cad=0#phys_par, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ Shevchenko, V. G. (April 2016), "Asteroid observations at low phase angles. IV. Average parameters for the new H, G1, G2 magnitude system", Planetary and Space Science 123: 101–116, doi:10.1016/j.pss.2015.11.007, Bibcode: 2016P&SS..123..101S
- ↑ Harris, A. W.; Warner, B. D.; Pravec, P. (2016). "Asteroid Lightcurve Derived Data V16.0". NASA Planetary Data System 246: EAR-A-5-DDR-DERIVED-LIGHTCURVE-V16.0. Bibcode: 2016PDSS..246.....H.
- ↑ Guide to the MPES, Minor Planet Center, p. 11, https://minorplanetcenter.net/iau/info/MPES.pdf, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ Meisel, D. D.; Morris, C. S. (1976), "Comet brightness parameters: Definition, determination, and correlations", NASA. Goddard Space Flight Center the Study of Comets, Part 1 393: 410–444, Bibcode: 1976NASSP.393..410M
- ↑ Comet C/2011 L4 (PANSTARRS), COBS, https://cobs.si/analysis2?plot_type=0&end_date=2013/06/01%2000:00&col=comet_id&fit_curve=1&perihelion=1&obs_type=1&id=654&start_date=2013/01/01%2000:00, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ Minor Planet & Comet Ephemeris Service, Minor Planet Center, https://minorplanetcenter.net/iau/MPEph/MPEph.html, retrieved 11 January 2019
- ↑ Kidger, M. (3 April 1997), Comet Hale-Bopp Light Curve, NASA JPL, http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/comet/news66.html, retrieved 31 May 2019
- ↑ Hughes, D. W. (16 June 1989). "Cometary Absolute Magnitudes, their Significance and Distribution". Asteroids, Comets, Meteors III, Proceedings of a Meeting (AMC 89) Held at the Astronomical Observatory of the Uppsala University (Uppsala): 337. Bibcode: 1990acm..proc..327H.
- ↑ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2014 UN271)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=54161348. Retrieved 15 September 2021.
- ↑ "The Largest Comet Ever Found Is Making Its Move Into a Sky Near You". The New York Times. 28 June 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/06/28/science/comet-largest-ever-seen.html. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- ↑ Farnham, Tony (6 July 2021). "Comet C/2014 UN271 (Bernardinelli-Bernstein) exhibited activity at 23.8 au". The Astronomer's Telegram. https://www.astronomerstelegram.org/?read=14759. Retrieved 6 July 2021.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 Yoshida, S. (24 January 2015), 289P/Blanpain, http://www.aerith.net/comet/catalog/0289P/index.html, retrieved 31 May 2019
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Jewitt, D. (2006). "Comet D/1819 W1 (Blanpain): Not Dead Yet". Astronomical Journal 131 (4): 2327–2331. doi:10.1086/500390. Bibcode: 2006AJ....131.2327J. http://www.ifa.hawaii.edu/publications/preprints/05preprints/Jewitt_05-165.pdf. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 289P/Blanpain (2013-07-17 last obs.), Jet Propulsion Laboratory, 18 May 2019, https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=289P#phys_par, retrieved 31 May 2019
- ↑ Lamy, P. L.; Toth, I.; Fernandez, Y. R.; Weaver, H. A. (2004), The sizes, shapes, albedos, and colors of cometary nuclei, University of Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 223–264, Bibcode: 2004come.book..223L, https://physics.ucf.edu/~yfernandez/papers/comets2chapter/comets2reprint.pdf
- ↑ "Glossary – Absolute magnitude of meteors". International Meteor Organization. http://www.imo.net/glossary#term66.
- ↑ "Solar System Dynamics Glossary – Absolute magnitude of Solar System bodies". NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/?glossary&term=H.
External links
- Reference zero-magnitude fluxes
- International Astronomical Union
- Absolute Magnitude of a Star calculator
- The Magnitude system
- About stellar magnitudes
- Obtain the magnitude of any star – SIMBAD
- Converting magnitude of minor planets to diameter
- Another table for converting asteroid magnitude to estimated diameter
 |