Chemistry:24S-hydroxycholesterol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
cholest-5-ene-3,24-diol
| |
| Other names
cerebrosterol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3218472 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H46O2 | |
| Molar mass | 402.653 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
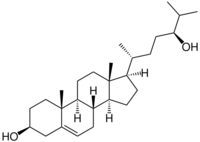
24S-hydroxycholesterol (24S-HC), also known as cholest-5-ene-3,24-diol or cerebrosterol, is an endogenous oxysterol produced by neurons in the brain to maintain cholesterol homeostasis.[1] It was discovered in 1953 by Alberto Ercoli, S. Di Frisco, and Pietro de Ruggieri, who first isolated the molecule in the horse brain[2] and then demonstrated its presence in the human brain.[3]
Structure
24S-HC is produced by a hydroxy group substitution at carbon number 24 in cholesterol, catalyzed by the enzyme cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46A1).[4]

Function
24S-HC binds to apolipoproteins such as apoE, apoJ, and apoA1 to form HDL-like complexes[5] which can cross the blood-brain barrier more easily than free cholesterol. Thus, 24S-HC production serves as one of several counterbalancing mechanisms for cholesterol synthesis in the brain.[1][6] After entering general blood circulation and traveling to the liver, 24S-HC can be sulfated, glucuronidated, or converted into bile acids, which can ultimately be excreted.[7]
24S-HC is an agonist of liver X receptors, a class of nuclear receptors that sense oxysterols. In the brain, liver X receptor beta is the primary LXR type which interacts with 24S-HC.[5] 24S-HC levels sensed by LXRs can regulate the expression of SREBP mRNA and protein, which in turn regulate cholesterol synthesis and fatty acid synthesis.[8]
24S-HC may participate in several aspects of brain development and function, such as axon and dendrite growth or synaptogenesis.[4] Regulation of 24S-HC metabolism in neurons may play a role in their health and function, as well as their response to injury or disease.[9] Blood plasma levels of 24S-HC may be altered after acute brain injuries such as stroke[10] or in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and multiple sclerosis.[11][12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Central Nervous System Lipoproteins: ApoE and Regulation of Cholesterol Metabolism.". Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36 (7): 1305–15. 2016. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307023. PMID 27174096.
- ↑ "Isolation, constitution and biological significance of cerebrosterol, a companion of cholesterol in the horse brain.". Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 29 (4): 494–7. 1953. PMID 13105923.
- ↑ "Isolation of cerebrosterol from human brain.". Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 29 (7): 1351–2. 1953. PMID 13140512.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Knockout of the cholesterol 24-hydroxylase gene in mice reveals a brain-specific mechanism of cholesterol turnover.". J Biol Chem 278 (25): 22980–8. 2003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M303415200. PMID 12686551.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "A second class of nuclear receptors for oxysterols: Regulation of RORalpha and RORgamma activity by 24S-hydroxycholesterol (cerebrosterol).". Biochim Biophys Acta 1801 (8): 917–23. 2010. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.02.012. PMID 20211758.
- ↑ "Rediscovery of cerebrosterol.". Lipids 42 (1): 5–14. 2007. doi:10.1007/s11745-006-1003-2. PMID 17393206.
- ↑ "Cholesterol metabolism in the brain: importance of 24S-hydroxylation.". Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 185: 33–42. 2006. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2006.00683.x. PMID 16866909.
- ↑ "24S-hydroxycholesterol effects on lipid metabolism genes are modeled in traumatic brain injury.". Brain Res 1319: 1–12. 2010. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.080. PMID 20053345.
- ↑ "24(S)-Hydroxycholesterol as a Modulator of Neuronal Signaling and Survival.". Neuroscientist 22 (2): 132–44. 2016. doi:10.1177/1073858414568122. PMID 25628343.
- ↑ "24S-hydroxycholesterol and 25-hydroxycholesterol differentially impact hippocampal neuronal survival following oxygen-glucose deprivation.". PLOS ONE 12 (3): e0174416. 2017. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0174416. PMID 28346482. Bibcode: 2017PLoSO..1274416S.
- ↑ "24S-hydroxycholesterol in plasma: a marker of cholesterol turnover in neurodegenerative diseases.". Biochimie 95 (3): 595–612. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2012.09.025. PMID 23041502.
- ↑ "Quantitative detection of free 24S-hydroxycholesterol, and 27-hydroxycholesterol from human serum.". BMC Neurosci 15: 137. 2014. doi:10.1186/s12868-014-0137-z. PMID 25539717.
