Chemistry:BMS-906024
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H26F6N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 556.509 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
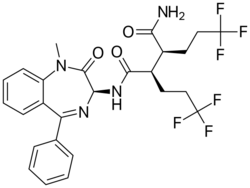
BMS-906024 is a drug with a benzodiazepine structure, developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb and disclosed at the spring 2013 American Chemical Society meeting in New Orleans to treat breast, lung, colon cancers and leukemia.[1] The drug works as a pan-Notch inhibitor. The structure is one of a set patented in 2012,[2] and is being studied in clinical trials.[3][4][5]
References
- ↑ "Liveblogging First-Time Disclosures of Drug Structures from #ACSNOLA". Chemical and Engineering News. American Chemical Society. 2013. http://cenblog.org/the-haystack/2013/04/liveblogging-first-time-disclosures-of-drug-structures-from-acsnola/.
- ↑ Quesnelle C, Kim SH, Lee F, Gavai A, "Bisfluoroalkyl-1,4-Benzodiazepinone Compounds", WO patent 2012129353, published 27 September 2012, assigned to Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- ↑ "Discovery of Clinical Candidate BMS-906024: A Potent Pan-Notch Inhibitor for the Treatment of Leukemia and Solid Tumors". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters 6 (5): 523–7. May 2015. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00001. PMID 26005526.
- ↑ "Gamma Secretase Inhibition by BMS-906024 Enhances Efficacy of Paclitaxel in Lung Adenocarcinoma". Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 16 (12): 2759–2769. December 2017. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0439. PMID 28978720.
- ↑ "Synergistic Effects of NOTCH/γ-Secretase Inhibition and Standard of Care Treatment Modalities in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells". Frontiers in Oncology 8: 460. 2018. doi:10.3389/fonc.2018.00460. PMID 30464927.
 |

