Chemistry:Avizafone
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
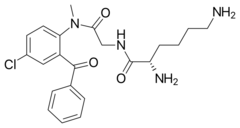
| Formula | C22H27ClN4O3 |
| Molar mass | 430.93 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Avizafone[1] (Pro-Diazepam) is a water-soluble prodrug of the benzodiazepine derivative diazepam. It can be administered intramuscularly.
Avizafone is metabolised by enzymes in the blood to form the active drug diazepam. It is used mainly as an antidote to poisoning with organophosphate nerve agents.[2][3][4]
See also
References
- ↑ GB patent 1517164
- ↑ "On the use of diazepam and pro-diazepam (2-benzoyl-4-chloro-N-methyl-N-lysylglycin anilide), as adjunct antidotes in the treatment of organophosphorus intoxication in the guinea-pig". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 42 (4): 247–51. April 1990. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1990.tb05401.x. PMID 1974291.
- ↑ "Compared efficacy of diazepam or avizafone to prevent soman-induced electroencephalographic disturbances and neuropathology in primates: relationship to plasmatic benzodiazepine pharmacokinetics". Archives of Toxicology 74 (8): 480–6. October 2000. doi:10.1007/s002040000146. PMID 11097386.
- ↑ "Comparative efficacy of diazepam and avizafone against sarin-induced neuropathology and respiratory failure in guinea pigs: influence of atropine dose". Toxicology 188 (2–3): 197–209. June 2003. doi:10.1016/s0300-483x(03)00086-6. PMID 12767691.
 |
