Chemistry:Flutazolam
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Coreminal (Japan ) |
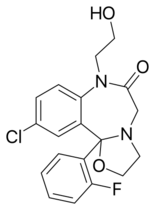
| Other names | 13-chloro- 2-(2-fluorophenyl)- 9-(2-hydroxyethyl)- 3-oxa- 6,9-diazatricyclo[8.4.0.02,6] tetradeca-1(10),11,13- trien- 8-one |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 3.5 hours (parent compound); 47-100 hours (major metabolite) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H18ClFN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 376.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Flutazolam[1] (Coreminal, MS-4101) is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was invented in Japan, and this is the main country in which it has been used medically. It has sedative, muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic effects similar to those produced by other benzodiazepine derivatives, and though it is around the same potency as diazepam, it produces a more marked sedation and impaired coordination. It is indicated for the treatment of insomnia.[2] Its major active metabolite is n-desalkylflurazepam, also known as norflurazepam, which is also a principal metabolite of flurazepam (trade name Dalmane).[3] While flutazolam has a very short half-life of only 3.5 hours, n-desalkylflurazepam has a long half-life of between 47–100 hours.[4]
Flutazolam is closely related in structure to another benzodiazepine, haloxazolam.[5][6]
See also
- Benzodiazepine
- Flurazepam
- N-desalkylflurazepam
References
- ↑ DE patent 1952486
- ↑ Mitsushima T, Ueki S. Psychopharmacological effects of flutazolam (MS-4101). Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1978 Nov;74(8):959-79. (Japanese).
- ↑ "A method for screening for various sedative-hypnotics in serum by liquid chromatography/single quadrupole mass spectrometry". Forensic Science International 157 (1): 57–70. February 2006. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2005.03.011. PMID 15869852.
- ↑ "Dalmane Prescribing Information". FDA. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/016721s076lbl.pdf.
- ↑ "The behavior of 1,4-benzodiazepine drugs in acidic media. V. Kinetics of hydrolysis of flutazolam and haloxazolam in aqueous solution.". Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin (Tokyo) 34 (1): 320–6. January 1986. doi:10.1248/cpb.34.320. PMID 2870816.
- ↑ "[The behavior of 1,4-benzodiazepine drugs in acidic media. IX. Effect of hydrolyzate of flutazolam on the central nervous system]" (in ja). Yakugaku Zasshi: Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan 107 (10): 830–4. October 1987. doi:10.1248/yakushi1947.107.10_830. PMID 2894449.
 |
