Chemistry:Haloxazolam
From HandWiki
Short description: Benzodiazepine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Somelin (Japan ) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
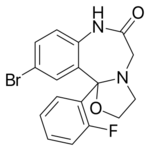
| Formula | C17H14BrFN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 377.213 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Haloxazolam (marketed in Japan under the brand name Somelin), is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative.[1][2][3] It has similar hypnotic properties as the benzodiazepine drugs triazolam, temazepam, and flunitrazepam and as such is indicated for the treatment of insomnia.[4] A study in cats comparing estazolam and haloxazolam found that haloxazolam only affects gamma motor neurons, whereas estazolam affects both alpha and gamma motor neurons.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ "Simultaneous determination of twelve benzodiazepines in human serum using a new reversed-phase chromatographic column on a 2-microns porous microspherical silica gel". Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications 682 (1): 173–8. June 1996. doi:10.1016/0378-4347(96)00121-1. PMID 8832439.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepine Names". non-benzodiazepines.org.uk. http://www.non-benzodiazepines.org.uk/benzodiazepine-names.html.
- ↑ "Solid-phase microextraction and GC-ECD of benzophenones for detection of benzodiazepines in urine". Journal of Analytical Toxicology 23 (1): 54–61. 1999. doi:10.1093/jat/23.1.54. PMID 10022210.
- ↑ "Long-, intermediate- and short-acting benzodiazepine effects on human sleep EEG spectra". Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 57 (1): 97–104. February 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1819.2003.01085.x. PMID 12519461.
- ↑ "Comparative study on the effects of haloxazolam and estazolam, new sleep inducing drugs, on the alpha- and gamma-motor systems". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology 33 (5): 1017–25. October 1983. doi:10.1254/jjp.33.1017. PMID 6139494.
 |
