Chemistry:Fludiazepam
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Erispan (Japan , TW) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
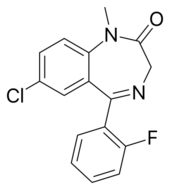
| Formula | C16H12ClFN2O |
| Molar mass | 302.7 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Fludiazepam,[1] marketed under the brand name Erispan (エリスパン)[2][3] is a potent benzodiazepine and 2ʹ-fluoro derivative of diazepam,[4] originally developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1960s.[5] It is marketed in Japan and Taiwan. [citation needed] It exerts its pharmacological properties via enhancement of GABAergic inhibition.[6] Fludiazepam has 4 times more binding affinity for benzodiazepine receptors than diazepam.[7] It possesses anxiolytic,[8][9][10] anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.[11] Fludiazepam has been used recreationally.[12]
See also
- Diazepam
- Diclazepam (the 2ʹ-chloro analog)
- Difludiazepam (the 2',6'-difluoro derivative)
- Flunitrazepam (the 7-nitro analog)
- Flualprazolam (the triazolo derivative)
- Ro20-8552
References
- ↑ US Patent 3371085 5-aryl-3h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2(1h)-ones
- ↑ "Utilization of psychotropic drugs in Taiwan: an overview of outpatient sector in 2000". Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese Medical Journal; Free China Ed) 65 (8): 378–91. August 2002. PMID 12455808.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepine Names". non-benzodiazepines.org.uk. http://www.non-benzodiazepines.org.uk/benzodiazepine-names.html.
- ↑ "A Fourier transform-Raman and infrared vibrational study of delorazepam, fludiazepam, flurazepam, and tetrazepam". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 83 (2): 143–51. February 1994. doi:10.1002/jps.2600830207. PMID 7909552.
- ↑ US Patent 3299053 -ARYL-JH-L,X-BENZODIAZEPIN-Z(LH)-ONES
- ↑ "Effects of benzodiazepines and pentobarbitone on the gaba-ergic recurrent inhibition of hippocampal neurons". European Journal of Pharmacology 48 (4): 421–4. April 1978. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(78)90169-3. PMID 648585.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepines and their metabolites: relationship between binding affinity to the benzodiazepine receptor and pharmacological activity". Life Sciences 36 (2): 113–9. January 1985. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(85)90089-X. PMID 2857046.
- ↑ "Effect of an anxiolytic on lipid profile in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus". The Journal of International Medical Research 22 (6): 338–42. 1994. doi:10.1177/030006059402200605. PMID 7895897.
- ↑ "Improvement of stress reduces glycosylated haemoglobin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes". The Journal of International Medical Research 23 (2): 119–22. 1995. doi:10.1177/030006059502300205. PMID 7601294.
- ↑ "How blood pressure in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus is influenced by stress". The Journal of International Medical Research 23 (5): 377–80. 1995. doi:10.1177/030006059502300508. PMID 8529781.
- ↑ "Screening and determination of benzodiazepines in whole blood using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry". Forensic Science International 113 (1–3): 367–73. September 2000. doi:10.1016/S0379-0738(00)00226-7. PMID 10978650.
- ↑ "[Studies on identification of drugs of abuse by diode array detection. I. Screening-test and identification of benzodiazepines by HPLC-DAD with ICOS software system]". Eisei Shikenjo Hokoku. Bulletin of National Institute of Hygienic Sciences (111): 47–56. 1993. PMID 7920567.
External links
- (in Japanese) Official Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Website
 |
