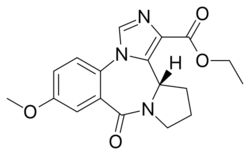
Chemistry:L-655,708
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H19N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 341.367 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
L-655,708 (FG-8094) is a nootropic drug invented in 1996 by a team working for Merck, Sharp and Dohme, that was the first compound developed which acts as a subtype-selective inverse agonist at the α5 subtype of the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor.[1] It acts as an inverse agonist at the α1, α2, α3 and α5 subtypes, but with much higher affinity for α5, and unlike newer α5 inverse agonists such as α5IA, L-655,708 exerts its subtype selectivity purely via higher binding affinity for this receptor subtype, with its efficacy as an inverse agonist being around the same at all the subtypes it binds to.[2]
A radiolabelled form of L-655,708 was used to map the distribution of the GABAA α5 subtype in the brain, and it was found to be expressed predominantly in the hippocampus,[3] an area of the brain involved with learning and memory. Activation of this subtype is thought to be largely responsible for producing the cognitive side effects displayed by many benzodiazepine and nonbenzodiazepine drugs, such as amnesia and difficulties with learning and memory, and so this led researchers to conclude that a drug acting as an inverse agonist at this subtype should have the opposite effect and enhance learning and memory.[4][5]
L-655,708 was indeed found to produce improved cognitive performance in animal studies, without producing the side effect of convulsions which is produced by non-selective inverse agonists like DMCM.[6] However it was found to be anxiogenic at doses which enhanced cognition,[7] most likely because of its inverse agonist effects on other subtypes such as α2 and α3, making it unlikely that this drug would be suitable for use as a nootropic in humans. Still, L-655,708 may find use in the clinic to combat postoperative cognitive dysfunction since administration of sub-nootropic doses of L-655,708 prevented persistent memory impairment in mice anesthetized with isoflurane.[8]
A study from 2015 found that L-655,708, and another α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptor-selective negative allosteric modulator, MRK-016, produced rapid, ketamine-like antidepressant effects in animal models of depression.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ "[3H]L-655,708, a novel ligand selective for the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors which contain the alpha 5 subunit". Neuropharmacology 35 (9–10): 1331–5. 1996. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(96)00061-5. PMID 9014149.
- ↑ "Identification of amino acid residues responsible for the alpha5 subunit binding selectivity of L-655,708, a benzodiazepine binding site ligand at the GABA(A) receptor". Journal of Neurochemistry 77 (2): 445–51. April 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00289.x. PMID 11299307.
- ↑ "Autoradiographic localization of alpha5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors in rat brain". Brain Research 822 (1–2): 265–70. March 1999. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(99)01152-X. PMID 10082908.
- ↑ "Identification of a novel, selective GABA(A) alpha5 receptor inverse agonist which enhances cognition". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46 (11): 2227–40. May 2003. doi:10.1021/jm020582q. PMID 12747794.
- ↑ "An orally bioavailable, functionally selective inverse agonist at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA alpha5 receptors with cognition enhancing properties". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 47 (24): 5829–32. November 2004. doi:10.1021/jm040863t. PMID 15537339.
- ↑ "L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for alpha5-containing GABAA receptors". Neuropharmacology 51 (6): 1023–9. November 2006. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.04.018. PMID 17046030.
- ↑ "Anxiogenic-like activity of L-655,708, a selective ligand for the benzodiazepine site of GABA(A) receptors which contain the alpha-5 subunit, in the elevated plus-maze test". Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 26 (7–8): 1389–92. December 2002. doi:10.1016/S0278-5846(02)00305-6. PMID 12502028.
- ↑ "Short-term memory impairment after isoflurane in mice is prevented by the α5 γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor inverse agonist L-655,708". Anesthesiology 113 (5): 1061–71. November 2010. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181f56228. PMID 20966663.
- ↑ "Rapid Antidepressant Action and Restoration of Excitatory Synaptic Strength After Chronic Stress by Negative Modulators of Alpha5-Containing GABAA Receptors". Neuropsychopharmacology 40 (11): 2499–509. October 2015. doi:10.1038/npp.2015.112. PMID 25900119.
{{Navbox | name = GABA receptor modulators | title = GABA receptor modulators | state = collapsed | bodyclass = hlist | groupstyle = text-align:center;
| group1 = Ionotropic | list1 = {{Navbox|subgroup | groupstyle = text-align:center | groupwidth = 5em
| group1 = GABAA | list1 =
- Agonists: (+)-Catechin
- Bamaluzole
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- BL-1020
- DAVA
- Dihydromuscimol
- GABA
- Gabamide
- GABOB
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- Homotaurine (tramiprosate, 3-APS)
- Ibotenic acid
- iso-THAZ
- iso-THIP
- Isoguvacine
- Isomuscimol
- Isonipecotic acid
- Kojic amine
- Lignans (e.g., honokiol)
- Methylglyoxal
- Monastrol
- Muscimol
- Nefiracetam
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone)
- Org 20599
- PF-6372865
- Phenibut
- Picamilon
- P4S
- Progabide
- Propofol
- Quisqualamine
- SL-75102
- TACA
- TAMP
- Terpenoids (e.g., borneol)
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- ZAPA
- Positive modulators (abridged; see here for a full list): α-EMTBL
- Alcohols (e.g., ethanol)
- Anabolic steroids
- Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam)
- Bromide compounds (e.g., potassium bromide)
- Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate)
- Carbamazepine
- Chloralose
- Chlormezanone
- Clomethiazole
- Dihydroergolines (e.g., ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine))
- Etazepine
- Etifoxine
- Fenamates (e.g., mefenamic acid)
- Flavonoids (e.g., apigenin, hispidulin)
- Fluoxetine
- Flupirtine
- Imidazoles (e.g., etomidate)
- Kava constituents (e.g., kavain)<!--PMID: 9776662-->
- Lanthanum
- Loreclezole
- Monastrol
- Neuroactive steroids (e.g., allopregnanolone, [[Chemistry:Cholecholesterol]], THDOC)
- Niacin
- Nicotinamide (niacinamide)
- Nonbenzodiazepines (e.g., β-carbolines (e.g., [[abecarnil), cyclopyrrolones (e.g., zopiclone), imidazopyridines (e.g., zolpidem), pyrazolopyrimidines (e.g., zaleplon))
- Norfluoxetine
- Petrichloral
- Phenols (e.g., propofol)
- Phenytoin
- Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide)
- Propanidid
- Pyrazolopyridines (e.g., etazolate)
- Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone)
- Retigabine (ezogabine)
- ROD-188
- Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin)
- Stiripentol
- Sulfonylalkanes (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal))
- Topiramate
- Valerian constituents (e.g., valerenic acid)
- Volatiles/gases (e.g., chloral hydrate, chloroform, [[Chemistry:Diethyl diethyl ether, Parparaldehyde]], sevoflurane)
- Antagonists: Bicuculline
- Coriamyrtin
- Dihydrosecurinine
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Hydrastine
- Hyenachin (mellitoxin)
- PHP-501
- Pitrazepin
- Securinine
- Sinomenine
- SR-42641
- SR-95103
- Thiocolchicoside
- Tutin
- Negative modulators: 1,3M1B
- 3M2B
- 11-Ketoprogesterone
- 17-Phenylandrostenol
- α5IA (LS-193,268)
- β-CCB
- β-CCE
- β-CCM
- β-CCP
- β-EMGBL
- Anabolic steroids
- Amiloride
- Anisatin
- β-Lactams (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems)
- Basmisanil
- Bemegride
- Bicyclic phosphates (TBPS, TBPO, IPTBO)
- BIDN
- Bilobalide
- Bupropion
- CHEB
- Chlorophenylsilatrane
- Cicutoxin
- Cloflubicyne
- Cyclothiazide
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- Dieldrin
- (+)-DMBB
- DMCM
- DMPC
- EBOB
- Etbicyphat
- FG-7142 (ZK-31906)
- Fiproles (e.g., fipronil)
- Flavonoids (e.g., amentoflavone, oroxylin A)
- Flumazenil
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- Flurothyl
- Furosemide
- Golexanolone
- Iomazenil (123I)
- IPTBO
- Isopregnanolone (sepranolone)
- L-655,708
- Laudanosine
- Leptazol
- Lindane
- MaxiPost
- Morphine
- Morphine-3-glucuronide
- MRK-016
- Naloxone
- Naltrexone
- Nicardipine
- Nonsteroidal antiandrogens (e.g., [[apalutamide, [[Chemistry:Bicalutbicalutamide, Enzalutenzalutamide, Chemistry:Flutamide|flut]]amide]], nilutamide)
- Oenanthotoxin
- Pentylenetetrazol (pentetrazol)
- Phenylsilatrane
- Picrotoxin (i.e., picrotin, picrotoxinin and dihydropicrotoxinin)
- Pregnenolone sulfate
- Propybicyphat
- PWZ-029
- Radequinil
- Ro 15-4513
- Ro 19-4603
- RO4882224
- RO4938581
- Sarmazenil
- SCS
- Suritozole
- TB-21007
- TBOB
- TBPS
- TCS-1105
- Terbequinil
- TETS
- Thujone
- U-93631
- Zinc
- ZK-93426
| group2 = GABAA-ρ | list2 =
- Agonists: BL-1020
- CACA
- CAMP
- Homohypotaurine
- GABA
- GABOB
- Ibotenic acid
- Isoguvacine
- Muscimol
- N4-Chloroacetylcytosine arabinoside
- Picamilon
- Progabide
- TACA
- TAMP
- Thiomuscimol
- Tolgabide
- Positive modulators: Allopregnanolone
- Alphaxolone
- ATHDOC
- Lanthanides
- Antagonists: (S)-2-MeGABA
- (S)-4-ACPBPA
- (S)-4-ACPCA
- 2-MeTACA
- 3-APMPA
- 4-ACPAM
- 4-GBA
- cis-3-ACPBPA
- CGP-36742 (SGS-742)
- DAVA
- Gabazine (SR-95531)
- Gaboxadol (THIP)
- I4AA
- Isonipecotic acid
- Loreclezole
- P4MPA
- P4S
- SKF-97541
- SR-95318
- SR-95813
- TPMPA
- trans-3-ACPBPA
- ZAPA
- Negative modulators: 5α-Dihydroprogesterone
- Bilobalide
- Loreclezole
- Picrotoxin (picrotin, picrotoxinin)
- Pregnanolone
- ROD-188
- THDOC
- Zinc
}}
| group2 = Metabotropic
| list2 =
| below =
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- GABAA receptor positive modulators
- GABA metabolism/transport modulators
}}
 |
