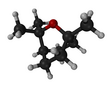
Chemistry:Eucalyptol
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
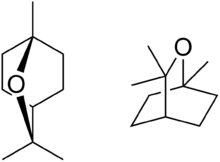
| IUPAC name
1,3,3-Trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane
| |||
| Other names
1,8-Cineole
1,8-Epoxy-p-menthane cajeputol 1,8-epoxy-p-menthane, 1,8-oxido-p-menthane eucalyptole 1,3,3-trimethyl-2-oxabicyclo[2.2.2]octane cineol cineole. | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 105109 5239941 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 131076 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H18O | |||
| Molar mass | 154.249 g/mol | ||
| Density | 0.9225 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 2.9 °C (37.2 °F; 276.0 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 176–177 °C (349–351 °F; 449–450 K) | ||
| −116.3×10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Pharmacology | |||
| 1=ATC code }} | R05CA13 (WHO) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |    
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H226, H304, H315, H317, H319, H411 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P272, P273, P280, P301+310, P302+352, P303+361+353, P305+351+338, P321, P331, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P370+378, P391, P403+235 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Eucalyptol (also called cineole) is a monoterpenoid colorless liquid, and a bicyclic ether.[1] It has a fresh camphor-like odor and a spicy, cooling taste.[1] It is insoluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Eucalyptol makes up about 70–90% of eucalyptus oil.[2][3] Eucalyptol forms crystalline adducts with hydrohalic acids, o-cresol, resorcinol, and phosphoric acid. Formation of these adducts is useful for purification.[4]
In 1870, F. S. Cloez identified and ascribed the name "eucalyptol" to the dominant portion of Eucalyptus globulus oil.[2]
Uses
Because of its pleasant, spicy aroma and taste, eucalyptol is used in flavorings, fragrances, and cosmetics.[1] Cineole-based eucalyptus oil is used as a flavoring at low levels (0.002%) in various products, including baked goods, confectionery, meat products, and beverages.[1][5] In a 1994 report released by five top cigarette companies, eucalyptol was listed as one of the 599 additives to cigarettes.[6] It is claimed to be added to improve the flavor.[1]
Eucalyptol is an ingredient in commercial mouthwashes,[1] and has been used in traditional medicine as a cough suppressant.[7]
Other
Eucalyptol exhibits insecticidal and insect repellent properties.[8][9]
In contrast, eucalyptol is one of many compounds that are attractive to males of various species of orchid bees, which gather the chemical to synthesize pheromones; it is commonly used as bait to attract and collect these bees for study.[10] One such study with Euglossa imperialis, a nonsocial orchid bee species, has shown that the presence of cineole (also eucalyptol) elevates territorial behavior and specifically attracts the male bees. It was even observed that these males would periodically leave their territories to forage for chemicals such as cineole, thought to be important for attracting and mating with females, to synthesize pheromones.[11]
Toxicology
Eucalyptol has a toxicity (LD50) of 2.48 grams per kg (rat).[1] Ingestion in significant quantities is likely to cause headache and gastric distress, such as nausea and vomiting.[1] Because of its low viscosity, it may directly enter the lungs if swallowed, or if subsequently vomited. Once in the lungs, it is difficult to remove and can cause delirium, convulsions, severe injury or death.[1]
Biosynthesis
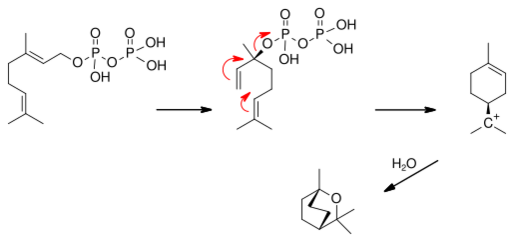
Eucalyptol is generated from geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) which isomerizes to (S)-linalyl diphosphate (LPP). Ionization of the pyrophosphate, catalyzed by cineole synthase, produces eucalyptol. The process involves the intermediacy of alpha-terpinyl cation.[12][13][14]
Plants containing eucalyptol
- Aframomum corrorima[15]
- Artemisia tridentata[16]
- Cannabis[17]
- Cinnamomum camphora, camphor laurel (50%)[18]
- Eucalyptus globulus[19]
- Eucalyptus largiflorens[20]
- Eucalyptus salmonophloia[21]
- Eucalyptus staigeriana[22]
- Eucalyptus wandoo[23]
- Hedychium coronarium, butterfly lily[24][25]
- Helichrysum gymnocephalum[26]
- Kaempferia galanga, galangal, (5.7%)[27]
- Salvia lavandulifolia, Spanish sage (13%)[28]
- Turnera diffusa, damiana[29]
- Umbellularia californica, pepperwood (22.0%)[30]
- Zingiber officinale, ginger[31]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "Eucalyptol". PubChem, US National Library of Medicine. 22 April 2023. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2758.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Boland, D. J.; Brophy, J. J.; House, A. P. N. (1991). Eucalyptus Leaf Oils: Use, Chemistry, Distillation and Marketing. Melbourne: Inkata Press. p. 6. doi:10.1002/ffj.2730070209. ISBN 0-909605-69-6. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ffj.2730070209.
- ↑ "GCMS – Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Analysis". https://www.newdirectionsaromatics.com/msds/GC_EucalyptusRadiataEssentialOil.pdf.
- ↑ Eggersdorfer, Manfred (2000). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_205.
- ↑ Harborne, J. B.; Baxter, H. (30 August 2001). Chemical Dictionary of Economic Plants. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-49226-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=ry11ai2iPS0C&pg=PA69.
- ↑ "Cigarette Ingredients – Chemicals in Cigarettes". New York State Department of Health. http://www.tricountycessation.org/tobaccofacts/Cigarette-Ingredients.html.
- ↑ "Tea tree oil". Drugs.com. 17 June 2019. https://www.drugs.com/npp/tea-tree-oil.html.
- ↑ Klocke, J. A.; Darlington, M. V.; Balandrin, M. F. (December 1987). "8-Cineole (Eucalyptol), a Mosquito Feeding and Ovipositional Repellent from Volatile Oil of Hemizonia fitchii (Asteraceae)". Journal of Chemical Ecology 13 (12): 2131–41. doi:10.1007/BF01012562. PMID 24301652.
- ↑ Sfara, V.; Zerba, E. N.; Alzogaray, R. A. (May 2009). "Fumigant Insecticidal Activity and Repellent Effect of Five Essential Oils and Seven Monoterpenes on First-Instar Nymphs of Rhodnius prolixus". Journal of Medical Entomology 46 (3): 511–515. doi:10.1603/033.046.0315. PMID 19496421.
- ↑ Schiestl, F. P.; Roubik, D. W. (2004). "Odor Compound Detection in Male Euglossine Bees". Journal of Chemical Ecology 29 (1): 253–257. doi:10.1023/A:1021932131526. PMID 12647866.
- ↑ Schemske, Douglas W.; Lande, Russell (1984). "Fragrance collection and territorial display by male orchid bees". Animal Behaviour 32 (3): 935–937. doi:10.1016/s0003-3472(84)80184-0.
- ↑ Rinkel, Jan; Rabe, Patrick; zur Horst, Laura; Dickschat, Jeroen S (2016-11-04). "A Detailed View on 1,8-Cineol Biosynthesis by Streptomyces clavuligerus". Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 12: 2317–2324. doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.225. ISSN 1860-5397. PMID 28144299.
- ↑ Wise, Mitchell L.; Savage, Thomas J.; Katahira, Eva; Croteau, Rodney (1998-06-12). "Monoterpene Synthases From Common Sage (Salvia Officinalis): cDNA Isolation, Characterization, and Functional Expression of (+)-Aabinene Synthase, 1,8-Cineole Synthase, and (+)-Bo..." (in en). Journal of Biological Chemistry 273 (24): 14891–14899. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.24.14891. ISSN 0021-9258.
- ↑ Croteau, R.; Alonso, W. R.; Koepp, A. E.; Johnson, M. A. (1994-02-01). "Biosynthesis of Monoterpenes: Partial Purification, Characterization, and Mechanism of Action of 1,8-Cineole Synthase" (in en). Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 309 (1): 184–192. doi:10.1006/abbi.1994.1101. ISSN 0003-9861. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003986184711015.
- ↑ Sebsebe Demissew (1993). "A description of some essential oil bearing plants in Ethiopia and their indigenous uses". Journal of Essential Oil Research (Taylor & Francis) 5 (5): 465–479. doi:10.1080/10412905.1993.9698266. "The chemical composition of … Aframomum corrorima (l, 8-cineole 41.9%) … is also presented.".
- ↑ Crowell, M.M. (2018). "Dietary partitioning of toxic leaves and fibrous stems differs between sympatric specialist and generalist mammalian herbivores". Journal of Mammalogy 99 (3): 565–577. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyy018.
- ↑ McPartland, J. M.; Russo, E. B. (2001). "Cannabis and cannabis extracts: greater than the sum of their parts?". Journal of Cannabis Therapeutics 1 (3–4): 103–132. doi:10.1300/J175v01n03_08. http://www.cannabis-med.org/index.php?tpl=journal&id=228&lng=en&fid=2001:3/4&red=journallist. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- ↑ Stubbs, B. J.; Brushett, D. (2001). "Leaf oil of Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Nees and Eberm. From Eastern Australia". Journal of Essential Oil Research 13 (1): 51–54. doi:10.1080/10412905.2001.9699604.
- ↑ Maciel, M. V.; Morais, S. M.; Bevilaqua, C. M.; Silva, R. A.; Barros, R. S.; Sousa, R. N.; Sousa, L. C.; Brito, E. S. et al. (2010). "Chemical composition of Eucalyptus spp. essential oils and their insecticidal effects on Lutzomyia longipalpis". Veterinary Parasitology 167 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.09.053. PMID 19896276. http://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/34137/1/PA10006.pdf.
- ↑ "Chemistry and bioactivity of Eucalyptus essential oils". Allelopathy Journal 25 (2): 313–330. 2010. https://researchoutput.csu.edu.au/ws/portalfiles/portal/8780096/Zhang+et+al+2010.pdf.
- ↑ Charles Austin Gardner (1 August 1952). "Trees of Western Australia - salmon gum and scarlet pear gum". Journal of the Department of Agriculture Western Australia Series 3 (Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development) 1 (4). https://library.dpird.wa.gov.au/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1089&context=journal_agriculture3. Retrieved 23 January 2023.
- ↑ Gilles, M.; Zhao, J.; An, M.; Agboola, S. (2010). "Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Properties of Essential Oils of three Australian Eucalyptus Species". Food Chemistry 119 (2): 731–737. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.07.021.
- ↑ Ameur, Elaissi; Sarra, Moumni; Yosra, Derbali; Mariem, Kouja; Nabil, Abid; Lynen, Frederic; Larbi, Khouja Mohamed (2021). "Chemical composition of essential oils of eight Tunisian Eucalyptus species and their antibacterial activity against strains responsible for otitis". BMC Complement Med Ther 21 (1): 209. doi:10.1186/s12906-021-03379-y. PMID 34384412.
- ↑ Ali, S.; Sotheeswaran, S.; Tuiwawa, M.; Smith, R. (2002). "Comparison of the Composition of the Essential Oils of Alpinia and Hedychium Species—Essential Oils of Fijian Plants, Part 1". Journal of Essential Oil Research 14 (6): 409–411. doi:10.1080/10412905.2002.9699904.
- ↑ Joy, B.; Rajan, A.; Abraham, E. (2007). "Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil from Hedychium coronarium". Phytotherapy Research 21 (5): 439–443. doi:10.1002/ptr.2091. PMID 17245683.
- ↑ Möllenbeck, S.; König, T.; Schreier, P.; Schwab, W.; Rajaonarivony, J.; Ranarivelo, L. (1997). "Chemical Composition and Analyses of Enantiomers of Essential Oils from Madagascar". Flavour and Fragrance Journal 12 (2): 63. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1026(199703)12:2<63::AID-FFJ614>3.0.CO;2-Z.
- ↑ Wong, K. C.; Ong, K. S.; Lim, C. L. (2006). "Composition of the Essential Oil of Rhizomes of Kaempferia galanga L.". Flavour and Fragrance Journal 7 (5): 263–266. doi:10.1002/ffj.2730070506.
- ↑ Perry, N. S.; Houghton, P. J.; Theobald, A.; Jenner, P.; Perry, E. K. (2000). "In-vitro inhibition of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase by Salvia lavandulaefolia essential oil and constituent terpenes". J Pharm Pharmacol 52 (7): 895–902. doi:10.1211/0022357001774598. PMID 10933142.
- ↑ Balch, P. A. (2002). Prescription for Nutritional Healing: the A to Z Guide to Supplements. Penguin. p. 233. ISBN 978-1-58333-143-9. https://archive.org/details/prescriptionfor000balc/page/233.
- ↑ Kelsey, R. G.; McCuistion, O.; Karchesy, J. (2007). "Bark and Leaf Essential Oil of Umbellularia californica, California Bay Laurel, from Oregon". Natural Product Communications 2 (7): 779–780. doi:10.1177/1934578X0700200715.
- ↑ "Composition of a monoterpenoid-rich essential oil from the rhizome of Zingiber officinale from north western Himalayas". Natural Product Communications 6 (1): 93–6. January 2011. doi:10.1177/1934578X1100600122. PMID 21366054.
 |