Chemistry:Lutetium(III) chloride
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lutetium(III) chloride
| |
| Other names
Lutetium chloride, lutetium trichloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| LuCl3 | |
| Molar mass | 281.325 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless or white monoclinic crystals |
| Density | 3.98 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 905 °C (1,661 °F; 1,178 K)[3] |
| Boiling point | sublimes above 750°C[1] |
| soluble[2] | |
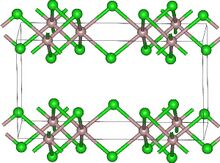
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mS16 | |
| C2/m, No. 12 | |
| Pharmacology | |
| License data | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Lutetium(III) oxide |
Other cations
|
Ytterbium(III) chloride Scandium(III) chloride Yttrium(III) chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lutetium(III) chloride or lutetium trichloride is the chemical compound composed of lutetium and chlorine with the formula LuCl3. It forms hygroscopic white monoclinic crystals[3] and also a hygroscopic hexahydrate LuCl3·6H2O.[6] Anhydrous lutetium(III) chloride has the YCl3 (AlCl3) layer structure with octahedral lutetium ions.[7]
Reactions
Pure lutetium metal can be produced from lutetium(III) chloride by heating it together with elemental calcium:[8]
See also
References
- ↑ "Chemistry: Periodic Table: Lutetium: compound data (lutetium (III) chloride)". WebElements. http://202.114.88.54/g/web18/wangluo/webelements/webelements/compounds/text/lu/cl3lu1-10099668.html.
- ↑ Perry, Dale L.; Phillips, Sidney L. (1995), Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, CRC Press, pp. 232, ISBN 0-8493-8671-3, https://books.google.com/books?id=0fT4wfhF1AsC&pg=PA232, retrieved 2008-06-27
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 472, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2, https://books.google.com/books?id=lFjg0L-uOxoC&pg=PT857, retrieved 2008-06-27
- ↑ "450960 Lutetium(III) chloride anhydrous, powder, 99.99% trace metals basis". Sigma-Aldrich. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/ALDRICH/450960.
- ↑ "Lutetium chloride" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/24919#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ "Lutetium(III) chloride hexahydrate 542075". https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/542075.
- ↑ Wells A.F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry 5th edition Oxford Science Publications ISBN:0-19-855370-6
- ↑ Patnaik, Pradyot (2004), Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals, Amsterdam: McGraw-Hill Professional, pp. 244, ISBN 0-07-049439-8, https://books.google.com/books?id=Xqj-TTzkvTEC&q=%22Lutetium+chloride%22&pg=PA510, retrieved 2008-06-27
 |


