Chemistry:Burimamide
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
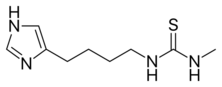
| IUPAC name
1-[4-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)butyl]-3-methylthiourea
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H16N4S | |
| Molar mass | 212.32 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Burimamide is an antagonist at the H2 and H3 histamine receptors. At physiological pH, it is largely inactive as an H2 antagonist,[1] but its H3 affinity is 100x higher. It is a thiourea derivative.
Burimamide was first developed by scientists at Smith, Kline & French (SK&F; now GlaxoSmithKline) in their intent to develop a histamine antagonist for the treatment of peptic ulcers.[2] The discovery of burimamide ultimately led to the development of cimetidine (Tagamet).[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Clayden, Jonathan; Greeves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Wothers, Peter (2001). Organic Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 205. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Tagamet: Discovery of Histamine H2-receptor Antagonists". National Historic Chemical Landmarks. American Chemical Society. http://portal.acs.org/portal/PublicWebSite/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/cimetidinetagamet/.
 |
