Chemistry:Sufotidine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
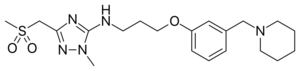
| Formula | C20H31N5O3S |
| Molar mass | 421.56 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Sufotidine (INN,[1] USAN, codenamed AH25352) is a long-acting competitive H2 receptor antagonist which was under development as an antiulcerant by Glaxo (now GlaxoSmithKline).[2] It was planned to be a follow-up compound to ranitidine (Zantac).[3] When taken in doses of 600 mg twice daily it induced virtually 24-hour gastric anacidity[4] thus closely resembling the antisecretory effect of the proton pump inhibitor omeprazole.[5] Its development was terminated in 1989[6] from phase III clinical trials based on the appearance of carcinoid tumors in long-term toxicity testing in rodents.[7]
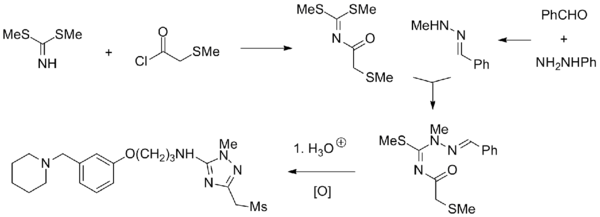
Synthesis
See also
- Lavoltidine (previously known as loxtidine) — a similar compound in which methylsulfone group is replaced with hydroxyl
References
- ↑ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances. Supplement to WHO Chronicle, 1986, Vol. 40, No. 6. Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 26". World Health Organization. p. 9. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/RL26.pdf.
- ↑ "Drug Profile: Sufotidine". Springer International Publishing AG. http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800000594.
- ↑ "Glaxo Plans to Follow Up Zantac with Long-acting Sufotidine; H2 Antagonist Is One of Seven Drugs Targeted for Worldwide Marketing Applications in 1988–90". Informa Business Intelligence, Inc., an Informa Company. November 30, 1987. https://www.pharmamedtechbi.com/publications/the-pink-sheet/49/048/glaxo-plans-to-follow-up-zantac-with-longacting-sufotidine-h2-antagonist-is-one-of-seven-drugs-targeted.
- ↑ "Sufotidine 600 mg bd virtually eliminates 24 hour intragastric acidity in duodenal ulcer subjects". Gut 31 (3): 291–3. March 1990. doi:10.1136/gut.31.3.291. PMID 1969833.
- ↑ "Effect of omeprazole on gastroesophageal reflux in Barrett's esophagus". The American Journal of Gastroenterology 84 (10): 1263–7. October 1989. PMID 2801676.
- ↑ Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents (1st ed.). London: Chapman & Hall. 1999. ISBN 9780412466304.
- ↑ Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 50 (1st ed.). London: Academic. 2011. p. 36. ISBN 978-0-12-381290-2.
 |
