Chemistry:Toreforant
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
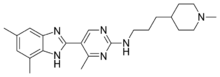
5-(4,6-dimethyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-4-methyl-N-[3-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)propyl]pyrimidin-2-amine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H32N6 | |
| Molar mass | 392.551 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Toreforant (JNJ-38518168) is an orally-dosed selective antagonist of the histamine H4 receptor that has been studied for various health conditions. It is the successor of a number of H4-selective compounds developed by Johnson & Johnson.[1] Phase IIa clinical trials completed as recently as November 2018 continue to suggest that toreforant is safe.[2]
As of the end of 2020, there is no regulator-approved H4 antagonist. In U.S. Phase II clinical trials, toreforant, by itself, did not show efficacy against eosinophilic asthma.[2] The drug did show at least partial efficacy against rheumatoid arthritis in patients who were nonresponsive to methotrexate.[3] As the H4 receptor is widely implicated in the regulation of inflammatory states, the potential uses for an H4 antagonist remain significant.[4][5][6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Clinical Development of Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonists". Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Health and Disease. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 241. 2017. pp. 301–320. doi:10.1007/164_2016_130. ISBN 978-3-319-58192-7.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "A phase 2a study of toreforant, a histamine H4 receptor antagonist, in eosinophilic asthma". Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology 121 (5): 568–574. 2018. doi:10.1016/j.anai.2018.08.001. PMID 30102965.
- ↑ "Toreforant, A Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonist, in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Methotrexate Therapy: Results of 2 Phase II Studies". The Journal of Rheumatology 43 (9): 1637–1642. September 2016. doi:10.3899/jrheum.160164. PMID 27422891.
- ↑ "Histamine H4 receptor: a novel target for inflammation therapy". Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 11 (2): 143–58. February 2011. doi:10.2174/138955711794519519. PMID 21222579.
- ↑ "Clinical Development of Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonists". Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Health and Disease. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. 241. 2017. pp. 301–320. doi:10.1007/164_2016_130. ISBN 978-3-319-58192-7.
- ↑ "The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets". Frontiers in Immunology 9: 1873. 2018. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01873. PMID 30150993.
 |
