Chemistry:Carbinoxamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Clistin, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a606008 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral: 4 mg tablet or 4 mg/5 mL liquid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 10 to 20 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
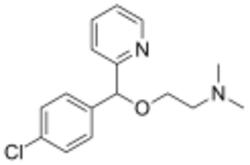
| Formula | C16H19ClN2O |
| Molar mass | 290.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Carbinoxamine is an antihistamine and anticholinergic agent. It is used for hay fever, vasomotor rhinitis, mild urticaria, angioedema, dermatographism and allergic conjunctivitis. Carbinoxamine is a histamine antagonist, specifically an H1-antagonist. The maleic acid salt of the levorotatory isomer is sold as the prescription drug rotoxamine.
It was patented in 1947 and came into medical use in 1953.[1] It was first launched in the United States by the McNeil Corporation under the brand name Clistin. Carbinoxamine is available in various countries around the world by itself, combined with decongestants such as pseudoephedrine, and also with other ingredients including paracetamol, aspirin, and codeine.
Society and culture
In June 2006 the FDA announced that more than 120 branded pharmacy products containing carbinoxamine were being illegally marketed and demanded they be removed from the marketplace. This action was precipitated by twenty-one reported deaths in children under the age of two who had been administered carbinoxamine-containing products. Despite the fact that the drug had not been studied in this age group, a multitude of OTC preparations containing carbinoxamine were being marketed for infants and toddlers. At present, all carbinoxamine-containing formulations are approved only for adults or children ages 3 or older.[2]
Brand names
Brand names include Clistin, Palgic, Rondec, Rhinopront, Ryvent.
Side effects
Continuous and/or cumulative use of anticholinergic medication, including first-generation antihistamines, is associated with a higher risk of cognitive decline and dementia in older people.[3][4]
See also
- Carbinoxamine/pseudoephedrine
- Tofenacin
- Clemastine
- Captodiamine
References
- ↑ (in en) Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 545. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA545.
- ↑ "Questions and Answers about Unapproved Drugs and FDA's Enforcement Action Against Carbinoxamine Products". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/enforcementactivitiesbyfda/selectedenforcementactionsonunapproveddrugs/ucm119635.pdf.
- ↑ "Cumulative use of strong anticholinergics and incident dementia: a prospective cohort study". JAMA Internal Medicine 175 (3): 401–407. March 2015. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.7663. PMID 25621434.
- ↑ "Drugs with anticholinergic properties, cognitive decline, and dementia in an elderly general population: the 3-city study". Archives of Internal Medicine 169 (14): 1317–1324. July 2009. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2009.229. PMID 19636034.
 |
