Chemistry:Amthamine
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
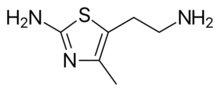
| IUPAC name
5-(2-Aminoethyl)-4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-amine
| |
| Other names
5-(2-Aminoethyl)-4-methyl-2-thiazolamine
2-Amino-5-(2-aminoethyl)-4-methylthiazole | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11N3S | |
| Molar mass | 157.236 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Amthamine is a histamine agonist selective for the H2 subtype.[1] It has been used in vitro and in vivo to study gastric secretion,[2] as well as other functions of the H2 receptor.[3][4][5]
References
- ↑ Eriks, J. C; Van Der Goot, H; Sterk, G. J; Timmerman, H (1992). "Histamine H2-receptor agonists. Synthesis, in vitro pharmacology, and qualitative structure-activity relationships of substituted 4- and 5-(2-aminoethyl)thiazoles". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 35 (17): 3239–46. doi:10.1021/jm00095a021. PMID 1507209.
- ↑ "The new potent and selective histamine H2 receptor agonist amthamine as a tool to study gastric secretion". Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 348 (1): 77–81. July 1993. doi:10.1007/BF00168540. PMID 8377843.
- ↑ Ezeamuzie, C. I; Philips, E (2000). "Histamine H(2) receptors mediate the inhibitory effect of histamine on human eosinophil degranulation". British Journal of Pharmacology 131 (3): 482–8. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703556. PMID 11015298.
- ↑ Fernandez, N; Monczor, F; Baldi, A; Davio, C; Shayo, C (2008). "Histamine H2 receptor trafficking: Role of arrestin, dynamin, and clathrin in histamine H2 receptor internalization". Molecular Pharmacology 74 (4): 1109–18. doi:10.1124/mol.108.045336. PMID 18617631.
- ↑ Threlfell, S; Exley, R; Cragg, S. J; Greenfield, S. A (2008). "Constitutive histamine H2 receptor activity regulates serotonin release in the substantia nigra". Journal of Neurochemistry 107 (3): 745–55. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05646.x. PMID 18761715.
 |

