Chemistry:Dicyclohexyl phosphorofluoridate
From HandWiki
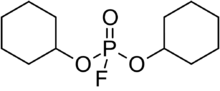
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
DCFP
Dicyclohexyl fluorophosphate TL-941 T-1840 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22FO3P | |
| Molar mass | 264.277 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Boiling point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Extremely toxic |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
110 mg/m3 (inhalation, mice, 10 minutes) 110 mg/m3 (inhalation, rabbits, 10 minutes) 110 mg/m3 (inhalation, rats, 10 minutes) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dicyclohexyl phosphorofluoridate (DCFP),[1] also known as TL-941 or T-1840,[2] is an extremely toxic organophosphorus compound with powerful anticholinesterase action. It's a colorless liquid that is extremely resistant to hydrolysis.[3] DCFP can be produced by reaction of cyclohexanol with phosphoryl dichloride fluoride.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ BERRY, WK (October 1951). "The turnover number of cholinesterase.". Biochemical Journal 49 (5): 615–20. doi:10.1042/bj0490615. PMID 14886354.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Chemical Warfare Agents, and Related Chemical Problems. Parts I-II.. 1958. https://ntrl.ntis.gov/NTRL/dashboard/searchResults/titleDetail/PB158508.xhtml.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Some Aspects Of The Chemistry And Toxic Action Of Organic Compounds Containing Phosphorus And Fluorine. 1957. https://archive.org/details/B-001-026-884-ALL.
 |

