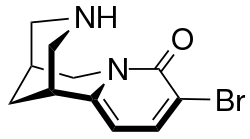
Chemistry:3-Bromocytisine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13BrN2O |
| Molar mass | 269.142 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
3-Bromocytisine is a derivative of the toxic alkaloid cytisine that acts as a highly potent agonist at neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, binding primarily to the α4β2 and α7 subtypes. 3-Bromocytisine is a full agonist at the α7 subtype while it is only a partial agonist at α4β2, but has an extremely strong binding affinity at α4β2 with 200-fold selectivity for α4β2 over α7. In animal studies 3-bromocytisine stimulates the release of dopamine and noradrenaline and increases locomotor activity.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ↑ "Syntheses and evaluation of halogenated cytisine derivatives and of bioisosteric thiocytisine as potent and selective nAChR ligands". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 36 (4): 375–88. April 2001. doi:10.1016/S0223-5234(01)01222-3. PMID 11461763.
- ↑ "Activity of cytisine and its brominated isosteres on recombinant human alpha7, alpha4beta2 and alpha4beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors". Journal of Neurochemistry 78 (5): 1029–43. September 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00481.x. PMID 11553677.
- ↑ "C3-halogenation of cytisine generates potent and efficacious nicotinic receptor agonists". European Journal of Pharmacology 536 (1–2): 1–11. April 2006. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.02.012. PMID 16563372.
- ↑ "Increase in locomotor activity after acute administration of the nicotinic receptor agonist 3-bromocytisine in rats". European Journal of Pharmacology 634 (1–3): 89–94. May 2010. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.02.030. PMID 20184877.
 |

