Chemistry:Sodium hexafluoroaluminate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sodium fluoroaluminate
Cryolite Kryolite Aluminate(3-), hexafluoro-, trisodium, (OC-6-11)- | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Na3AlF6 | |
| Molar mass | 209.94 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 2.9 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 950 °C (1,740 °F; 1,220 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| 0.04% (20°C)[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | essentially 0 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LDLo (lowest published)
|
600 mg/kg (guinea pigs, oral)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 2.5 mg/m3[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 2.5 mg/m3[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
250 mg/m3 (as F)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
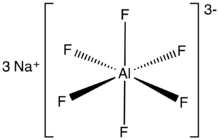
Sodium hexafluoroaluminate is an inorganic compound with formula Na3AlF6. This white solid, discovered in 1799 by Peder Christian Abildgaard (1740–1801),[4][5] occurs naturally as the mineral cryolite and is used extensively in the industrial production of aluminium metal. The compound is the sodium (Na+) salt of the hexafluoroaluminate (AlF63−) ion.
Production
Most cryolite is manufactured by a variety of related pathways. One route entails combining sodium aluminate and hydrofluoric acid:[2]
- Na3Al(OH)6 + 6 HF → Na3AlF6 + 6 H2O
Other routes include:[6]
- 6 HF + 3 NaAlO
2 → Na
3AlF
6 + Al
2O
3 + 3 H
2O - 4 AlF
3 + 3 Na
2O → 2 Na
3AlF
6 + Al
2O
3
Often the hexafluoroaluminic acid, which is recovered from phosphate mining, is the precursor in a two-step process beginning with neutralization with ammonia to give ammonium hexafluoroaluminate:
- H3AlF6 + 3 NH3 → (NH4)3AlF6
- (NH4)3AlF6 + 3 NaOH → Na3AlF6 + 3 NH3 + 3 H2O
The mineral form of sodium hexafluoroaluminate, which is called cryolite, was mined at Ivigtût on the west coast of Greenland until the deposit was depleted in 1987.
Use
The dominant application of synthetic cryolite is as a solvent (or flux) for electrolysis of aluminium oxides such as bauxite. The conversion of aluminium oxides into metallic aluminium requires that the metal ions be dissolved so that they can accept the electrons provided in the electrolysis cell. A mixture of cryolite and some aluminium trifluoride is used as that solvent. Unlike typical solutions, this one requires temperatures approaching 1000 °C to melt. Other uses include a whitener for enamels and an opacifier for glass.[2]
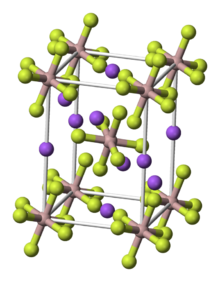
Structure
It adopts a perovskite-like structure. The AlF3−
6 centers are nearly idealized octahedra. Na+ occupy both six- and distorted 8-coordinate sites.[7]
Safety
The -1">50 is 600 mg/kg for the comparable compound aluminium trifluoride.[2] Cryolite is poorly soluble in water.
Related compounds
- Chiolite ( Na
5Al
3F
14), another sodium fluoroaluminate.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0559". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0559.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Aigueperse, Jean; Mollard, Paul; Devilliers, Didier; Chemla, Marius; Faron, Robert; Romano, René; Cuer, Jean Pierre (2000). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_307.
- ↑ GHS: GESTIS 001900
- ↑ (Staff) (1799). "Norwegische Titanerze und andre neue Fossilien" (in German). Allgemeine Journal der Chemie 2: 502. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015066692560&view=1up&seq=520. "Zugleich theilte er … wie gefrorne Salzlauge schmilzt." (At the same time he also communicated a report on an especially white, spar-like mineral [that had been] brought a few years ago from Greenland to Denmark. According to one of the investigations undertaken regarding it, it consisted of alumina and hydrofluoric acid. A compound of which no similar example has yet occurred in the mineral realm. It has received the name "cryolite" because it melts like frozen brine before the [flame of a] blowpipe.)
- ↑ Abildgaard, P. C. (1800). "Om Norske Titanertser og om en nye Steenart fra Grönland, som bestaaer af Flusspatsyre og Alunjord" (in Danish). Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabers-Selskabs (The Royal Danish Scientific Society). 3rd series 1: 305–316. http://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=umn.31951d00004536u;view=1up;seq=333. "[From p. 312] Han har kaldt denne grönlandske Steen Kryolith eller Iissteen formedelst dens Udseende, og fordi den smelter saa meget let for Blæsröret.". (He has named this Greenlandic stone cryolite or ice stone on account of its appearance, and because it melts so easily under a blowpipe.)
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 209. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ F. C. Hawthorne; R. B. Ferguson (1975). "Refinement of the crystal structure of cryolite". The Canadian Mineralogist 13: 377–382.
External links
 |

