Chemistry:Gestonorone caproate
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Depostat, Primostat |
| Other names | Gestronol hexanoate; Norhydroxyprogesterone caproate; SH-582; SH-80582; NSC-84054; 17α-Hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione hexanoate; 17α-Hydroxy-19-norprogesterone hexanoate |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection[1][2][3] |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestin; Progestogen ester; Antigonadotropin |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: Low[4] IM: High[5] |
| Metabolism | Reduction (at the C5, C3, and C20 positions)[6] |
| Metabolites | • 19-Norpregnanetriol[6] • 19-Norpregnanediol-20-one[6] |
| Elimination half-life | IM: 7.5 ± 3.1 days[5] |
| Duration of action | IM: ≥21 days[5] |
| Excretion | Urine: 28%[5] Feces: 72%[5] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H38O4 |
| Molar mass | 414.586 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Gestonorone caproate, also known as gestronol hexanoate or norhydroxyprogesterone caproate and sold under the brand names Depostat and Primostat, is a progestin medication which is used in the treatment of enlarged prostate and cancer of the endometrium.[5][3][7][1][8] It is given by injection into muscle typically once a week.[4]
Side effects of gestonorone caproate include worsened glucose tolerance, decreased libido in men, and injection site reactions.[5] Gestonorone caproate is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone.[9][10] It has no other important hormonal activity.[5][11][12][13]
Gestonorone caproate was discovered in 1960 and was introduced for medical use by 1973.[14][15] It has been used widely throughout Europe, including in the United Kingdom , and has also been marketed in certain other countries such as Japan , China , and Mexico.[1][16][17][18] However, it has since mostly been discontinued, and it remains available today only in a handful of countries, including the Czech Republic, Japan, Mexico, and Russia .[18][19]
Medical uses
Gestonorone caproate is used in the palliative treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy and endometrial cancer.[5][3][20] It is used at a dose of 100 to 200 mg once a week by intramuscular injection.[5]
Side effects
Side effects of gestonorone caproate have been reported to include worsened glucose tolerance, decreased libido in men, and local injection site reactions such as irritation.[5]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Gestonorone caproate is a potent, long-acting, and pure progestogen,[9][10][13] possessing no androgenic, anabolic, antiandrogenic, estrogenic, antiestrogenic, glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid, or teratogenic effects.[5][11][12][13][21] It is approximately 20 to 25 times more potent than progesterone or hydroxyprogesterone caproate in animal bioassays when all are given by subcutaneous injection.[5][13][22] In humans, 100 or 200 mg intramuscular gestonorone caproate has been said to be equivalent to 1,000 mg intramuscular hydroxyprogesterone caproate.[23][24] Hence, gestonorone caproate is approximately 5- to 10-fold more potent than hydroxyprogesterone caproate in humans.[11][23][24] The biological effects of gestonorone caproate in women have been studied.[25][26]
Like other potent progestins, gestonorone caproate possesses potent antigonadotropic activity and is capable of markedly suppressing the gonadal production and circulating levels of sex hormones such as testosterone and estradiol.[13][27][28] A clinical study found that 400 mg/week intramuscular gestonorone caproate suppressed testosterone levels by 75% in men, while orchiectomy as a comparator reduced testosterone levels by 91%.[29][30] Levels of luteinizing hormone, conversely, remained unchanged.[29] In general, progestogens can maximally suppress testosterone levels by about 70 to 80%.[31][32][33][29][30] In accordance with its lack of glucocorticoid activity, gestonorone caproate has no anticorticotropic effects, and does not influence the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone.[5]
17α-Hydroxyprogesterone has weak progestogenic activity, but C17α esterification results in higher progestogenic activity.[6] Of a variety of different esters, the caproate (hexanoate) ester was found to have the strongest progestogenic activity, and this formed the basis for the development of gestonorone caproate, as well as other caproate progestogen esters such as hydroxyprogesterone caproate.[6]
Gestonorone caproate has been found to decrease the weights of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles by 40 to 70% in adult male rats.[5] It has been shown in canines to mediate these effects both via its antigonadotropic effects and by direct actions in these tissues.[5] Gestonorone caproate decreases the uptake of testosterone into the prostate gland.[5] It has also been found to have direct antiproliferative effects on human ovarian cancer cells in vitro.[5]
Gestonorone caproate has been reported to act to some extent as a 5α-reductase inhibitor, similarly to progesterone.[34][35]
Pharmacokinetics
Like the closely related progestins hydroxyprogesterone caproate and 19-norprogesterone, gestonorone caproate shows poor activity orally and must be administered parenterally; specifically, via intramuscular injection.[4] Gestonorone caproate is administered by intramuscular injection, and acts as a long-lasting depot by this route.[5][36][37][38] After an intramuscular injection, gestonorone caproate is completely released from the local depot and is highly bioavailable.[5] A single intramuscular injection of 25 to 50 mg gestonorone caproate in oil solution has been found to have a duration of action of 8 to 13 days in terms of clinical biological effect in the uterus in women.[26][39][40] At high doses, the duration of action of gestonorone caproate by intramuscular injection has been found to be at least 21 days.[5] Clinical studies have found gestonorone caproate to be satisfactorily effective as a progestogen when injected once a month, whereas it was poorly effective as an injectable contraceptive when it was injected once every two months.[41][42]
Following a single intramuscular injection of 200 mg radiolabeled gestonorone caproate in 1 mL of solution in men with prostate cancer, maximal levels of gestonorone caproate occurred after 3 ± 1 days and were 420 ± 160 ng/mL.[5] The elimination half-life of gestonorone caproate and its metabolites was 7.5 ± 3.1 days.[5] Approximately 5% of the radioactive steroid content in the blood was unchanged gestonorone caproate.[5] No free gestonorone was observed in circulation or in urine.[5] Gestonorone caproate and its metabolites were eliminated 72% in feces and 28% in urine.[5][43] Approximately 48 ± 18% of the injected dose had been eliminated after 14 days and approximately 85 ± 12% of the injected dose had been excreted after 30 days.[5]
The metabolism of unesterified gestonorone (17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone) is analogous to that of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, with the corresponding 19-norpregnane metabolites produced.[6] Gestonorone caproate has been found to undergo 5α-reduction similarly to progesterone, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, and gestonorone, and at a similar rate as these steroids.[6] Conversely however, due to its caproate ester, 5β-reduction of gestonorone caproate is decreased relative to these steroids.[6] As progesterone is metabolized mainly into 5β-pregnanes, decreased 5β-reduction of gestonorone caproate may be involved in its greater potency compared to progesterone.[6] The major metabolites of gestonorone caproate have been reported to be isomers of 19-norpregnanetriol and 19-norpregnanediol-20-one.[6][21] These metabolites indicate that gestonorone caproate is metabolized mainly by reduction at the C3, C5, and C20 positions.[6] Following an intramuscular injection of 300 mg gestonorone caproate, only a slight increase in urinary pregnanetriol excretion has been observed.[6] Cleavage of the caproate ester of gestonorone caproate is minimal, which indicates that it is not a prodrug of the unesterified steroid.[6]
Chemistry
Gestonorone caproate, also known as norhydroxyprogesterone caproate, 17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 17α-hexanoate, or 17α-hydroxy-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione 17α-hexanoate, is a synthetic norpregnane steroid and a derivative of progesterone.[44][16] It is specifically a combined derivative of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 19-norprogesterone, or of gestronol (17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone), with a hexanoate (caproate) ester at the C17α position.[44][16] Analogues and derivatives of gestonorone caproate include algestone acetophenide (dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide), demegestone, nomegestrol acetate, norgestomet, and segesterone acetate, as well as 18-methylsegesterone acetate and the caproate esters chlormadinone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone caproate, megestrol caproate, and methenmadinone caproate.[44][16]
Synthesis
Chemical syntheses of gestonorone caproate have been published.[5][7][45]
History
Gestonorone caproate was first described in 1960.[14] It was developed by Schering and has been marketed since at least 1968.[12][15]
Society and culture
Generic names
Gestonorone caproate is the generic name of the drug and its INN, USAN, and JAN, while gestronol hexanoate is its BANM.[44][16] It has also been referred to as norhydroxyprogesterone caproate, and is also known by its former developmental code names SH-582 and SH-80582.[44][16][17]
Brand names
Gestonorone caproate has been marketed exclusively under the brand names Depostat and Primostat.[44][16][17][18][19]
Availability
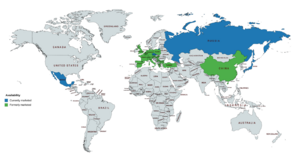
Gestonorone caproate has been available widely in Europe, including in the United Kingdom , and has also been marketed in Japan , China , Mexico, and certain other countries.[1][16][17][18] However, it has been discontinued in most countries and its availability is more limited today; it appears to remain marketed only in the Czech Republic, Japan, Mexico, and Russia .[18][19][46] It has not been marketed in the United States , Canada , and many other countries.[16][17][18][19]
Research
Gestonorone caproate was studied in the treatment of prostate cancer in men at a dosage of 400 mg per week by intramuscular injection but, in contrast to the case of benign prostatic hyperplasia, was found to be ineffective.[47][48]
SH-834 was a combination of 90 mg estradiol valerate and 300 mg gestonorone caproate for weekly intramuscular injection that was developed by Schering in the 1960s and 1970s.[49][22][50] It was investigated clinically as a treatment for breast cancer and was found to be effective.[49][51][50] However, its effectiveness was found to be no better than that of an estrogen alone, and the combination was ultimately never marketed.[52]
Gestonorone caproate was studied by Schering for use as a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive across a dose range of 2.5 to 200 mg once every one or two months but was never marketed.[42][53][54][55][56][57][58][59] There is very little clinical experience of gestonorone caproate for this indication.[42]
Gestonorone caproate has been studied in the treatment of ovarian cancer (in combination with cyclophosphamide),[5][22][60][61] menstrual cycle-related mouth ulcers,[21] and as a component of menopausal hormone therapy.[41]
See also
- Estradiol valerate/gestonorone caproate
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Muller (19 June 1998). European Drug Index: European Drug Registrations (Fourth ed.). CRC Press. pp. 338–. ISBN 978-3-7692-2114-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=HiSdvzs2pPAC&pg=PA338.
- ↑ Meyler's Side Effects of Endocrine and Metabolic Drugs. Elsevier. 21 February 2009. pp. 289–. ISBN 978-0-08-093292-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=BWMeSwVwfTkC&pg=PA289.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 132–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=tsjrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA132.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "[Studies on the metabolism of 17-alpha-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone caproate by humans in vivo and of 17-alpha-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone by rats in vitro]" (in de). Acta Endocrinologica 51 (1): 114–130. January 1966. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0510114. PMID 4285463.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 5.19 5.20 5.21 5.22 5.23 5.24 5.25 5.26 5.27 5.28 Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis: Band 8: Stoffe E-O. Springer-Verlag. 2 July 2013. pp. 343–. ISBN 978-3-642-57994-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=8vSjBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA343.
- ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 Die Gestagene. Springer-Verlag. 27 November 2013. pp. 6,278–279. ISBN 978-3-642-99941-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=t8GpBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA6.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1761–1762. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=_J2ti4EkYpkC&pg=PA1761.
- ↑ Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs. CRC Press. 22 November 2006. pp. 154–155. ISBN 978-1-4200-0890-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=5uB19xhhyDsC&pg=PA154.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Hormones and Embryonic Development: Advances in The Biosciences. Elsevier Science. 22 October 2013. pp. 79. ISBN 978-1-4831-5171-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=Xp3pAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA79.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "The effect of depostat (SH 582) on the baboon prostate". Journal of Surgical Oncology 1 (4): 317–324. 1969. doi:10.1002/jso.2930010404. PMID 5000209.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 "Genital Cycle". Ovarian Function and its Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapy. Developments in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Springer Science & Business Media. 1981. pp. 70–129. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-8195-9_11. ISBN 978-94-009-8195-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=7IrpCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA313. "Gestonorone caproate is a depot gestagen, five times more potent than 17α-hydroxyprogesterone caproate."
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Schering, A. G. (1968). Depostat (SH 582): A New Treatment for Prostatic Hypertrophy. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=13658296147916476056
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 "The effect of 17-alpha-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone caproate (SH582) on benign prostatic hypertrophy". The British Journal of Surgery 58 (9): 648–652. September 1971. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800580904. PMID 4105896.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Klinische Erfahrungen mit Norprogesteronderivaten". ZBL. Gynäk 82: 2009. 1960.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "The treatment of benign enlargement of the prostate with nor progesterone caproate (primostat)". The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Surgery 42 (3): 304–307. February 1973. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.1973.tb06805.x. PMID 4129814.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 16.6 16.7 16.8 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. p. 278. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA278.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 "List of Progestins". https://www.drugs.com/international/gestonorone-caproate.html.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 "Micromedex Products: Please Login". http://www.micromedexsolutions.com/micromedex2/librarian/.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 "Sex hormones and their modulators". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. 2009. p. 2105. ISBN 978-0-85369-840-1. https://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/martindale/2009/9055-s.htm.
- ↑ Smith and Williams' Introduction to the Principles of Drug Design and Action, Fourth Edition. CRC Press. 10 October 2005. pp. 493–. ISBN 978-0-203-30415-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=P2W6B9FQRKsC&pg=PA493.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 "Progeston therapy for menstrually related aphthae". International Journal of Oral Surgery 7 (5): 463–470. October 1978. doi:10.1016/S0300-9785(78)80038-6. PMID 102602.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 "Progestogen therapy for ovarian carcinoma". The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of the British Commonwealth 79 (6): 555–559. June 1972. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.1972.tb14200.x. PMID 4555897.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Progesterone treatment for local recurrence and metastases in carcinoma corporis uteri". Acta Radiologica 10 (2): 187–192. April 1971. doi:10.3109/02841867109129755. PMID 5556820. "The preparations used were Proluton Depot (17a-hydroxy-progesterone caproate) and in 3 patients SH 5132 (17a-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone caproate); 100 mg of the latter corresponds to 1000 mg of Proluton Depot.".
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Short-term progestogen treatment of endometrial carcinoma. Histological, histochemical and hormonal studies". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 51 (1): 55–62. 1972. doi:10.3109/00016347209154968. PMID 4261828. "Thirteen patients with primary adenocarcinoma of the uterine corpus were treated for 21 days with 17alpha-hydroxy-progesterone-caproate (Primolut Depot®, Schering), 1000 mg daily, or 17alpha-hydroxy-19-nor-progesterone-caproate (Depostat®, Schering), 200 mg daily. These doses can be considered as equivalent.".
- ↑ "[Clinical observations on the effect of depot gestagen 17 alpha-hydroxy-19-nor-progesterone caproate in women with eumenorrhea]". Klinische Wochenschrift 47 (3): 162–165. February 1969. doi:10.1007/BF01746052. PMID 5369019.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Effects, Duration of Action and Metabolism in Man". Pharmacology of the Endocrine System and Related Drugs: Progesterone, Progestational Drugs and Antifertility Agents. II. Pergamon Press. September 1972. pp. 13–24. ISBN 978-0080168128. OCLC 278011135. https://books.google.com/books?id=Nv5sAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ International Symposium on the Treatment of Carcinoma of the Prostate, Berlin, November 13 to 15, 1969: Life Science Monographs. Elsevier. 22 October 2013. pp. 169. ISBN 978-1-4831-8711-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=8RjLBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA169.
- ↑ "Evaluation of Depostat in prostatic adenoma on the ground of clinical and sphincterotonometric studies". International Urology and Nephrology 3 (1): 21–29. 1971. doi:10.1007/BF02081794. PMID 4117491.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 "On gestagen treatment of advanced prostatic carcinoma". Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 12 (2): 119–121. 1978. doi:10.3109/00365597809179977. PMID 694436.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "Effects of norgestrel and ethinyloestradiol ingestion on serum levels of sex hormones and gonadotrophins in men". Clinical Endocrinology 11 (5): 497–504. November 1979. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.1979.tb03102.x. PMID 519881. "Another synthetic gestogen, 17-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone caproate (Depostat-Schering), 400 mg by i.m. weekly injections suppressed T levels to 25% of pretreatment values (Sander er al., 1978).".
- ↑ Campbell-Walsh Urology: Expert Consult Premium Edition: Enhanced Online Features and Print, 4-Volume Set. Elsevier Health Sciences. 25 August 2011. pp. 2938–. ISBN 978-1-4160-6911-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=fu3BBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA2938.
- ↑ "Effect of flutamide or cyproterone acetate on pituitary and testicular hormones in normal men". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 59 (5): 963–969. November 1984. doi:10.1210/jcem-59-5-963. PMID 6237116.
- ↑ "Treatment of advanced prostatic cancer with parenteral cyproterone acetate: a phase III randomised trial". British Journal of Urology 52 (3): 208–215. June 1980. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410x.1980.tb02961.x. PMID 7000222.
- ↑ "Testosterone metabolism in benign prostatic hypertrophy: in vivo studies of gestonorone caproate and cyproterone acetate". British Journal of Urology 48 (6): 485–491. December 1976. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.1976.tb06687.x. PMID 64267.
- ↑ "Mode of action of progesterone, gestonorone capronate (Depostat) and cyproterone acetate (Androcur) on the metabolism of testosterone in human prostatic adenoma: in vitro and in vivo investigations". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 6 (6): 845–851. June 1975. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(75)90313-1. PMID 1177428.
- ↑ The Medical Management of Prostate Cancer. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 112–. ISBN 978-3-642-73238-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=T78hBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT112. "Gestonorone caproate, another progestational agent, was investigated at our institution. Eighteen patients with painful metastatic [prostate cancer] with objective relapse after orchiectomy were treated with 400 mg/week i.m."
- ↑ Future Aspects in Contraception: Proceeding of an International Symposium held in Heidelberg, 5–8 September 1984 Part 1 Male Contraception. Springer Science & Business Media. 6 December 2012. pp. 133–. ISBN 978-94-009-4910-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=GX2oBgAAQBAJ&pg=PA133. "Gestonorone [caproate] 100 or 200 mg/week i.m."
- ↑ "Conservative treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia". Current Medical Research and Opinion 4 (7): 513–520. 2008. doi:10.1185/03007997709109342. PMID 66118. "A study was carried out in 30 male patients with benign prostate hyperplasia to assess the effectiveness of treatment with a progestational agent, gestonorone caproate (200 mg), given intramuscularly every 7 days over a period of 2 to 3 months.".
- ↑ "Die gestagene Wirkung von Hydroxy-nor-Progesteronestern bei der Frau". Gewebs- und Neurohormone. Symposion der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Endokrinologie. Springer. 1962. pp. 248–255. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-86860-3_27. ISBN 978-3-540-02909-0. "Das Hydroxy-nor-Progesteron-Capronat stand in öliger Lösung zm intramuskulären Injektion zur Verfügung. Die Wirkungsdauer betrug 10-13 Tage. Nach Verabreichung von 25 mg waren als beginnende Sekretionszeichen (1) an den geschlängelten Drüsen basale Vacuolen der Epithelien zu sehen. Eine volle Umwandlung der Schleimhaut erfolgte erst auf 50 mg des Capronsäureesters (Abb. l und 2)."
- ↑ "Hormonal Treatment of Disorders of the Menstrual Cycle". Ovarian Function and its Disorders: Diagnosis and Therapy. Developments in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Springer Science & Business Media. 1981. pp. 309–332. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-8195-9_11. ISBN 978-94-009-8195-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=7IrpCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA313.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "Comparative effects of oestrogen and a progestogen on bone loss in postmenopausal women". Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 54 (2): 193–195. February 1978. doi:10.1042/cs0540193. PMID 340117.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 42.2 "The clinical use of monthly injectable contraceptive preparations". Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey 32 (6): 335–347. June 1977. doi:10.1097/00006254-197706000-00001. PMID 865726.
- ↑ "Verteilungsstudien und pharmakokinetische Parameter nach i.m. Gabe von Gestonoron-capronat (Depostat) und Cyproteron-acetat (Androcur) beim Menschen". 24. Tagung vom 13. Bis 16. September 1972 in Hannover. Verhandlungsbericht der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Urologie. 24. 1973. pp. 133–138. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-80738-1_36. ISBN 978-3-540-06186-1.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 44.2 44.3 44.4 44.5 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 595–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA595.
- ↑ Pharmaceutical substances: syntheses, patents, applications. Thieme. 2001. p. 962. ISBN 978-3-13-558404-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=y25qAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ "Find product information about medicines". http://www.mhra.gov.uk/spc-pil/.
- ↑ Cancer of the Prostate and Kidney. Springer Science & Business Media. 29 June 2013. pp. 309–. ISBN 978-1-4684-4349-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=gtAFCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA309.
- ↑ "On gestagen treatment of advanced prostatic carcinoma". Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 12 (2): 119–121. 1977. doi:10.3109/00365597809179977. PMID 694436.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 "Hormonal treatment of mammary carcinoma with Progynon-Depot and Depostat". Acta Radiologica 14 (5): 433–442. October 1975. doi:10.3109/02841867509132684. PMID 1202923.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 "[Effect of estrogen-gestagen combination therapy in advanced breast carcinoma with special reference to pulmonary metastases"] (in de). Strahlentherapie 141 (5): 540–548. May 1971. PMID 5088730. https://www.popline.org/node/485956. Retrieved 2019-05-20.
- ↑ "[The combined estrogen-gestagen treatment of metastasizing mammary carcinoma using with SH 834]". Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 95 (48): 2399+. November 1970. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1108843. PMID 5529652.
- ↑ "[Additive treatment of metastasizing breast cancer with special reference to postmenopausal age (results of a randomized study)]" (in de). Strahlentherapie 152 (3): 235–247. September 1976. PMID 968923.
- ↑ "Monthly Injectable Contraceptives". Long-Acting Contraception. 1983. pp. 93–103. OCLC 35018604. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?cluster=14664537528797672080.
- ↑ Principles of Medicinal Chemistry Volume 2. Pragati Books Pvt. Ltd.. July 2007. pp. 381–. ISBN 978-81-85790-03-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=Z7Pb3lJuRksC&pg=PA381.
- ↑ "Injectable steroids as a method of contraception". Ain Shams Medical Journal 21 (5): 543–550. September 1970. PMID 12313080. https://www.popline.org/node/520035.
- ↑ "Effect of norhydroxyprogesterone caproate on cervical sperm penetration and secretion of ovarian steroids in the human female". Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences 78 (3): 189–190. July 1973. doi:10.3109/03009737309178626. PMID 4797435.
- ↑ "Empleo del capronato de 17-hidroxi-19-norprogesterona como anticonceptivo inyectable de depósito". Revista Peruana de Ginecología y Obstetricia 14 (2): 223–233. 2015. doi:10.31403/rpgo.v14i1457. http://spog.org.pe/web/revista/index.php/RPGO/article/view/1457.
- ↑ "[Possible biological effects of contraceptives"] (in es). Revista Médica de Chile 101 (3): 234–236. March 1973. PMID 4732140. https://www.popline.org/node/490180.
- ↑ "17-alpha-hydroxy 19 norprogesterone capronate as a prolonged-action injectable contraceptive agent.". Revista Colombiana de Obstetricia y Ginecologia 20: 247–255. 1969. https://www.popline.org/node/479231.
- ↑ "The treatment of advanced cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary with gestronol and continuous oral cyclophosphamide". British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 86 (7): 497–500. July 1979. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb10799.x. PMID 476014.
- ↑ "The effect of sex steroids on the in vitro synthesis of DNA by malignant ovarian tumours". British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 85 (8): 627–633. August 1978. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.1978.tb14933.x. PMID 687544.
{{Navbox
| name = Drugs used in benign prostatic hypertrophy | title = Drugs used in [[Medicine:Benign prostatic hyperpbenign prostatic hyperplasia (G04C) | state = collapsed | listclass = hlist
| group1 = 5α-Reductase inhibitors | list1 =
| group2 = Alpha-1 blockers | list2 =
| group3 = Steroidal antiandrogens | list3 =
| group4 = Herbal products | list4 =
| group5 = Others | list5 =
}}
 |
