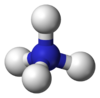
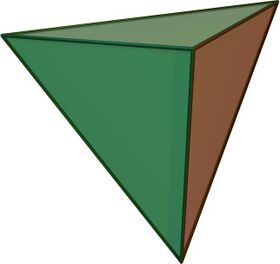
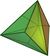
Tetrahedron
| Regular tetrahedron | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Platonic solid |
| Elements | F = 4, E = 6 V = 4 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 4{3} |
| Conway notation | T |
| Schläfli symbols | {3,3} |
| h{4,3}, s{2,4}, sr{2,2} | |
| Face configuration | V3.3.3 |
| Wythoff symbol | 3 | 2 3 | 2 2 2 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry | Td, A3, [3,3], (*332) |
| Rotation group | T, [3,3]+, (332) |
| References | U01, C15, W1 |
| Properties | regular, convexdeltahedron |
| Dihedral angle | 70.528779° = arccos(1⁄3) |
 3.3.3 (Vertex figure) |
 Self-dual (dual polyhedron) |
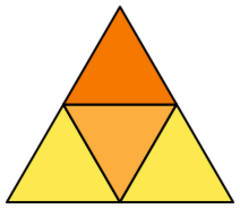 Net | |
File:Tetrahedron.stl In geometry, a tetrahedron (pl.: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra.[1]
The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex.
The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid".
Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets.[1]
For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere (the insphere) tangent to the tetrahedron's faces.[2]
Regular tetrahedron
A regular tetrahedron is a tetrahedron in which all four faces are equilateral triangles. It is one of the five regular Platonic solids, which have been known since antiquity.
In a regular tetrahedron, all faces are the same size and shape (congruent) and all edges are the same length.
Regular tetrahedra alone do not tessellate (fill space), but if alternated with regular octahedra in the ratio of two tetrahedra to one octahedron, they form the alternated cubic honeycomb, which is a tessellation. Some tetrahedra that are not regular, including the Schläfli orthoscheme and the Hill tetrahedron, can tessellate.
The regular tetrahedron is self-dual, which means that its dual is another regular tetrahedron. The compound figure comprising two such dual tetrahedra form a stellated octahedron or stella octangula.
Coordinates for a regular tetrahedron
The following Cartesian coordinates define the four vertices of a tetrahedron with edge length 2, centered at the origin, and two level edges:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \left(\pm 1, 0, -\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right) \quad \mbox{and} \quad \left(0, \pm 1, \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right) }[/math]
Expressed symmetrically as 4 points on the unit sphere, centroid at the origin, with lower face parallel to the [math]\displaystyle{ xy }[/math] plane, the vertices are:
[math]\displaystyle{ v_1 = \left(\sqrt{\frac{8}{9}},0,-\frac{1}{3}\right) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ v_2 = \left(-\sqrt{\frac{2}{9}},\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}},-\frac{1}{3}\right) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ v_3 = \left(-\sqrt{\frac{2}{9}},-\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}},-\frac{1}{3}\right) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ v_4 = (0,0,1) }[/math]
with the edge length of [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\frac{8}{3}} }[/math].
Still another set of coordinates are based on an alternated cube or demicube with edge length 2. This form has Coxeter diagram ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() and Schläfli symbol h{4,3}. The tetrahedron in this case has edge length 2√2. Inverting these coordinates generates the dual tetrahedron, and the pair together form the stellated octahedron, whose vertices are those of the original cube.
and Schläfli symbol h{4,3}. The tetrahedron in this case has edge length 2√2. Inverting these coordinates generates the dual tetrahedron, and the pair together form the stellated octahedron, whose vertices are those of the original cube.
- Tetrahedron: (1,1,1), (1,−1,−1), (−1,1,−1), (−1,−1,1)
- Dual tetrahedron: (−1,−1,−1), (−1,1,1), (1,−1,1), (1,1,−1)
Angles and distances
For a regular tetrahedron of edge length a:
| Face area | [math]\displaystyle{ A_0=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}a^2\, }[/math] |
| Surface area[3] | [math]\displaystyle{ A=4\,A_0={\sqrt{3}}a^2\, }[/math] |
| Height of pyramid[4] | [math]\displaystyle{ h=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}a=\sqrt{\frac23}\,a\, }[/math] |
| Centroid to vertex distance | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac34\,h = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{4}\,a = \sqrt{\frac{3}{8}}\,a\, }[/math] |
| Edge to opposite edge distance | [math]\displaystyle{ l=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\,a\, }[/math] |
| Volume[3] | [math]\displaystyle{ V=\frac13 A_0h =\frac{\sqrt{2}}{12}a^3=\frac{a^3}{6\sqrt{2}}\, }[/math] |
| Face-vertex-edge angle | [math]\displaystyle{ \arccos\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right) = \arctan\left(\sqrt{2}\right)\, }[/math] (approx. 54.7356°) |
| Face-edge-face angle, i.e., "dihedral angle"[3] | [math]\displaystyle{ \arccos\left(\frac13\right) = \arctan\left(2\sqrt{2}\right)\, }[/math] (approx. 70.5288°) |
| Vertex-Center-Vertex angle,[5] the angle between lines from the tetrahedron center to any two vertices. It is also the angle between Plateau borders at a vertex. In chemistry it is called the tetrahedral bond angle. This angle (in radians) is also the length of the circular arc on the unit sphere resulting from centrally projecting one edge of the tetrahedron to the sphere. | [math]\displaystyle{ \arccos\left(-\frac13\right ) = 2\arctan\left(\sqrt{2}\right)\, }[/math] (approx. 109.4712°) |
| Solid angle at a vertex subtended by a face | [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align}\arccos\left(\frac{23}{27}\right)&=\frac{\pi}{2}-3\arcsin \left(\frac{1}{3}\right)\\
&=3\arccos \left(\frac{1}{3}\right)-\pi\end{align}
}[/math] (approx. 0.55129 steradians) (approx. 1809.8 square degrees) |
| Radius of circumsphere[3] | [math]\displaystyle{ R=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{4}a=\sqrt{\frac38}\,a\, }[/math] |
| Radius of insphere that is tangent to faces[3] | [math]\displaystyle{ r=\frac13R=\frac{a}{\sqrt{24}}\, }[/math] |
| Radius of midsphere that is tangent to edges[3] | [math]\displaystyle{ r_\mathrm{M}=\sqrt{rR}=\frac{a}{\sqrt{8}}\, }[/math] |
| Radius of exspheres | [math]\displaystyle{ r_\mathrm{E}=\frac{a}{\sqrt{6}}\, }[/math] |
| Distance to exsphere center from the opposite vertex | [math]\displaystyle{ d_\mathrm{VE}=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{2}a={\sqrt{\frac32}}a\, }[/math] |
With respect to the base plane the slope of a face (2√2) is twice that of an edge (√2), corresponding to the fact that the horizontal distance covered from the base to the apex along an edge is twice that along the median of a face. In other words, if C is the centroid of the base, the distance from C to a vertex of the base is twice that from C to the midpoint of an edge of the base. This follows from the fact that the medians of a triangle intersect at its centroid, and this point divides each of them in two segments, one of which is twice as long as the other (see proof).
For a regular tetrahedron with side length a, radius R of its circumscribing sphere, and distances di from an arbitrary point in 3-space to its four vertices, we have[6]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align}\frac{d_1^4 + d_2^4 + d_3^4 + d_4^4}{4} + \frac{16R^4}{9}&= \left(\frac{d_1^2 + d_2^2 + d_3^2 + d_4^2}{4} + \frac{2R^2}{3}\right)^2;\\ 4\left(a^4 + d_1^4 + d_2^4 + d_3^4 + d_4^4\right) &= \left(a^2 + d_1^2 + d_2^2 + d_3^2 + d_4^2\right)^2.\end{align} }[/math]
Isometries of the regular tetrahedron
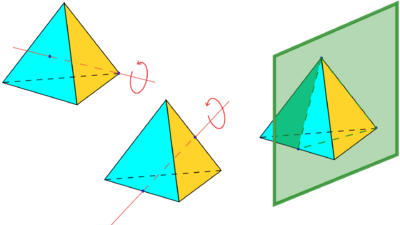
The vertices of a cube can be grouped into two groups of four, each forming a regular tetrahedron (see above, and also animation, showing one of the two tetrahedra in the cube). The symmetries of a regular tetrahedron correspond to half of those of a cube: those that map the tetrahedra to themselves, and not to each other.
The tetrahedron is the only Platonic solid that is not mapped to itself by point inversion.
The regular tetrahedron has 24 isometries, forming the symmetry group Td, [3,3], (*332), isomorphic to the symmetric group, S4. They can be categorized as follows:
- T, [3,3]+, (332) is isomorphic to alternating group, A4 (the identity and 11 proper rotations) with the following conjugacy classes (in parentheses are given the permutations of the vertices, or correspondingly, the faces, and the unit quaternion representation):
- identity (identity; 1)
- rotation about an axis through a vertex, perpendicular to the opposite plane, by an angle of ±120°: 4 axes, 2 per axis, together 8 ((1 2 3), etc.; 1 ± i ± j ± k/2)
- rotation by an angle of 180° such that an edge maps to the opposite edge: 3 ((1 2)(3 4), etc.; i, j, k)
- reflections in a plane perpendicular to an edge: 6
- reflections in a plane combined with 90° rotation about an axis perpendicular to the plane: 3 axes, 2 per axis, together 6; equivalently, they are 90° rotations combined with inversion (x is mapped to −x): the rotations correspond to those of the cube about face-to-face axes
Orthogonal projections of the regular tetrahedron
The regular tetrahedron has two special orthogonal projections, one centered on a vertex or equivalently on a face, and one centered on an edge. The first corresponds to the A2 Coxeter plane.
| Centered by | Face/vertex | Edge |
|---|---|---|
| Image | 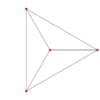
|
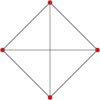
|
| Projective symmetry |
[3] | [4] |
Cross section of regular tetrahedron

The two skew perpendicular opposite edges of a regular tetrahedron define a set of parallel planes. When one of these planes intersects the tetrahedron the resulting cross section is a rectangle.[7] When the intersecting plane is near one of the edges the rectangle is long and skinny. When halfway between the two edges the intersection is a square. The aspect ratio of the rectangle reverses as you pass this halfway point. For the midpoint square intersection the resulting boundary line traverses every face of the tetrahedron similarly. If the tetrahedron is bisected on this plane, both halves become wedges.
This property also applies for tetragonal disphenoids when applied to the two special edge pairs.
Spherical tiling
The tetrahedron can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and projected onto the plane via a stereographic projection. This projection is conformal, preserving angles but not areas or lengths. Straight lines on the sphere are projected as circular arcs on the plane.
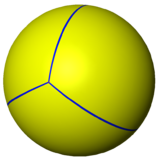
|
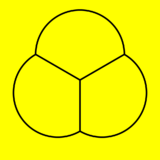
|
| Orthographic projection | Stereographic projection |
|---|
Helical stacking
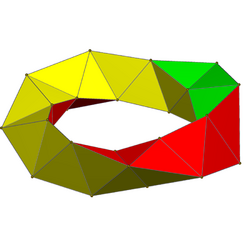
Regular tetrahedra can be stacked face-to-face in a chiral aperiodic chain called the Boerdijk–Coxeter helix.
In four dimensions, all the convex regular 4-polytopes with tetrahedral cells (the 5-cell, 16-cell and 600-cell) can be constructed as tilings of the 3-sphere by these chains, which become periodic in the three-dimensional space of the 4-polytope's boundary surface.
Irregular tetrahedra
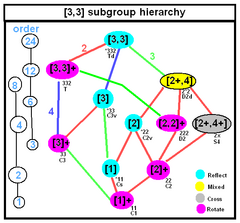 Tetrahedral symmetry subgroup relations |
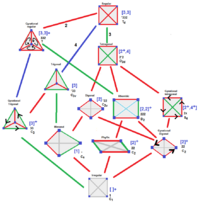 Tetrahedral symmetries shown in tetrahedral diagrams |
Tetrahedra which do not have four equilateral faces are categorized and named by the symmetries they do possess.
If all three pairs of opposite edges of a tetrahedron are perpendicular, then it is called an orthocentric tetrahedron. When only one pair of opposite edges are perpendicular, it is called a semi-orthocentric tetrahedron.
An isodynamic tetrahedron is one in which the cevians that join the vertices to the incenters of the opposite faces are concurrent.
An isogonic tetrahedron has concurrent cevians that join the vertices to the points of contact of the opposite faces with the inscribed sphere of the tetrahedron.
Trirectangular tetrahedron
In a trirectangular tetrahedron the three face angles at one vertex are right angles, as at the corner of a cube.
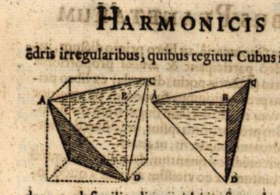
Kepler discovered the relationship between the cube, regular tetrahedron and trirectangular tetrahedron.[8]
Disphenoid

A disphenoid is a tetrahedron with four congruent triangles as faces; the triangles necessarily have all angles acute. The regular tetrahedron is a special case of a disphenoid. Other names for the same shape include bisphenoid, isosceles tetrahedron and equifacial tetrahedron.
Orthoschemes
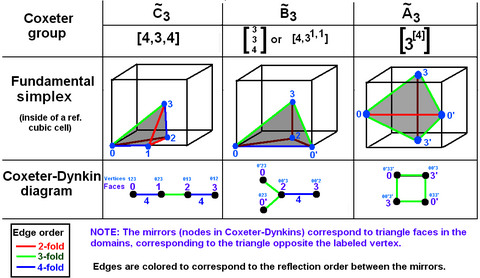
A 3-orthoscheme is a tetrahedron where all four faces are right triangles.[lower-alpha 1] An orthoscheme is an irregular simplex that is the convex hull of a tree in which all edges are mutually perpendicular. In a 3-dimensional orthoscheme, the tree consists of three perpendicular edges connecting all four vertices in a linear path that makes two right-angled turns. The 3-orthoscheme is a tetrahedron having two right angles at each of two vertices, so another name for it is birectangular tetrahedron. It is also called a quadrirectangular tetrahedron because it contains four right angles.[9]
Coxeter also calls quadrirectangular tetrahedra characteristic tetrahedra, because of their integral relationship to the regular polytopes and their symmetry groups.[10] For example, the special case of a 3-orthoscheme with equal-length perpendicular edges is characteristic of the cube, which means that the cube can be subdivided into instances of this orthoscheme. If its three perpendicular edges are of unit length, its remaining edges are two of length √2 and one of length √3, so all its edges are edges or diagonals of the cube. The cube ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() can be dissected into six such 3-orthoschemes
can be dissected into six such 3-orthoschemes ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() four different ways, with all six surrounding the same √3 cube diagonal. The cube can also be dissected into 48 smaller instances of this same characteristic 3-orthoscheme (just one way, by all of its symmetry planes at once).[lower-alpha 2] The characteristic tetrahedron of the cube is an example of a Heronian tetrahedron.
four different ways, with all six surrounding the same √3 cube diagonal. The cube can also be dissected into 48 smaller instances of this same characteristic 3-orthoscheme (just one way, by all of its symmetry planes at once).[lower-alpha 2] The characteristic tetrahedron of the cube is an example of a Heronian tetrahedron.
Every regular polytope, including the regular tetrahedron, has its characteristic orthoscheme.[lower-alpha 3] There is a 3-orthoscheme which is the characteristic tetrahedron of the regular tetrahedron. The regular tetrahedron ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is subdivided into 24 instances of its characteristic tetrahedron
is subdivided into 24 instances of its characteristic tetrahedron ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() by its planes of symmetry.[lower-alpha 4]
by its planes of symmetry.[lower-alpha 4]
| Characteristics of the regular tetrahedron[13] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| edge | arc | dihedral | |||
| 𝒍 | [math]\displaystyle{ 2 }[/math] | 109°28′16″ | [math]\displaystyle{ \pi - 2\text{𝜿} }[/math] | 70°31′44″ | [math]\displaystyle{ \pi - 2\text{𝟁} }[/math] |
| 𝟀 | [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{4}{3}} \approx 1.155 }[/math] | 70°31′44″ | [math]\displaystyle{ 2\text{𝜿} }[/math] | 60° | [math]\displaystyle{ \tfrac{\pi}{3} }[/math] |
| 𝝉[lower-alpha 5] | [math]\displaystyle{ 1 }[/math] | 54°44′8″ | [math]\displaystyle{ \tfrac{\pi}{2} - \text{𝜿} }[/math] | 60° | [math]\displaystyle{ \tfrac{\pi}{3} }[/math] |
| 𝟁 | [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{3}} \approx 0.577 }[/math] | 54°44′8″ | [math]\displaystyle{ \tfrac{\pi}{2} - \text{𝜿} }[/math] | 60° | [math]\displaystyle{ \tfrac{\pi}{3} }[/math] |
| [math]\displaystyle{ _0R/l }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{3}{2}} \approx 1.225 }[/math] | ||||
| [math]\displaystyle{ _1R/l }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{2}} \approx 0.707 }[/math] | ||||
| [math]\displaystyle{ _2R/l }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{6}} \approx 0.408 }[/math] | ||||
| [math]\displaystyle{ \text{𝜿} }[/math] | 35°15′52″ | [math]\displaystyle{ \tfrac{\text{arc sec }3}{2} }[/math] | |||
If the regular tetrahedron has edge length 𝒍 = 2, its characteristic tetrahedron's six edges have lengths [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{4}{3}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ 1 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{3}} }[/math] around its exterior right-triangle face (the edges opposite the characteristic angles 𝟀, 𝝉, 𝟁),[lower-alpha 5] plus [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{3}{2}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{2}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{6}} }[/math] (edges that are the characteristic radii of the regular tetrahedron). The 3-edge path along orthogonal edges of the orthoscheme is [math]\displaystyle{ 1 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{3}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{6}} }[/math], first from a tetrahedron vertex to an tetrahedron edge center, then turning 90° to an tetrahedron face center, then turning 90° to the tetrahedron center. The orthoscheme has four dissimilar right triangle faces. The exterior face is a 60-90-30 triangle which is one-sixth of a tetrahedron face. The three faces interior to the tetrahedron are: a right triangle with edges [math]\displaystyle{ 1 }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{3}{2}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{2}} }[/math], a right triangle with edges [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{3}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{2}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{6}} }[/math], and a right triangle with edges [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{4}{3}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{3}{2}} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \sqrt{\tfrac{1}{6}} }[/math].
Space-filling tetrahedra
A space-filling tetrahedron packs with directly congruent or enantiomorphous (mirror image) copies of itself to tile space.[14] The cube can be dissected into six 3-orthoschemes, three left-handed and three right-handed (one of each at each cube face), and cubes can fill space, so the characteristic 3-orthoscheme of the cube is a space-filling tetrahedron in this sense.[lower-alpha 6] A disphenoid can be a space-filling tetrahedron in the directly congruent sense, as in the disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb. Regular tetrahedra, however, cannot fill space by themselves.[lower-alpha 7]
Fundamental domains
An irregular tetrahedron which is the fundamental domain[15] of a symmetry group is an example of a Goursat tetrahedron. The Goursat tetrahedra generate all the regular polyhedra (and many other uniform polyhedra) by mirror reflections, a process referred to as Wythoff's kaleidoscopic construction.
For polyhedra, Wythoff's construction arranges three mirrors at angles to each other, as in a kaleidoscope. Unlike a cylindrical kaleidoscope, Wythoff's mirrors are located at three faces of a Goursat tetrahedron such that all three mirrors intersect at a single point.[lower-alpha 8]
Among the Goursat tetrahedra which generate 3-dimensional honeycombs we can recognize an orthoscheme (the characteristic tetrahedron of the cube), a double orthoscheme (the characteristic tetrahedron of the cube face-bonded to its mirror image), and the space-filling disphenoid illustrated above.[16] The disphenoid is the double orthoscheme face-bonded to its mirror image (a quadruple orthoscheme). Thus all three of these Goursat tetrahedra, and all the polyhedra they generate by reflections, can be dissected into characteristic tetrahedra of the cube.
Isometries of irregular tetrahedra
The isometries of an irregular (unmarked) tetrahedron depend on the geometry of the tetrahedron, with 7 cases possible. In each case a 3-dimensional point group is formed. Two other isometries (C3, [3]+), and (S4, [2+,4+]) can exist if the face or edge marking are included. Tetrahedral diagrams are included for each type below, with edges colored by isometric equivalence, and are gray colored for unique edges.
| Tetrahedron name | Edge equivalence diagram |
Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | |||||
| Schön. | Cox. | Orb. | Ord. | ||
| Regular tetrahedron | 
|
Four equilateral triangles It forms the symmetry group Td, isomorphic to the symmetric group, S4. A regular tetrahedron has Coxeter diagram | |||
| Td T |
[3,3] [3,3]+ |
*332 332 |
24 12 | ||
| Triangular pyramid | 
|
An equilateral triangle base and three equal isosceles triangle sides It gives 6 isometries, corresponding to the 6 isometries of the base. As permutations of the vertices, these 6 isometries are the identity 1, (123), (132), (12), (13) and (23), forming the symmetry group C3v, isomorphic to the symmetric group, S3. A triangular pyramid has Schläfli symbol {3}∨( ).
| |||
| C3v C3 |
[3] [3]+ |
*33 33 |
6 3 | ||
| Mirrored sphenoid | Two equal scalene triangles with a common base edge This has two pairs of equal edges (1,3), (1,4) and (2,3), (2,4) and otherwise no edges equal. The only two isometries are 1 and the reflection (34), giving the group Cs, also isomorphic to the cyclic group, Z2.
| ||||
| Cs =C1h =C1v |
[ ] | * | 2 | ||
| Irregular tetrahedron (No symmetry) |
Four unequal triangles
Its only isometry is the identity, and the symmetry group is the trivial group. An irregular tetrahedron has Schläfli symbol ( )∨( )∨( )∨( ). | ||||
| C1 | [ ]+ | 1 | 1 | ||
| Disphenoids (Four equal triangles) | |||||
| Tetragonal disphenoid | 
|
Four equal isosceles triangles
It has 8 isometries. If edges (1,2) and (3,4) are of different length to the other 4 then the 8 isometries are the identity 1, reflections (12) and (34), and 180° rotations (12)(34), (13)(24), (14)(23) and improper 90° rotations (1234) and (1432) forming the symmetry group D2d. A tetragonal disphenoid has Coxeter diagram | |||
| D2d S4 |
[2+,4] [2+,4+] |
2*2 2× |
8 4 | ||
| Rhombic disphenoid | Four equal scalene triangles
It has 4 isometries. The isometries are 1 and the 180° rotations (12)(34), (13)(24), (14)(23). This is the Klein four-group V4 or Z22, present as the point group D2. A rhombic disphenoid has Coxeter diagram | ||||
| D2 | [2,2]+ | 222 | 4 | ||
| Generalized disphenoids (2 pairs of equal triangles) | |||||
| Digonal disphenoid | 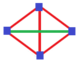 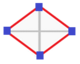
|
Two pairs of equal isosceles triangles This gives two opposite edges (1,2) and (3,4) that are perpendicular but different lengths, and then the 4 isometries are 1, reflections (12) and (34) and the 180° rotation (12)(34). The symmetry group is C2v, isomorphic to the Klein four-group V4. A digonal disphenoid has Schläfli symbol { }∨{ }.
| |||
| C2v C2 |
[2] [2]+ |
*22 22 |
4 2 | ||
| Phyllic disphenoid | Two pairs of equal scalene or isosceles triangles
This has two pairs of equal edges (1,3), (2,4) and (1,4), (2,3) but otherwise no edges equal. The only two isometries are 1 and the rotation (12)(34), giving the group C2 isomorphic to the cyclic group, Z2. | ||||
| C2 | [2]+ | 22 | 2 | ||
General properties
Volume
The volume of a tetrahedron is given by the pyramid volume formula:
- [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac13 A_0\,h \, }[/math]
where A0 is the area of the base and h is the height from the base to the apex. This applies for each of the four choices of the base, so the distances from the apices to the opposite faces are inversely proportional to the areas of these faces.
For a tetrahedron with vertices a = (a1, a2, a3), b = (b1, b2, b3), c = (c1, c2, c3), and d = (d1, d2, d3), the volume is 1/6|det(a − d, b − d, c − d)|, or any other combination of pairs of vertices that form a simply connected graph. This can be rewritten using a dot product and a cross product, yielding
- [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac { |(\mathbf{a}-\mathbf{d}) \cdot ((\mathbf{b}-\mathbf{d}) \times (\mathbf{c}-\mathbf{d}))| } {6}. }[/math]
If the origin of the coordinate system is chosen to coincide with vertex d, then d = 0, so
- [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac { |\mathbf{a} \cdot (\mathbf{b} \times \mathbf{c})| } {6}, }[/math]
where a, b, and c represent three edges that meet at one vertex, and a · (b × c) is a scalar triple product. Comparing this formula with that used to compute the volume of a parallelepiped, we conclude that the volume of a tetrahedron is equal to 1/6 of the volume of any parallelepiped that shares three converging edges with it.
The absolute value of the scalar triple product can be represented as the following absolute values of determinants:
- [math]\displaystyle{ 6 \cdot V =\begin{Vmatrix} \mathbf{a} & \mathbf{b} & \mathbf{c} \end{Vmatrix} }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ 6 \cdot V =\begin{Vmatrix} \mathbf{a} \\ \mathbf{b} \\ \mathbf{c} \end{Vmatrix} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{cases}\mathbf{a} = (a_1,a_2,a_3), \\ \mathbf{b} = (b_1,b_2,b_3), \\ \mathbf{c} = (c_1,c_2,c_3), \end{cases} }[/math] are expressed as row or column vectors.
Hence
- [math]\displaystyle{ 36 \cdot V^2 =\begin{vmatrix} \mathbf{a^2} & \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{b} & \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{c} \\ \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{b} & \mathbf{b^2} & \mathbf{b} \cdot \mathbf{c} \\ \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{c} & \mathbf{b} \cdot \mathbf{c} & \mathbf{c^2} \end{vmatrix} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{cases}\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{b} = ab\cos{\gamma}, \\ \mathbf{b} \cdot \mathbf{c} = bc\cos{\alpha}, \\ \mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{c} = ac\cos{\beta}. \end{cases} }[/math]
which gives
- [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac {abc} {6} \sqrt{1 + 2\cos{\alpha}\cos{\beta}\cos{\gamma}-\cos^2{\alpha}-\cos^2{\beta}-\cos^2{\gamma}}, \, }[/math]
where α, β, γ are the plane angles occurring in vertex d. The angle α, is the angle between the two edges connecting the vertex d to the vertices b and c. The angle β, does so for the vertices a and c, while γ, is defined by the position of the vertices a and b.
If we do not require that d = 0 then
- [math]\displaystyle{ 6 \cdot V = \left| \det \left( \begin{matrix} a_1 & b_1 & c_1 & d_1 \\ a_2 & b_2 & c_2 & d_2 \\ a_3 & b_3 & c_3 & d_3 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 \end{matrix} \right) \right|\,. }[/math]
Given the distances between the vertices of a tetrahedron the volume can be computed using the Cayley–Menger determinant:
- [math]\displaystyle{ 288 \cdot V^2 = \begin{vmatrix} 0 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 & d_{12}^2 & d_{13}^2 & d_{14}^2 \\ 1 & d_{12}^2 & 0 & d_{23}^2 & d_{24}^2 \\ 1 & d_{13}^2 & d_{23}^2 & 0 & d_{34}^2 \\ 1 & d_{14}^2 & d_{24}^2 & d_{34}^2 & 0 \end{vmatrix} }[/math]
where the subscripts i, j ∈ {1, 2, 3, 4} represent the vertices {a, b, c, d} and dij is the pairwise distance between them – i.e., the length of the edge connecting the two vertices. A negative value of the determinant means that a tetrahedron cannot be constructed with the given distances. This formula, sometimes called Tartaglia's formula, is essentially due to the painter Piero della Francesca in the 15th century, as a three dimensional analogue of the 1st century Heron's formula for the area of a triangle.[17]
Let a, b, c be three edges that meet at a point, and x, y, z the opposite edges. Let V be the volume of the tetrahedron; then[18]
- [math]\displaystyle{ V=\frac{\sqrt{4 a^2 b^2 c^2-a^2 X^2-b^2 Y^2-c^2 Z^2+X Y Z}}{12} }[/math]
where
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align}X&=b^2+c^2-x^2, \\ Y&=a^2+c^2-y^2, \\ Z&=a^2+b^2-z^2. \end{align} }[/math]
The above formula uses six lengths of edges, and the following formula uses three lengths of edges and three angles.
- [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac {abc} {6} \sqrt{1 + 2\cos{\alpha}\cos{\beta}\cos{\gamma}-\cos^2{\alpha}-\cos^2{\beta}-\cos^2{\gamma}} }[/math]
Heron-type formula for the volume of a tetrahedron
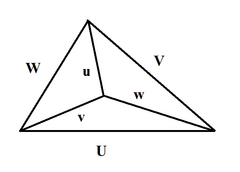
If U, V, W, u, v, w are lengths of edges of the tetrahedron (first three form a triangle; with u opposite U, v opposite V, w opposite W), then[19]
- [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac{\sqrt {\,( - p + q + r + s)\,(p - q + r + s)\,(p + q - r + s)\,(p + q + r - s)}}{192\,u\,v\,w} }[/math]
where
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} p & = \sqrt {xYZ}, & q & = \sqrt {yZX}, & r & = \sqrt {zXY}, & s & = \sqrt {xyz}, \end{align} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} X & = (w - U + v)\,(U + v + w), & x & = (U - v + w)\,(v - w + U), \\ Y & = (u - V + w)\,(V + w + u), & y & = (V - w + u)\,(w - u + V), \\ Z & = (v - W + u)\,(W + u + v), & z & = (W - u + v)\,(u - v + W). \end{align} }[/math]
Volume divider
Any plane containing a bimedian (connector of opposite edges' midpoints) of a tetrahedron bisects the volume of the tetrahedron.[20]
Non-Euclidean volume
For tetrahedra in hyperbolic space or in three-dimensional elliptic geometry, the dihedral angles of the tetrahedron determine its shape and hence its volume. In these cases, the volume is given by the Murakami–Yano formula.[21] However, in Euclidean space, scaling a tetrahedron changes its volume but not its dihedral angles, so no such formula can exist.
Distance between the edges
Any two opposite edges of a tetrahedron lie on two skew lines, and the distance between the edges is defined as the distance between the two skew lines. Let d be the distance between the skew lines formed by opposite edges a and b − c as calculated here. Then another volume formula is given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac {d |(\mathbf{a} \times \mathbf{(b-c)})| } {6}. }[/math]
Properties analogous to those of a triangle
The tetrahedron has many properties analogous to those of a triangle, including an insphere, circumsphere, medial tetrahedron, and exspheres. It has respective centers such as incenter, circumcenter, excenters, Spieker center and points such as a centroid. However, there is generally no orthocenter in the sense of intersecting altitudes.[22]
Gaspard Monge found a center that exists in every tetrahedron, now known as the Monge point: the point where the six midplanes of a tetrahedron intersect. A midplane is defined as a plane that is orthogonal to an edge joining any two vertices that also contains the centroid of an opposite edge formed by joining the other two vertices. If the tetrahedron's altitudes do intersect, then the Monge point and the orthocenter coincide to give the class of orthocentric tetrahedron.
An orthogonal line dropped from the Monge point to any face meets that face at the midpoint of the line segment between that face's orthocenter and the foot of the altitude dropped from the opposite vertex.
A line segment joining a vertex of a tetrahedron with the centroid of the opposite face is called a median and a line segment joining the midpoints of two opposite edges is called a bimedian of the tetrahedron. Hence there are four medians and three bimedians in a tetrahedron. These seven line segments are all concurrent at a point called the centroid of the tetrahedron.[23] In addition the four medians are divided in a 3:1 ratio by the centroid (see Commandino's theorem). The centroid of a tetrahedron is the midpoint between its Monge point and circumcenter. These points define the Euler line of the tetrahedron that is analogous to the Euler line of a triangle.
The nine-point circle of the general triangle has an analogue in the circumsphere of a tetrahedron's medial tetrahedron. It is the twelve-point sphere and besides the centroids of the four faces of the reference tetrahedron, it passes through four substitute Euler points, one third of the way from the Monge point toward each of the four vertices. Finally it passes through the four base points of orthogonal lines dropped from each Euler point to the face not containing the vertex that generated the Euler point.[24]
The center T of the twelve-point sphere also lies on the Euler line. Unlike its triangular counterpart, this center lies one third of the way from the Monge point M towards the circumcenter. Also, an orthogonal line through T to a chosen face is coplanar with two other orthogonal lines to the same face. The first is an orthogonal line passing through the corresponding Euler point to the chosen face. The second is an orthogonal line passing through the centroid of the chosen face. This orthogonal line through the twelve-point center lies midway between the Euler point orthogonal line and the centroidal orthogonal line. Furthermore, for any face, the twelve-point center lies at the midpoint of the corresponding Euler point and the orthocenter for that face.
The radius of the twelve-point sphere is one third of the circumradius of the reference tetrahedron.
There is a relation among the angles made by the faces of a general tetrahedron given by[25]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{vmatrix} -1 & \cos{(\alpha_{12})} & \cos{(\alpha_{13})} & \cos{(\alpha_{14})}\\ \cos{(\alpha_{12})} & -1 & \cos{(\alpha_{23})} & \cos{(\alpha_{24})} \\ \cos{(\alpha_{13})} & \cos{(\alpha_{23})} & -1 & \cos{(\alpha_{34})} \\ \cos{(\alpha_{14})} & \cos{(\alpha_{24})} & \cos{(\alpha_{34})} & -1 \\ \end{vmatrix} = 0\, }[/math]
where αij is the angle between the faces i and j.
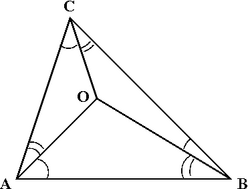
The geometric median of the vertex position coordinates of a tetrahedron and its isogonic center are associated, under circumstances analogous to those observed for a triangle. Lorenz Lindelöf found that, corresponding to any given tetrahedron is a point now known as an isogonic center, O, at which the solid angles subtended by the faces are equal, having a common value of π sr, and at which the angles subtended by opposite edges are equal.[26] A solid angle of π sr is one quarter of that subtended by all of space. When all the solid angles at the vertices of a tetrahedron are smaller than π sr, O lies inside the tetrahedron, and because the sum of distances from O to the vertices is a minimum, O coincides with the geometric median, M, of the vertices. In the event that the solid angle at one of the vertices, v, measures exactly π sr, then O and M coincide with v. If however, a tetrahedron has a vertex, v, with solid angle greater than π sr, M still corresponds to v, but O lies outside the tetrahedron.
Geometric relations
A tetrahedron is a 3-simplex. Unlike the case of the other Platonic solids, all the vertices of a regular tetrahedron are equidistant from each other (they are the only possible arrangement of four equidistant points in 3-dimensional space).
A tetrahedron is a triangular pyramid, and the regular tetrahedron is self-dual.
A regular tetrahedron can be embedded inside a cube in two ways such that each vertex is a vertex of the cube, and each edge is a diagonal of one of the cube's faces. For one such embedding, the Cartesian coordinates of the vertices are
- (+1, +1, +1);
- (−1, −1, +1);
- (−1, +1, −1);
- (+1, −1, −1).
This yields a tetrahedron with edge-length 2√2, centered at the origin. For the other tetrahedron (which is dual to the first), reverse all the signs. These two tetrahedra's vertices combined are the vertices of a cube, demonstrating that the regular tetrahedron is the 3-demicube.
The volume of this tetrahedron is one-third the volume of the cube. Combining both tetrahedra gives a regular polyhedral compound called the compound of two tetrahedra or stella octangula.
The interior of the stella octangula is an octahedron, and correspondingly, a regular octahedron is the result of cutting off, from a regular tetrahedron, four regular tetrahedra of half the linear size (i.e., rectifying the tetrahedron).
The above embedding divides the cube into five tetrahedra, one of which is regular. In fact, five is the minimum number of tetrahedra required to compose a cube. To see this, starting from a base tetrahedron with 4 vertices, each added tetrahedra adds at most 1 new vertex, so at least 4 more must be added to make a cube, which has 8 vertices.
Inscribing tetrahedra inside the regular compound of five cubes gives two more regular compounds, containing five and ten tetrahedra.
Regular tetrahedra cannot tessellate space by themselves, although this result seems likely enough that Aristotle claimed it was possible. However, two regular tetrahedra can be combined with an octahedron, giving a rhombohedron that can tile space as the tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb.
However, several irregular tetrahedra are known, of which copies can tile space, for instance the characteristic orthoscheme of the cube and the disphenoid of the disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb. The complete list remains an open problem.[27]
If one relaxes the requirement that the tetrahedra be all the same shape, one can tile space using only tetrahedra in many different ways. For example, one can divide an octahedron into four identical tetrahedra and combine them again with two regular ones. (As a side-note: these two kinds of tetrahedron have the same volume.)
The tetrahedron is unique among the uniform polyhedra in possessing no parallel faces.
A law of sines for tetrahedra and the space of all shapes of tetrahedra
A corollary of the usual law of sines is that in a tetrahedron with vertices O, A, B, C, we have
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sin\angle OAB\cdot\sin\angle OBC\cdot\sin\angle OCA = \sin\angle OAC\cdot\sin\angle OCB\cdot\sin\angle OBA.\, }[/math]
One may view the two sides of this identity as corresponding to clockwise and counterclockwise orientations of the surface.
Putting any of the four vertices in the role of O yields four such identities, but at most three of them are independent: If the "clockwise" sides of three of them are multiplied and the product is inferred to be equal to the product of the "counterclockwise" sides of the same three identities, and then common factors are cancelled from both sides, the result is the fourth identity.
Three angles are the angles of some triangle if and only if their sum is 180° (π radians). What condition on 12 angles is necessary and sufficient for them to be the 12 angles of some tetrahedron? Clearly the sum of the angles of any side of the tetrahedron must be 180°. Since there are four such triangles, there are four such constraints on sums of angles, and the number of degrees of freedom is thereby reduced from 12 to 8. The four relations given by this sine law further reduce the number of degrees of freedom, from 8 down to not 4 but 5, since the fourth constraint is not independent of the first three. Thus the space of all shapes of tetrahedra is 5-dimensional.[28]
Law of cosines for tetrahedra
Let {P1 ,P2, P3, P4} be the points of a tetrahedron. Let Δi be the area of the face opposite vertex Pi and let θij be the dihedral angle between the two faces of the tetrahedron adjacent to the edge PiPj.
The law of cosines for this tetrahedron,[29] which relates the areas of the faces of the tetrahedron to the dihedral angles about a vertex, is given by the following relation:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta_i^2 = \Delta_j^2 + \Delta_k^2 + \Delta_l^2 - 2(\Delta_j\Delta_k\cos\theta_{il} + \Delta_j\Delta_l \cos\theta_{ik} + \Delta_k\Delta_l \cos\theta_{ij}) }[/math]
Interior point
Let P be any interior point of a tetrahedron of volume V for which the vertices are A, B, C, and D, and for which the areas of the opposite faces are Fa, Fb, Fc, and Fd. Then[30]:p.62,#1609
- [math]\displaystyle{ PA \cdot F_\mathrm{a} + PB \cdot F_\mathrm{b} + PC \cdot F_\mathrm{c} + PD \cdot F_\mathrm{d} \geq 9V. }[/math]
For vertices A, B, C, and D, interior point P, and feet J, K, L, and M of the perpendiculars from P to the faces, and suppose the faces have equal areas, then[30]:p.226,#215
- [math]\displaystyle{ PA+PB+PC+PD \geq 3(PJ+PK+PL+PM). }[/math]
Inradius
Denoting the inradius of a tetrahedron as r and the inradii of its triangular faces as ri for i = 1, 2, 3, 4, we have[30]:p.81,#1990
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{r_1^2} + \frac{1}{r_2^2} + \frac{1}{r_3^2} + \frac{1}{r_4^2} \leq \frac{2}{r^2}, }[/math]
with equality if and only if the tetrahedron is regular.
If A1, A2, A3 and A4 denote the area of each faces, the value of r is given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ r=\frac{3V}{A_1+A_2+A_3+A_4} }[/math].
This formula is obtained from dividing the tetrahedron into four tetrahedra whose points are the three points of one of the original faces and the incenter. Since the four subtetrahedra fill the volume, we have [math]\displaystyle{ V = \frac13A_1r+\frac13A_2r+\frac13A_3r+\frac13A_4r }[/math].
Circumradius
Denote the circumradius of a tetrahedron as R. Let a, b, c be the lengths of the three edges that meet at a vertex, and A, B, C the length of the opposite edges. Let V be the volume of the tetrahedron. Then[31][32]
- [math]\displaystyle{ R=\frac{\sqrt{(aA+bB+cC)(aA+bB-cC)(aA-bB+cC)(-aA+bB+cC)}}{24V}. }[/math]
Circumcenter
The circumcenter of a tetrahedron can be found as intersection of three bisector planes. A bisector plane is defined as the plane centered on, and orthogonal to an edge of the tetrahedron. With this definition, the circumcenter C of a tetrahedron with vertices x0,x1,x2,x3 can be formulated as matrix-vector product:[33]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} C &= A^{-1}B & \text{where} & \ & A = \left(\begin{matrix}\left[x_1 - x_0\right]^T \\ \left[x_2 - x_0\right]^T \\ \left[x_3 - x_0\right]^T \end{matrix}\right) & \ & \text{and} & \ & B = \frac{1}{2}\left(\begin{matrix} \|x_1\|^2 - \|x_0\|^2 \\ \|x_2\|^2 - \|x_0\|^2 \\ \|x_3\|^2 - \|x_0\|^2 \end{matrix}\right) \\ \end{align} }[/math]
In contrast to the centroid, the circumcenter may not always lay on the inside of a tetrahedron. Analogously to an obtuse triangle, the circumcenter is outside of the object for an obtuse tetrahedron.
Centroid
The tetrahedron's center of mass computes as the arithmetic mean of its four vertices, see Centroid.
Faces
The sum of the areas of any three faces is greater than the area of the fourth face.[30]:p.225,#159
Integer tetrahedra
There exist tetrahedra having integer-valued edge lengths, face areas and volume. These are called Heronian tetrahedra. One example has one edge of 896, the opposite edge of 990 and the other four edges of 1073; two faces are isosceles triangles with areas of 436800 and the other two are isosceles with areas of 47120, while the volume is 124185600.[34]
A tetrahedron can have integer volume and consecutive integers as edges, an example being the one with edges 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, and 11 and volume 48.[35]
Related polyhedra and compounds
A regular tetrahedron can be seen as a triangular pyramid.
A regular tetrahedron can be seen as a degenerate polyhedron, a uniform digonal antiprism, where base polygons are reduced digons.
A regular tetrahedron can be seen as a degenerate polyhedron, a uniform dual digonal trapezohedron, containing 6 vertices, in two sets of colinear edges.
A truncation process applied to the tetrahedron produces a series of uniform polyhedra. Truncating edges down to points produces the octahedron as a rectified tetrahedron. The process completes as a birectification, reducing the original faces down to points, and producing the self-dual tetrahedron once again.
| Family of uniform tetrahedral polyhedra | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [3,3], (*332) | [3,3]+, (332) | ||||||
|
|

|

|
||||
| {3,3} | t{3,3} | r{3,3} | t{3,3} | {3,3} | rr{3,3} | tr{3,3} | sr{3,3} |
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | |||||||
|

|

|

| ||||
| V3.3.3 | V3.6.6 | V3.3.3.3 | V3.6.6 | V3.3.3 | V3.4.3.4 | V4.6.6 | V3.3.3.3.3 |
This polyhedron is topologically related as a part of sequence of regular polyhedra with Schläfli symbols {3,n}, continuing into the hyperbolic plane.
The tetrahedron is topologically related to a series of regular polyhedra and tilings with order-3 vertex figures.
- Compounds of tetrahedra
An interesting polyhedron can be constructed from five intersecting tetrahedra. This compound of five tetrahedra has been known for hundreds of years. It comes up regularly in the world of origami. Joining the twenty vertices would form a regular dodecahedron. There are both left-handed and right-handed forms, which are mirror images of each other. Superimposing both forms gives a compound of ten tetrahedra, in which the ten tetrahedra are arranged as five pairs of stellae octangulae. A stella octangula is a compound of two tetrahedra in dual position and its eight vertices define a cube as their convex hull.
The square hosohedron is another polyhedron with four faces, but it does not have triangular faces.
The Szilassi polyhedron and the tetrahedron are the only two known polyhedra in which each face shares an edge with each other face. Furthermore, the Császár polyhedron (itself is the dual of Szilassi polyhedron) and the tetrahedron are the only two known polyhedra in which every diagonal lies on the sides.
Applications
Numerical analysis
In numerical analysis, complicated three-dimensional shapes are commonly broken down into, or approximated by, a polygonal mesh of irregular tetrahedra in the process of setting up the equations for finite element analysis especially in the numerical solution of partial differential equations. These methods have wide applications in practical applications in computational fluid dynamics, aerodynamics, electromagnetic fields, civil engineering, chemical engineering, naval architecture and engineering, and related fields.
Structural engineering
A tetrahedron having stiff edges is inherently rigid. For this reason it is often used to stiffen frame structures such as spaceframes.
Aviation
At some airfields, a large frame in the shape of a tetrahedron with two sides covered with a thin material is mounted on a rotating pivot and always points into the wind. It is built big enough to be seen from the air and is sometimes illuminated. Its purpose is to serve as a reference to pilots indicating wind direction.[36]
Chemistry
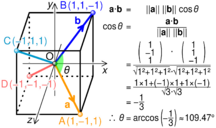
The tetrahedron shape is seen in nature in covalently bonded molecules. All sp3-hybridized atoms are surrounded by atoms (or lone electron pairs) at the four corners of a tetrahedron. For instance in a methane molecule (CH4) or an ammonium ion (NH+4), four hydrogen atoms surround a central carbon or nitrogen atom with tetrahedral symmetry. For this reason, one of the leading journals in organic chemistry is called Tetrahedron. The central angle between any two vertices of a perfect tetrahedron is arccos(−1/3), or approximately 109.47°.[5]
Water, H2O, also has a tetrahedral structure, with two hydrogen atoms and two lone pairs of electrons around the central oxygen atoms. Its tetrahedral symmetry is not perfect, however, because the lone pairs repel more than the single O–H bonds.
Quaternary phase diagrams of mixtures of chemical substances are represented graphically as tetrahedra.
However, quaternary phase diagrams in communication engineering are represented graphically on a two-dimensional plane.
Electricity and electronics
If six equal resistors are soldered together to form a tetrahedron, then the resistance measured between any two vertices is half that of one resistor.[37][38]
Since silicon is the most common semiconductor used in solid-state electronics, and silicon has a valence of four, the tetrahedral shape of the four chemical bonds in silicon is a strong influence on how crystals of silicon form and what shapes they assume.
Color space
Tetrahedra are used in color space conversion algorithms specifically for cases in which the luminance axis diagonally segments the color space (e.g. RGB, CMY).[39]
Games
The Royal Game of Ur, dating from 2600 BC, was played with a set of tetrahedral dice.
Especially in roleplaying, this solid is known as a 4-sided die, one of the more common polyhedral dice, with the number rolled appearing around the bottom or on the top vertex. Some Rubik's Cube-like puzzles are tetrahedral, such as the Pyraminx and Pyramorphix.
Geology
The tetrahedral hypothesis, originally published by William Lowthian Green to explain the formation of the Earth,[40] was popular through the early 20th century.[41][42]
Popular culture
Stanley Kubrick originally intended the monolith in 2001: A Space Odyssey to be a tetrahedron, according to Marvin Minsky, a cognitive scientist and expert on artificial intelligence who advised Kubrick on the HAL 9000 computer and other aspects of the movie. Kubrick scrapped the idea of using the tetrahedron as a visitor who saw footage of it did not recognize what it was and he did not want anything in the movie regular people did not understand.[43]
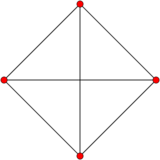
Tetrahedral graph
| Tetrahedral graph | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Vertices | 4 |
| Edges | 6 |
| Radius | 1 |
| Diameter | 1 |
| Girth | 3 |
| Automorphisms | 24 |
| Chromatic number | 4 |
| Properties | Hamiltonian, regular, symmetric, distance-regular, distance-transitive, 3-vertex-connected, planar graph |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
The skeleton of the tetrahedron (comprising the vertices and edges) forms a graph, with 4 vertices, and 6 edges. It is a special case of the complete graph, K4, and wheel graph, W4.[44] It is one of 5 Platonic graphs, each a skeleton of its Platonic solid.
 3-fold symmetry |
See also
- Boerdijk–Coxeter helix
- Möbius configuration
- Caltrop
- Demihypercube and simplex – n-dimensional analogues
- Pentachoron – 4-dimensional analogue
- Synergetics (Fuller)
- Tetrahedral kite
- Tetrahedral number
- Tetrahedron packing
- Triangular dipyramid – constructed by joining two tetrahedra along one face
- Trirectangular tetrahedron
- Orthoscheme
Notes
- ↑ A 3-orthoscheme is not a disphenoid, because its opposite edges are not of equal length. It is not possible to construct a disphenoid with right triangle or obtuse triangle faces.
- ↑ For a regular k-polytope, the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of the characteristic k-orthoscheme is the k-polytope's diagram without the generating point ring. The regular k-polytope is subdivided by its symmetry (k-1)-elements into g instances of its characteristic k-orthoscheme that surround its center, where g is the order of the k-polytope's symmetry group.[11]
- ↑ A regular polytope of dimension k has a characteristic k-orthoscheme, and also a characteristic (k-1)-orthoscheme. A regular polyhedron has a characteristic tetrahedron (3-orthoscheme) into which it is subdivided by its planes of symmetry, and also a characteristic triangle (2-orthoscheme) into which its surface is subdivided by its faces' lines of symmetry. After subdividing its surface into characteristic right triangles surrounding each face center, its interior can be subdivided into characteristic tetrahedra by adding radii joining the vertices of the surface right triangles to the polyhedron's center.[12] The interior triangles thus formed will also be right triangles.
- ↑ The 24 characteristic tetrahedra of the regular tetrahedron occur in two mirror-image forms, 12 of each.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 (Coxeter 1973) uses the greek letter 𝝓 (phi) to represent one of the three characteristic angles 𝟀, 𝝓, 𝟁 of a regular polytope. Because 𝝓 is commonly used to represent the golden ratio constant ≈ 1.618, for which Coxeter uses 𝝉 (tau), we reverse Coxeter's conventions, and use 𝝉 to represent the characteristic angle.
- ↑ The characteristic orthoscheme of the cube is one of the Hill tetrahedra, a family of space-filling tetrahedra. All space-filling tetrahedra are scissors-congruent to a cube. Every convex polyhedron is scissors-congruent to an orthoscheme. Every regular convex polyhedron (Platonic solid) can be dissected into some even number of instances of its characteristic orthoscheme.
- ↑ The tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb fills space with alternating regular tetrahedron cells and regular octahedron cells in a ratio of 2:1.
- ↑ The Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of the generated polyhedron contains three nodes representing the three mirrors. The dihedral angle between each pair of mirrors is encoded in the diagram, as well as the location of a single generating point which is multiplied by mirror reflections into the vertices of the polyhedron. For a regular polyhedron, the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of the generating characteristic orthoscheme is the generated polyhedron's diagram without the generating point marking.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weisstein, Eric W.. "Tetrahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Tetrahedron.html.
- ↑ Ford, Walter Burton; Ammerman, Charles (1913), Plane and Solid Geometry, Macmillan, pp. 294–295, https://archive.org/stream/planeandsolidge01hedrgoog#page/n315
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald; Regular Polytopes, Methuen and Co., 1948, Table I(i)
- ↑ Köller, Jürgen, "Tetrahedron", Mathematische Basteleien, 2001
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Brittin, W. E. (1945). "Valence angle of the tetrahedral carbon atom". Journal of Chemical Education 22 (3): 145. doi:10.1021/ed022p145. Bibcode: 1945JChEd..22..145B.
- ↑ Park, Poo-Sung. "Regular polytope distances", Forum Geometricorum 16, 2016, 227–232. http://forumgeom.fau.edu/FG2016volume16/FG201627.pdf
- ↑ "Sections of a Tetrahedron". http://www.matematicasvisuales.com/english/html/geometry/space/sectetra.html.
- ↑ Kepler 1619, p. 181.
- ↑ Coxeter, H.S.M. (1989). "Trisecting an Orthoscheme". Computers Math. Applic. 17 (1–3): 59–71. doi:10.1016/0898-1221(89)90148-X.
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, pp. 71-72, §4.7 Characteristic tetrahedra.
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, pp. 130–133, §7.6 The symmetry group of the general regular polytope.
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, p. 130, §7.6; "simplicial subdivision".
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, pp. 292–293, Table I(i); "Tetrahedron, 𝛼3".
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, pp. 33–34, §3.1 Congruent transformations.
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, p. 63, §4.3 Rotation groups in two dimensions; notion of a fundamental region.
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, pp. 71–72, §4.7 Characteristic tetrahedra.
- ↑ "Simplex Volumes and the Cayley-Menger Determinant", MathPages.com
- ↑ Kahan, William M. (2012-04-03), What has the Volume of a Tetrahedron to do with Computer Programming Languages?, pp. 11, http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~wkahan/VtetLang.pdf
- ↑ Kahan, William M. (2012-04-03), What has the Volume of a Tetrahedron to do with Computer Programming Languages?, pp. 16–17, http://www.cs.berkeley.edu/~wkahan/VtetLang.pdf
- ↑ Bottema, O. "A Theorem of Bobillier on the Tetrahedron." Elemente der Mathematik 24 (1969): 6–10.
- ↑ Murakami, Jun; Yano, Masakazu (2005), "On the volume of a hyperbolic and spherical tetrahedron", Communications in Analysis and Geometry 13 (2): 379–400, doi:10.4310/cag.2005.v13.n2.a5, ISSN 1019-8385
- ↑ Havlicek, Hans; Weiß, Gunter (2003). "Altitudes of a tetrahedron and traceless quadratic forms". American Mathematical Monthly 110 (8): 679–693. doi:10.2307/3647851. http://www.geometrie.tuwien.ac.at/havlicek/pub/hoehen.pdf.
- ↑ Leung, Kam-tim; and Suen, Suk-nam; "Vectors, matrices and geometry", Hong Kong University Press, 1994, pp. 53–54
- ↑ Outudee, Somluck; New, Stephen. The Various Kinds of Centres of Simplices. Dept of Mathematics, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok. http://www.math.sc.chula.ac.th/ICAA2002/pages/Somluck_Outudee.pdf.
- ↑ Audet, Daniel (May 2011). "Déterminants sphérique et hyperbolique de Cayley-Menger". Bulletin AMQ. http://archimede.mat.ulaval.ca/amq/bulletins/mai11/Chronique_note_math.mai11.pdf.
- ↑ Lindelof, L. (1867). "Sur les maxima et minima d'une fonction des rayons vecteurs menés d'un point mobile à plusieurs centres fixes". Acta Societatis Scientiarum Fennicae 8 (Part 1): 189–203.
- ↑ "Which tetrahedra fill space?". Mathematics Magazine (Mathematical Association of America) 54 (5): 227–243. 1981. doi:10.2307/2689983.
- ↑ Rassat, André; Fowler, Patrick W. (2004). "Is There a "Most Chiral Tetrahedron"?". Chemistry: A European Journal 10 (24): 6575–6580. doi:10.1002/chem.200400869. PMID 15558830.
- ↑ Lee, Jung Rye (June 1997). "The Law of Cosines in a Tetrahedron". J. Korea Soc. Math. Educ. Ser. B: Pure Appl. Math..
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 Inequalities proposed in “Crux Mathematicorum”, [1].
- ↑ Crelle, A. L. (1821). "Einige Bemerkungen über die dreiseitige Pyramide" (in de). Sammlung mathematischer Aufsätze u. Bemerkungen 1. Berlin: Maurer. pp. 105–132. https://archive.org/stream/sammlungmathemat01crel#page/104. Retrieved 7 August 2018.
- ↑ Todhunter, I. (1886), Spherical Trigonometry: For the Use of Colleges and Schools, p. 129, //www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/19770 ( Art. 163 )
- ↑ Lévy, Bruno; Liu, Yang (2010). Lp Centroidal Voronoi Tessellation and its applications. ACM. pp. 119.
- ↑ "Problem 930", Crux Mathematicorum 11 (5): 162–166, May 1985, https://cms.math.ca/crux/backfile/Crux_v11n05_May.pdf
- ↑ Wacław Sierpiński, Pythagorean Triangles, Dover Publications, 2003 (orig. ed. 1962), p. 107. Note however that Sierpiński repeats an erroneous calculation of the volume of the Heronian tetrahedron example above.
- ↑ Federal Aviation Administration (2009), Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge, U. S. Government Printing Office, p. 13-10, ISBN 9780160876110, https://books.google.com/books?id=0l8WO6Drz50C&pg=SA13-PA10.
- ↑ Klein, Douglas J. (2002). "Resistance-Distance Sum Rules". Croatica Chemica Acta 75 (2): 633–649. http://jagor.srce.hr/ccacaa/CCA-PDF/cca2002/v75-n2/CCA_75_2002_633_649_KLEIN.pdf. Retrieved 2006-09-15.
- ↑ Záležák, Tomáš (18 October 2007); "Resistance of a regular tetrahedron"[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}] (PDF), retrieved 25 January 2011
- ↑ Vondran, Gary L. (April 1998). "Radial and Pruned Tetrahedral Interpolation Techniques". HP Technical Report HPL-98-95: 1–32. http://www.hpl.hp.com/techreports/98/HPL-98-95.pdf. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ↑ Green, William Lowthian (1875). Vestiges of the Molten Globe, as exhibited in the figure of the earth, volcanic action and physiography. Part I. London: E. Stanford. OCLC 3571917. Bibcode: 1875vmge.book.....G. https://books.google.com/books?id=9DkDAAAAQAAJ.
- ↑ Holmes, Arthur (1965). Principles of physical geology. Nelson. p. 32. ISBN 9780177612992. https://archive.org/details/principlesofphys0000holm.
- ↑ Hitchcock, Charles Henry (January 1900). "William Lowthian Green and his Theory of the Evolution of the Earth's Features". The American Geologist (Geological Publishing Company) XXV: pp. 1–10. https://books.google.com/books?id=_Ty8AAAAIAAJ&pg=PA1.
- ↑ "Marvin Minsky: Stanley Kubrick Scraps the Tetrahedron". Web of Stories. http://www.webofstories.com/play/53140?o=R.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Tetrahedral graph". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/TetrahedralGraph.html.
Bibliography
- Kepler, Johannes (1619). Harmonices Mundi (The Harmony of the World). Johann Planck.
- Coxeter, H.S.M. (1973). Regular Polytopes (3rd ed.). New York: Dover.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Tetrahedron". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Tetrahedron.html.
- Free paper models of a tetrahedron and many other polyhedra
- An Amazing, Space Filling, Non-regular Tetrahedron that also includes a description of a "rotating ring of tetrahedra", also known as a kaleidocycle.
Fundamental convex regular and uniform polytopes in dimensions 2–10
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | An | Bn | I2(p) / Dn | E6 / E7 / E8 / F4 / G2 | Hn | |||||||
| Regular polygon | Triangle | Square | p-gon | Hexagon | Pentagon | |||||||
| Uniform polyhedron | Tetrahedron | Octahedron • Cube | Demicube | Dodecahedron • Icosahedron | ||||||||
| Uniform 4-polytope | 5-cell | 16-cell • Tesseract | Demitesseract | 24-cell | 120-cell • 600-cell | |||||||
| Uniform 5-polytope | 5-simplex | 5-orthoplex • 5-cube | 5-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 6-polytope | 6-simplex | 6-orthoplex • 6-cube | 6-demicube | 122 • 221 | ||||||||
| Uniform 7-polytope | 7-simplex | 7-orthoplex • 7-cube | 7-demicube | 132 • 231 • 321 | ||||||||
| Uniform 8-polytope | 8-simplex | 8-orthoplex • 8-cube | 8-demicube | 142 • 241 • 421 | ||||||||
| Uniform 9-polytope | 9-simplex | 9-orthoplex • 9-cube | 9-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform 10-polytope | 10-simplex | 10-orthoplex • 10-cube | 10-demicube | |||||||||
| Uniform n-polytope | n-simplex | n-orthoplex • n-cube | n-demicube | 1k2 • 2k1 • k21 | n-pentagonal polytope | |||||||
| Topics: Polytope families • Regular polytope • List of regular polytopes and compounds | ||||||||||||
 |