Chemistry:Quinalizarin
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
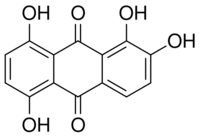
1,2,5,8-Tetrahydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H8O6 | |
| Molar mass | 272.212 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Quinalizarin or 1,2,5,8-tetrahydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound with formula C14H8O6. It is one of many tetrahydroxyanthraquinone isomers, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of four hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups at the 1, 2, 5, and 8 positions.
Quinalizarin is an inhibitor of the enzyme protein kinase CK2. It is more potent and selective than emodin.[1] It is also a potent catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor.[2][3]
See also
- 1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone (quinizarin)
- Alizarin, a related simpler dye
References
- ↑ Cozza, G.; Mazzorana, M.; Papinutto, E.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; di Maira, G.; Gianoncelli, A.; Pagano, M. A. et al. (2009). "Quinalizarin as a Potent, Selective and Cell-Permeable Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2". The Biochemical Journal 421 (3): 387–395. doi:10.1042/BJ20090069. PMID 19432557. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00479150/file/PEER_stage2_10.1042%252FBJ20090069.pdf.
- ↑ "Antiestrogen action of 2-hydroxyestrone on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells". J. Biol. Chem. 259 (8): 4840–5. April 1984. PMID 6325410. https://www.jbc.org/content/259/8/4840.short.
- ↑ "Catecholestrogens are agonists of estrogen receptor dependent gene expression in MCF-7 cells". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 48 (5-6): 453–61. April 1994. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(94)90193-7. PMID 8180106.
 |
