Biology:Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme
 Generic protein structure example |
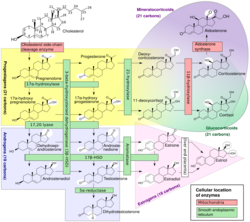
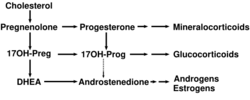
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme is commonly referred to as P450scc, where "scc" is an acronym for side-chain cleavage. P450scc is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. This is the first reaction in the process of steroidogenesis in all mammalian tissues that specialize in the production of various steroid hormones.[1]
P450scc is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes (family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1) and is encoded by the CYP11A1 gene.[2]
Nomenclature
| cholesterol monooxygenase (side-chain-cleaving) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.14.15.6 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 37292-81-2 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The systematic name of this enzyme class is cholesterol, reduced-adrenal-ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (side-chain-cleaving). Other names include:
|
Tissue and intracellular localization
The highest level of the cholesterol side-chain cleavage system is found in the adrenal cortex and the corpus luteum.[1] The system is also expressed at high levels in steroidogenic theca cells in the ovary, and Leydig cells in the testis.[1] During pregnancy, the placenta also expresses significant levels of this enzyme system.[3] P450scc is also present at much lower levels in several other tissue types, including the brain.[4] In the adrenal cortex, the concentration of adrenodoxin is similar to that of P450scc, but adrenodoxin reductase is expressed at lower levels.[5]
Immunofluorescence studies using specific antibodies against P450scc system enzymes have demonstrated that proteins are located exclusively within the mitochondria.[6][7] P450scc is associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, facing the interior (matrix).[8][9] Adrenodoxin and adrenodoxin reductase are soluble peripheral membrane proteins located inside the mitochondrial matrix that appear to associate with each other primarily through electrostatic interactions.[10]
Mechanism of action
P450scc catalyzes the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone in three monooxygenase reactions. These involve 2 hydroxylations of the cholesterol side-chain, which generate, first, 22R-hydroxycholesterol and then 20alpha,22R-dihydroxycholesterol. The final step cleaves the bond between carbons 20 and 22, resulting in the production of pregnenolone and isocaproic aldehyde.
Each monooxygenase step requires 2 electrons (reducing equivalents). The initial source of the electrons is NADPH.[11] The electrons are transferred from NADPH to P450scc via two electron transfer proteins: adrenodoxin reductase[12] and adrenodoxin.[13][14] All three proteins together constitute the cholesterol side-chain cleavage complex.
The involvement of three proteins in cholesterol side-chain cleavage reaction raises the question of whether the three proteins function as a ternary complex as reductase:adrenodoxin:P450. Both spectroscopic studies of adrenodoxin binding to P450scc and kinetic studies in the presence of varying concentrations of adrenodoxin reductase demonstrated that the reductase competes with P450scc for binding to adrenodoxin. These results demonstrated that the formation of a functional ternary complex is not possible.[13] From these studies, it was concluded that the binding sites of adrenodoxin to its reductase and to P450 are overlapping and, as a consequence, adrenodoxin functions as a mobile electron shuttle between reductase and P450.[13] These conclusions have been confirmed by structural analysis of adrenodoxin and P450 complex.[15]
The process of electron transfer from NADPH to P450scc is not tightly coupled; that is, during electron transfer from adrenodoxin reductase via adrenodoxin to P450scc, a certain portion of the electrons leak outside of the chain and react with O2, generating superoxide radicals.[16] Steroidogenic cells include a diverse array of antioxidant systems to cope with the radicals generated by the steroidogenic enzymes.[17]
Regulation
In each steroidogenic cell, the expression of the P450scc system proteins is regulated by the trophic hormonal system specific for the cell type.[1] In adrenal cortex cells from zona fasciculata, the expression of the mRNAs encoding all three P450scc proteins is induced by corticotropin (ACTH).[7][18] The trophic hormones increase CYP11A1 gene expression through transcription factors such as steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1), by the α isoform of activating protein 2 (AP-2) in the human, and many others.[18][19] The production of this enzyme is inhibited notably by the nuclear receptor DAX-1.[18]
P450scc is always active, however its activity is limited by the supply of cholesterol in the inner membrane. The supplying of cholesterol to this membrane (from the outer mitochondrial membrane) is, thus, considered the true rate-limiting step in steroid production. This step is mediated primarily by the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR or STARD1). Upon stimulation of a cell to make steroid, the amount of StAR available to transfer cholesterol to the inner membrane limits how fast the reaction can go (the acute phase). With prolonged (chronic) stimulation, it is thought that cholesterol supply becomes no longer an issue and that the capacity of the system to make steroid (i.e., level of P450scc in the mitochondria) is now more important.
Corticotropin (ACTH) is a hormone that is released from the anterior pituitary in response to stress situations. A study of the steroidogenic capacity of the adrenal cortex in infants with acute respiratory disease demonstrated that indeed during disease state there is a specific increase in the steroidogenic capacity for the synthesis of the glucocorticoid cortisol but not for the mineralocorticoid aldosterone or androgen DHEAS that are secreted from other zones of the adrenal cortex.[20]
Pathology
Mutations in the CYP11A1 gene result in a steroid hormone deficiency, causing a minority of cases of the rare and potentially fatal condition lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia.[21][22][23] Deficiency of CYP11A1 can result in hyperpigmentation, hypoglycemia, and recurrent infections.[24]
Inhibitors
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme inhibitors include aminoglutethimide, ketoconazole, and mitotane, among others.[25][26][27]
See also
- Steroidogenic enzyme
- Cytochrome P450 oxidase
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Steroidogenic enzymes: structure, function, and role in regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 43 (8): 779–804. December 1992. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(92)90307-5. PMID 22217824. https://zenodo.org/record/890723.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: CYP11A1 cytochrome P450, family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1583.
- ↑ "Placental steroid hormone synthesis: unique features and unanswered questions". Biology of Reproduction 54 (2): 303–311. February 1996. doi:10.1095/biolreprod54.2.303. PMID 8788180.
- ↑ "Neurosteroid metabolism in the human brain". European Journal of Endocrinology 145 (6): 669–679. December 2001. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1450669. PMID 11720889.
- ↑ "Stoichiometry of mitochondrial cytochromes P-450, adrenodoxin and adrenodoxin reductase in adrenal cortex and corpus luteum. Implications for membrane organization and gene regulation". European Journal of Biochemistry 157 (1): 27–31. May 1986. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09633.x. PMID 3011431. https://zenodo.org/record/890737.
- ↑ "Induction and mitochondrial localization of cytochrome P450scc system enzymes in normal and transformed ovarian granulosa cells". The Journal of Cell Biology 111 (4): 1373–1381. October 1990. doi:10.1083/jcb.111.4.1373. PMID 2170421.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Mechanism of corticotropin and cAMP induction of mitochondrial cytochrome P450 system enzymes in adrenal cortex cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 265 (33): 20602–20608. November 1990. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)30545-8. PMID 2173715. https://zenodo.org/record/890729.
- ↑ Topological studies of cytochromes P-450scc and P-45011 beta in bovine adrenocortical inner mitochondrial membranes. Effects of controlled tryptic digestion. J. Biol. Chem. 1979 254: 10443-8.
- ↑ "Preparation of antiserum to rat cytochrome P-450 cholesterol side chain cleavage, and its use for ultrastructural localization of the immunoreactive enzyme by protein A-gold technique". Endocrinology 118 (4): 1353–1365. April 1986. doi:10.1210/endo-118-4-1353. PMID 3948785.
- ↑ "Mechanisms of ionic activation of adrenal mitochondrial cytochromes P-450scc and P-45011 beta". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 256 (9): 4329–4335. May 1981. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)69437-8. PMID 6783659.
- ↑ "Routes and regulation of NADPH production in steroidogenic mitochondria". Endocrine Research 21 (1–2): 231–241. 1995. doi:10.3109/07435809509030439. PMID 7588385.
- ↑ "Isolation of a cDNA for adrenodoxin reductase (ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase). Implications for mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 systems". European Journal of Biochemistry 169 (3): 449–455. December 1987. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13632.x. PMID 3691502.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 "Mitochondrial cytochrome P-450scc. Mechanism of electron transport by adrenodoxin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 255 (7): 3057–3061. April 1980. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)85851-9. PMID 6766943.
- ↑ "Adrenal mitochondrial cytochrome P-450scc. Cholesterol and adrenodoxin interactions at equilibrium and during turnover". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 256 (9): 4321–4328. May 1981. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)69436-6. PMID 7217084.
- ↑ "Structural basis for pregnenolone biosynthesis by the mitochondrial monooxygenase system". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108 (25): 10139–10143. June 2011. doi:10.1073/pnas.1019441108. PMID 21636783. Bibcode: 2011PNAS..10810139S.
- ↑ "Electron leakage from the mitochondrial NADPH-adrenodoxin reductase-adrenodoxin-P450scc (cholesterol side chain cleavage) system". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 305 (2): 489–498. September 1993. doi:10.1006/abbi.1993.1452. PMID 8396893. https://zenodo.org/record/890721.
- ↑ "Antioxidant protective mechanisms against reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by mitochondrial P450 systems in steroidogenic cells". Drug Metabolism Reviews 38 (1–2): 171–196. 2006. doi:10.1080/03602530600570040. PMID 16684656. https://zenodo.org/record/890701.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 "Transcriptional regulation of steroidogenic genes: STARD1, CYP11A1 and HSD3B". Experimental Biology and Medicine 234 (8): 880–907. August 2009. doi:10.3181/0903-MR-97. PMID 19491374.
- ↑ "Transcriptional regulation of human CYP11A1 in gonads and adrenals". Journal of Biomedical Science 14 (4): 509–515. July 2007. doi:10.1007/s11373-007-9177-z. PMID 17594537.
- ↑ "Selective increases in adrenal steroidogenic capacity during acute respiratory disease in infants". European Journal of Endocrinology 133 (5): 552–556. November 1995. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1330552. PMID 7581984.
- ↑ "Phenotypic variations in lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia". Pediatric Endocrinology Reviews 3 (3): 258–271. March 2006. PMID 16639391.
- ↑ "Homozygous mutation of P450 side-chain cleavage enzyme gene (CYP11A1) in 46, XY patient with adrenal insufficiency, complete sex reversal, and agenesis of corpus callosum". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 91 (8): 2821–2826. August 2006. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2230. PMID 16705068.
- ↑ "Severe combined adrenal and gonadal deficiency caused by novel mutations in the cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 93 (3): 696–702. March 2008. doi:10.1210/jc.2007-2330. PMID 18182448.
- ↑ "Primary adrenal insufficiency: New genetic causes and their long-term consequences". Clinical Endocrinology 92 (1): 11–20. 2020. doi:10.1111/cen.14109. PMID 31610036.
- ↑ Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2001. pp. 735–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=FVfzRvaucq8C&pg=PA735.
- ↑ Endocrinology - E-Book: Adult and Pediatric. Elsevier Health Sciences. 18 May 2010. pp. 301–302. ISBN 978-1-4557-1126-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=W4dZ-URK8ZoC&pg=PA301.
- ↑ Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry. Springer. 13 March 2015. pp. 851–879. ISBN 978-3-319-12108-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=abZnBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA851.
Further reading
- "Twin genes and endocrine disease: CYP21 and CYP11B genes". Acta Endocrinologica 129 (2): 97–108. August 1993. doi:10.1530/acta.0.1290097. PMID 8372604.
- "Peripheral benzodiazepine receptor in cholesterol transport and steroidogenesis". Steroids 62 (1): 21–28. January 1997. doi:10.1016/S0039-128X(96)00154-7. PMID 9029710.
- "Intramitochondrial cholesterol transfer". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1486 (1): 184–197. June 2000. doi:10.1016/S1388-1981(00)00056-1. PMID 10856721.
- "Genetic susceptibility and environmental estrogen-like compounds". Mutation Research 482 (1–2): 77–82. October 2001. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(01)00212-3. PMID 11535251.
- "Some new thoughts on the pathophysiology and genetics of polycystic ovary syndrome". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 997 (1): 42–48. November 2003. doi:10.1196/annals.1290.005. PMID 14644808. Bibcode: 2003NYASA.997...42S.
- "Identification by site-directed mutagenesis of two lysine residues in cholesterol side chain cleavage cytochrome P450 that are essential for adrenodoxin binding". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 267 (32): 22877–22882. November 1992. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)50028-4. PMID 1429635.
- "Regulated expression of cytochrome P-450scc (cholesterol-side-chain cleavage enzyme) in cultured cell lines detected by antibody against bacterially expressed human protein". The Biochemical Journal 274 (Pt 3): 813–817. March 1991. doi:10.1042/bj2740813. PMID 1849407.
- "Regional mapping of genes encoding human steroidogenic enzymes: P450scc to 15q23-q24, adrenodoxin to 11q22; adrenodoxin reductase to 17q24-q25; and P450c17 to 10q24-q25". DNA and Cell Biology 10 (5): 359–365. June 1991. doi:10.1089/dna.1991.10.359. PMID 1863359.
- "Site-specific mutations in human ferredoxin that affect binding to ferredoxin reductase and cytochrome P450scc". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 266 (28): 18606–18612. October 1991. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)55106-1. PMID 1917982.
- "Study of cholesterol side-chain cleavage (20,22 desmolase) deficiency causing congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia using bovine-sequence P450scc oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes". Endocrinology 118 (4): 1296–1305. April 1986. doi:10.1210/endo-118-4-1296. PMID 2419119.
- "Human cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc: cDNA cloning, assignment of the gene to chromosome 15, and expression in the placenta". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 83 (23): 8962–8966. December 1986. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.23.8962. PMID 3024157. Bibcode: 1986PNAS...83.8962C.
- "Gene structure of human cytochrome P-450(SCC), cholesterol desmolase". Journal of Biochemistry 101 (4): 879–887. April 1987. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121955. PMID 3038854.
- "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene 138 (1–2): 171–174. January 1994. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- "Association of the steroid synthesis gene CYP11a with polycystic ovary syndrome and hyperandrogenism". Human Molecular Genetics 6 (3): 397–402. March 1997. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.3.397. PMID 9147642.
- "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene 200 (1–2): 149–156. October 1997. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- "Expression of cytochrome P450 genes encoding enzymes active in the metabolism of tamoxifen in human uterine endometrium". Pharmacology & Toxicology 82 (2): 93–97. February 1998. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1998.tb01404.x. PMID 9498238.
- "Prominent sex steroid metabolism in human lymphocytes". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 138 (1–2): 61–69. March 1998. doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(98)00052-5. PMID 9685215.
Steroid hormone synthesis
Additional images
External links
- Cytochrome+P450scc at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |