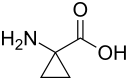
Chemistry:1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | ACC |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H7NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 101.1 c |
| Melting point | 198–201 °C (388–394 °F; 471–474 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) is a disubstituted cyclic α-amino acid in which a cyclopropane ring is fused to the Cα atom of the amino acid. It is a white solid. Many cyclopropane-substituted amino acids are known, but this one occurs naturally.[2][verification needed] Like glycine, but unlike most α-amino acids, ACC is not chiral.
Biochemistry
ACC is the precursor to the plant hormone ethylene.[3][4] It is synthesized by the enzyme ACC synthase (EC 4.4.1.14) from methionine and converted to ethylene by ACC oxidase (EC 1.14.17.4).[5]
ACC also exhibits ethylene-independent signaling that plays a critical role in pollination and seed production by activating proteins similar to those involved in nervous system responses in humans and animals. More specifically, ACC signaling promotes secretion of the pollen tube chemoattractant LURE1.2 in ovular sporophytic tissue thus enhancing pollen tube attraction. Additionally, ACC activates Ca2+-containing ion currents via glutamate receptor-like (GLR) channels in root protoplasts.[6]
ACC can be used by soil microorganisms (both bacteria and fungi) as a source of nitrogen and carbon.[7] As such, using ACC to incubate soils has been proven to induce the gene abundance encoding ACC-deaminases, which may have positive consequences on plant growth and stress tolerance.[7][8]
ACC has also been extracted from kelp.[9]
ACC is also an exogenous partial agonist of the mammalian NMDA receptor.[10]
In 2019, the United States Environmental Protection Agency issued notice of an application for an experimental use permit to be issued for use of ACC as a pesticide.[11]
References
- ↑ "MetaCyc: a multiorganism database of metabolic pathways and enzymes". Nucleic Acids Research 34 (Database issue): D511-6. January 2006. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj128. PMID 16381923.
- ↑ "Natural Occurrence, Syntheses, and Applications of Cyclopropyl-Group-Containing α-Amino Acids. 1. 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic Acid and Other 2,3-Methanoamino Acids". Chemical Reviews 107 (11): 4493–4537. November 2007. doi:10.1021/cr078376j. PMID 17944521.
- ↑ "Ethylene biosynthesis and its regulation in higher plants". Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 35: 155–189. 1984. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.35.060184.001103.
- ↑ "Ethylene biosynthesis". Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 44: 283–307. 1993. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.44.060193.001435.
- ↑ "Enzymes of ethylene biosynthesis". Plant Physiology 91 (1): 1–4. September 1989. doi:10.1104/pp.91.1.1. PMID 16666977.
- ↑ "Ethylene-independent signaling by the ethylene precursor ACC in Arabidopsis ovular pollen tube attraction". Nature Communications 11 (1): 4082. August 2020. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17819-9. PMID 32796832. Bibcode: 2020NatCo..11.4082M.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Soil amendments with ethylene precursor alleviate negative impacts of salinity on soil microbial properties and productivity". Scientific Reports 9 (1): 6892. May 2019. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-43305-4. PMID 31053834. Bibcode: 2019NatSR...9.6892L.
- ↑ "Alleviation of salinity stress in wheat by ACC deaminase-producing Bacillus aryabhattai EWR29 with multifarious plant growth-promoting attributes". Plant Archives 20 (1): 417–429. 2020. https://scholar.cu.edu.eg/?q=farahat/publications/alleviation-salinity-stress-wheat-acc-deaminase-producing-bacillus-aryabhattai-.
- ↑ "Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid in seaweed concentrate". Botanica Marina 28 (9): 415-417. 1985. doi:10.1515/botm.1985.28.9.415.
- ↑ "Mechanism of partial agonist action at the NR1 subunit of NMDA receptors". Neuron 47 (1): 71–84. July 2005. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.05.022. PMID 15996549.
- ↑ "Pesticide Experimental Use Permit; Receipt of Application; Comment Request". Federal Register 84 (152): 38624. August 7, 2019. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2019-08-07/pdf/2019-16810.pdf.
 |

