Chemistry:Rhynchophylline
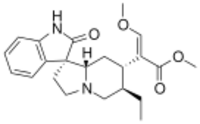
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl (7R,16E)-17-methoxy-2-oxo-16,17-didehydro-20α-corynoxan-16-carboxylate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl (2E)-2-[(1′R,6′R,7′S,8a′S)-6′-ethyl-2-oxo-1,2,2′,3′,6′,7′,8′,8a′-octahydro-5′H-spiro[indole-3,1′-indolizin]-7′-yl]-3-methoxyprop-2-enoate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H28N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 384.476 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Rhynchophylline is an alkaloid found in certain Uncaria species (Rubiaceae), notably Uncaria rhynchophylla[1] and Uncaria tomentosa.[2] It also occurs in the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa (kratom),[3] a tree native to Thailand. Chemically, it is related to the alkaloid mitragynine.
Rhynchophylline is a non-competitive NMDA antagonist (IC50 = 43.2 μM) and a calcium channel blocker.[4][5]
Uncaria species have had a variety of uses in traditional herbal medicine, such as for lightheadedness, convulsions, numbness, and hypertension.[6] These uses have been associated with the presence of rhynchophylline and have encouraged its investigation as a drug candidate for several cardiovascular and central nervous system diseases; however, few clinically relevant studies have been conducted.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Pharmacological Actions of Uncaria Alkaloids, Rhynchophylline and Isorhynchophylline". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 24 (2): 97–101. 2003. PMID 12546715. http://www.chinaphar.com/1671-4083/24/97.pdf.
- ↑ "Effects of Uncaria tomentosa Total Alkaloid and its Components on Experimental Amnesia in Mice: Elucidation Using the Passive Avoidance Test". Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 52 (12): 1553–1561. 2000. doi:10.1211/0022357001777612. PMID 11197086.
- ↑ "Mitragyna Speciosa (Kratom) - World Roots". https://worldroots.com/.
- ↑ "Rhynchophylline and Isorhynchophylline Inhibit NMDA Receptors Expressed in Xenopus Oocytes". European Journal of Pharmacology 455 (1): 27–34. 2002. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(02)02581-5. PMID 12433591.
- ↑ "Protective Effect of Rhynchophylline and Isorhynchophylline on in vitro Ischemia-Induced Neuronal Damage in the Hippocampus: Putative Neurotransmitter Receptors Involved in their Action". Life Sciences 76 (3): 331–343. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.08.012. PMID 15531384.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Antihypertensive and neuroprotective activities of rhynchophylline: the role of rhynchophylline in neurotransmission and ion channel activity". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 132 (1): 15–27. 2010. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2010.08.041. PMID 20736055.
 |
