Chemistry:Budipine
Budipine (brand name Parkinsan) is an antiparkinson agent marketed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.[1][2][3]
While its exact mechanism of action is not well characterized,[1] it is believed to be an NMDA receptor antagonist,[4][5] but also promoting the synthesis of dopamine.[6]
Because it provides additional benefits relative to existing treatments, it probably does not precisely mimic the mechanism of an existing known treatment.[6][7]
It is an hERG blocker and can produce long QT syndrome as a side effect.[8]
Analogues include prodipine and medipine.[9][10]
Synthesis
Budipine can be prepared from the 1-tert-butyl-4-piperidone [1465-76-5] directly by treatment with benzene in the presence triflic acid.[11] This method of synthesis enables a 99% yield of product.
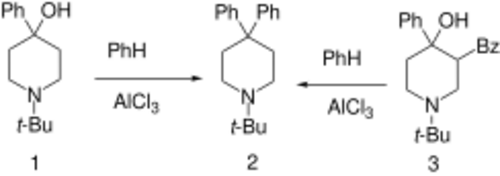
4-Phenyl-1-t-butyl-4-piperidinol,[13] (1)
1-t-butyl-3-benzoyl-4-phenyl-4-piperidinol [81831-81-4] (3)
See also
- AD-1211
- Delucemine
- Diphenidine
- Ephenidine
- Fluorolintane
- Lanicemine
- Methoxphenidine (MXP)
- MT-45
- Remacemide
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Budipine in Parkinson's tremor". Journal of the Neurological Sciences 248 (1–2): 53–55. October 2006. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2006.05.039. PMID 16784759.
- ↑ "Clinical efficacy of budipine in Parkinson's disease". Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease — State of the Art. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa. 56. 1999. 75–82. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-6360-3_3. ISBN 978-3-211-83275-2.
- ↑ "Budipine". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800003459.
- ↑ "The antiparkinsonian drug budipine binds to NMDA and sigma receptors in postmortem human brain tissue". Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementum 46: 131–137. 1995. PMID 8821048.
- ↑ "Neuroprotection by NMDA receptor antagonists in a variety of neuropathologies". Current Drug Targets 2 (3): 241–271. September 2001. doi:10.2174/1389450013348335. PMID 11554551.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Budipine provides additional benefit in patients with Parkinson disease receiving a stable optimum dopaminergic drug regimen". Archives of Neurology 59 (5): 803–806. May 2002. doi:10.1001/archneur.59.5.803. PMID 12020263.
- ↑ "Effects of amantadine and budipine on antidepressant drug-evoked changes in extracellular dopamine in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats". Brain Research 1117 (1): 206–212. October 2006. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.07.039. PMID 16996043.
- ↑ "Drug binding to aromatic residues in the HERG channel pore cavity as possible explanation for acquired Long QT syndrome by antiparkinsonian drug budipine". Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 368 (5): 404–414. November 2003. doi:10.1007/s00210-003-0805-5. PMID 14557918.
- ↑ "The interaction of 1-alkyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidines with the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine receptor binding site". J Neural Transm 65 (3–4): 157–166. 1986. doi:10.1007/BF01249078. PMID 3011983. "Other representatives of this class of substances, the 1-alkyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidines, such as, e.g., the 1-isopropyl analogue (prodipine) or the 1-methyl analogue (medipine) have similar pharmacological properties including marked tremorin and reserpin antagonism (Schaefer et al., 1984). The mechanism of action of the 1-alkyl-4,4- diphenylpiperidines is not yet understood in detail.".
- ↑ "Xenobiotic and endobiotic inhibitors of cytochrome P-450dbl function, the target of the debrisoquine/sparteine type polymorphism". Biochem Pharmacol 37 (20): 3829–3835. October 1988. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(88)90063-9. PMID 2903741. "Budipine (1-t-butyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidine) (Parkinson's disease treatment); Prodipine (1-isopropyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidine); Medipine (1-methyl-4,4-diphenylpiperidine)".
- ↑ Klumpp, D. A., Garza, M., Jones, A., Mendoza, S. (1 September 1999). "Synthesis of Aryl-Substituted Piperidines by Superacid Activation of Piperidones". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 64 (18): 6702–6705. doi:10.1021/jo990454i.
- ↑ "[Synthesis, physical-chemical properties and pharmacologically-oriented screening studies on budipine and related 4,4-diphenylpiperidines]" (in German). Arzneimittel-Forschung 34 (3): 233–240. 1984. PMID 6539602.
- ↑ "4-Phenyl-1-t-butyl-4-piperidinol". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/20536606.
 |
